Abstract
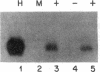
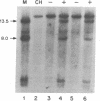
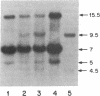
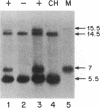
DNA probes for pre-pro-epidermal growth factor (EGF) and the precursor of the beta subunit of nerve growth factor (NGF) were used to chromosomally map human and mouse EGF and NGF genes in panels of human-mouse and mouse-Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids. The EGF and NGF genes were mapped to human chromosomes 4 and 1, respectively, by using human-mouse cell hybrids. A combination of regional mapping using a chromosome 1 translocation and comparative gene mapping suggests that the human NGF gene is in the p21-p22.1 region of chromosome 1. In mouse-Chinese hamster cell hybrids, both genes were assigned to mouse chromosome 3. A knowledge of the chromosomal assignment of these genes should help in our understanding of their regulation and role in development and disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner T., O'Brien S. J., Nash W. G., Rapp U. R., Morton C. C., Leder P. The human homologs of the raf (mil) oncogene are located on human chromosomes 3 and 4. Science. 1984 Jan 6;223(4631):71–74. doi: 10.1126/science.6691137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A. Nerve growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:191–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A. What cloned genes can tell us about nerve growth factor. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):751–751. doi: 10.1038/303751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breakefield X. O., Orloff G., Castiglione C., Coussens L., Axelrod F. B., Ullrich A. Structural gene for beta-nerve growth factor not defective in familial dysautonomia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4213–4216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. The biochemistry and physiology of the receptor-kinase for epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1983 Jul;31(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(83)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterton W. Z., Escobedo M. B., Sexson W. R., Gray M. E., Sundell H. W., Stahlman M. T. Effect of epidermal growth factor on lung maturation in fetal rabbits. Pediatr Res. 1979 Feb;13(2):104–108. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197902000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. J., Hamerton J. L. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosome 1. Oslo Conference (1981): Sixth International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1982;32(1-4):111–120. doi: 10.1159/000131691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSchryver-Kecskemeti K., Clouse R. E., Goldstein M. N., Gersell D., O'Neal L. Intestinal ganglioneuromatosis. A manifestation of overproduction of nerve growth factor? N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 17;308(11):635–639. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303173081106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Devare S. G., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A., Antoniades H. N. Simian sarcoma virus onc gene, v-sis, is derived from the gene (or genes) encoding a platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.6304883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant R. N., Todaro G. J. Increased serum levels of nerve growth factor in von Recklinghausen's disease. Arch Neurol. 1981 Jul;38(7):401–405. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1981.00510070035003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., de Martinville B., Coussens L., Ullrich A. The human gene for the beta subunit of nerve growth factor is located on the proximal short arm of chromosome 1. Science. 1983 Dec 16;222(4629):1248–1251. doi: 10.1126/science.6648531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J. S. Growth factors in mammalian cell culture. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:531–558. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A., Dull T. J., Ullrich A. Nucleotide sequence of epidermal growth factor cDNA predicts a 128,000-molecular weight protein precursor. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):722–725. doi: 10.1038/303722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortsch M., Schlessinger J., Gootwine E., Webb C. G. Appearance of functional EGF receptor kinase during rodent embryogenesis. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1937–1941. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01682.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., Francke U., Minna J. D. Homologous genes for enolase, phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, phosphoglucomutase, and adenylate kinase are syntenic on mouse chromosome 4 and human chromosome 1p. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2382–2386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Todaro G. J. Rat transforming growth factor type 1: structure and relation to epidermal growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 9;223(4640):1079–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.6320373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKusick V. A. The human gene map. 15 November 1983. Clin Genet. 1984 Jan;25(1):89–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb00472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Server A. C., Ishii D. N., Riopelle R. J., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor (first of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 17;297(20):1096–1104. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711172972005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Shows T. B., Law M. L., Goeddel D. V., Gray P. W. Human immune interferon gene is located on chromosome 12. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):1020–1027. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson E. B., Meera Khan P. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosomes 7, 8, and 9. Oslo Conference (1981): Sixth International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1982;32(1-4):144–152. doi: 10.1159/000131694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roderick T. H., Lalley P. A., Davisson M. T., O'Brien S. J., Womack J. E., Créau-Goldberg N., Echard G., Moore K. L. Report of the Committee on Comparative Mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;37(1-4):312–339. doi: 10.1159/000132013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronne H., Anundi H., Rask L., Peterson P. A. 7S Nerve growth factor alpha and gamma subunits are closely related proteins. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 13;23(6):1229–1234. doi: 10.1021/bi00301a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. P., Breakefield X. O. Altered nerve growth factor in fibroblasts from patients with familial dysautonomia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1154–1158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Selby M., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Bell G. I., Rutter W. J. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the precursor of mouse nerve growth factor. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):538–540. doi: 10.1038/302538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Sanchez-Pescador R., Fong N., Selby M., Rutter W. J., Bell G. I. Structure of a mouse submaxillary messenger RNA encoding epidermal growth factor and seven related proteins. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):236–240. doi: 10.1126/science.6602382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seigel L. J., Harper M. E., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Nash W. G., O'Brien S. J. Gene for T-cell growth factor: location on human chromosome 4q and feline chromosome B1. Science. 1984 Jan 13;223(4632):175–178. doi: 10.1126/science.6318318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Brown J. A., Haley L. L., Byers M. G., Eddy R. L., Cooper E. S., Goggin A. P. Assignment of the beta-glucuronidase structural gene to the pter leads to q22 region of chromosome 7 in man. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;21(1-2):99–104. doi: 10.1159/000130882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Brown J. A. Mapping chromosomes 1 and 2 employing a 1/2 translocation in somatic cell hybrids. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(3):251–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T., Eddy R., Haley L., Byers M., Henry M., Fujita T., Matsui H., Taniguchi T. Interleukin 2 (IL2) is assigned to human chromosome 4. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 May;10(3):315–318. doi: 10.1007/BF01535253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenfeld K. H., Ishii D. N. Nerve growth factor effects and receptors in cultured human neuroblastoma cell lines. J Neurosci Res. 1982;8(2-3):375–391. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490080226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundell H. W., Gray M. E., Serenius F. S., Escobedo M. B., Stahlman M. T. Effects of epidermal growth factor on lung maturation in fetal lambs. Am J Pathol. 1980 Sep;100(3):707–726. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taparowsky E., Shimizu K., Goldfarb M., Wigler M. Structure and activation of the human N-ras gene. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):581–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90390-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tricoli J. V., Shows T. B. Regional assignment of human amylase (AMY) to p22----p21 of chromosome 1. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Mar;10(2):205–210. doi: 10.1007/BF01534909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchihashi M., Hirata Y., Nakajima H., Fujita T., Matsukura S. Urinary excretion of human epidermal growth factor (hEGF) in patients with malignant tumors. Horm Metab Res. 1983 May;15(5):261–262. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Berman C., Dull T. J. Human beta-nerve growth factor gene sequence highly homologous to that of mouse. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):821–825. doi: 10.1038/303821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield M. D., Scrace G. T., Whittle N., Stroobant P., Johnsson A., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Heldin C. H., Huang J. S., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor is structurally related to the putative transforming protein p28sis of simian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):35–39. doi: 10.1038/304035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel B. U., Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Bell G. I., Shows T. B. High-resolution chromosomal localization of human genes for amylase, proopiomelanocortin, somatostatin, and a DNA fragment (D3S1) by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6932–6936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]