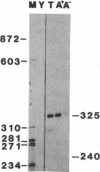
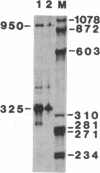
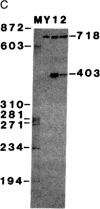
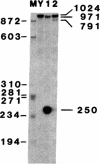
Abstract
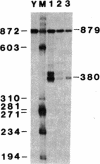
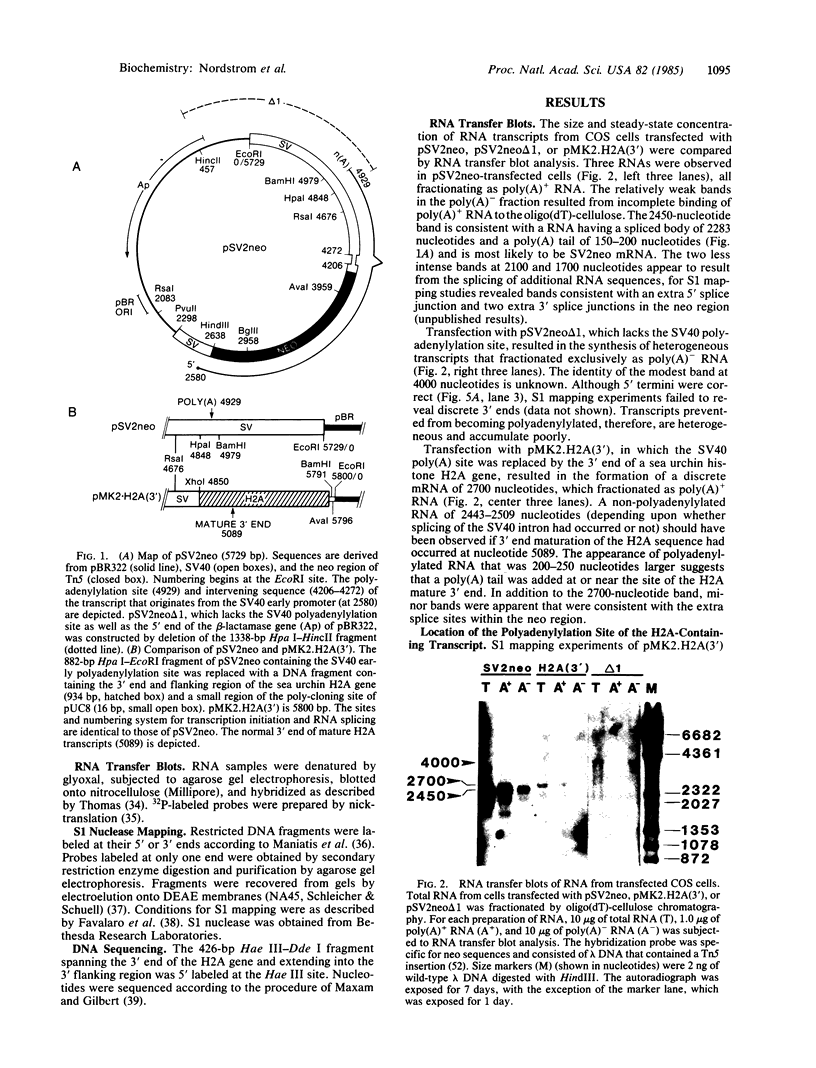
The region of pSV2neo that encompasses the simian virus 40 early polyadenylylation signal was replaced with a DNA fragment that spans the 3' end of a sea urchin (Psammechinus miliaris) histone H2A gene. This clone, pMK2.H2A(3'), was used to transfect COS cells. RNA analysis revealed that transcripts from pMK2.H2A(3') were polyadenylylated at a site 85 nucleotides downstream from the expected 3' end of mature H2A mRNA. Nucleotide sequencing showed that the site of poly(A) addition was located 10 nucleotides downstream from a cluster of four A-A-U-A-A-A sequences. The lower accumulation of MK2.H2A(3') mRNA, which was 5-10% that of SV2neo mRNA, suggests that the H2A polyadenylylation signal is relatively inefficient. The relationship of the above findings to the 3' end processing of other histone mRNAs is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. M., Richter J. D., Chamberlin M. E., Price D. H., Britten R. J., Smith L. D., Davidson E. H. Sequence organization of the poly(A) RNA synthesized and accumulated in lampbrush chromosome stage Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):281–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannon G. A., Calzone F. J., Bowen J. K., Allis C. D., Gorovsky M. A. Multiple, independently regulated, polyadenylated messages for histone H3 and H4 in Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):3903–3917. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendig M. M., Hentschel C. C. Transcription of sea urchin histone genes in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2337–2346. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Folk W., Birnstiel M. L. The terminal RNA stem-loop structure and 80 bp of spacer DNA are required for the formation of 3' termini of sea urchin H2A mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Schümperli D., Sconzo G., Birnstiel M. L. 3' editing of mRNAs: sequence requirements and involvement of a 60-nucleotide RNA in maturation of histone mRNA precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1057–1061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borun T. W., Ajiro K., Zweidler A., Dolby T. W., Stephens R. E. Studies of human histone messenger RNA. II. The resolution of fractions containing individual human histone messenger RNA species. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz M. O., Barsacchi-Pilone G., Mahon K. A., Gall J. G. Transcripts from both strands of a satellite DNA occur on lampbrush chromosome loops of the newt Notophthalmus. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):649–659. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. D., Sugarman B. J., Dodgson J. B. A chicken histone H3 gene contains intervening sequences. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):434–436. doi: 10.1038/297434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrner K., Yarger J., Hereford L. Yeast histone mRNA is polyadenylated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5725–5737. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The site at which late mRNAs are polyadenylated is altered in SV40 mutant dl882. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:53–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli F., Baglioni C. Regulation of maternal mRNA translation in developing embryos of the surf clam Spisula solidissima. Nature. 1977 Oct 6;269(5628):529–531. doi: 10.1038/269529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Stunnenberg H. G., Birnstiel M. L. Biochemical complementation with RNA in the Xenopus oocyte: a small RNA is required for the generation of 3' histone mRNA termini. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):823–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90539-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C., Irminger J. C., Bucher P., Birnstiel M. L. Sea urchin histone mRNA termini are located in gene regions downstream from putative regulatory sequences. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):147–151. doi: 10.1038/285147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huez G., Marbaix G., Gallwitz D., Weinberg E., Devos R., Hubert E., Cleuter Y. Functional stabilisation of HeLa cell histone messenger RNAs injected into Xenopus oocytes by 3'-OH polyadenylation. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):572–573. doi: 10.1038/271572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H. Histone genes and histone messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:837–870. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Formation of the 3' end of histone mRNA by post-transcriptional processing. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):203–206. doi: 10.1038/308203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson R. G., Marcu K. B. On the existence of polyadenylated histone mRNA in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Accurate and specific polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in a soluble whole-cell lysate. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90440-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molgaard H. V., Perucho M., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Histone H5 messenger RNA is polyadenylated. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):502–504. doi: 10.1038/283502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Inhibition of RNA cleavage but not polyadenylation by a point mutation in mRNA 3' consensus sequence AAUAAA. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):600–605. doi: 10.1038/305600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom J. L., Roop D. R., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Identification of potential ovomucoid mRNA precursors in chick oviduct nuclei. Nature. 1979 Mar 22;278(5702):328–331. doi: 10.1038/278328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V., Pardue M. L. A portion of all major classes of histone messenger RNA in amphibian oocytes is polyadenylated. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):2018–2025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V., Pardue M. L. Cell-free translation analysis of messenger RNA in echinoderm and amphibian early development. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):48–68. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V., Woodland H. R., Sturgess E. A. Modulations of histone messenger RNA during the early development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1979 Jul;71(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner P. C., Woodland H. R. H3 and H4 histone cDNA sequences from Xenopus: a sequence comparison of H4 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3769–3780. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland H. R. Histone synthesis during the development of Xenopus. FEBS Lett. 1980 Nov 17;121(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woudt L. P., Pastink A., Kempers-Veenstra A. E., Jansen A. E., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. The genes coding for histone H3 and H4 in Neurospora crassa are unique and contain intervening sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5347–5360. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Bonner W. M. Separation of basal histone synthesis from S-phase histone synthesis in dividing cells. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90415-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zernik M., Heintz N., Boime I., Roeder R. G. Xenopus laevis histone genes: variant H1 genes are present in different clusters. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90557-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dongen W., Zaal R., Moorman A., Destrée O. Quantitation of the accumulation of histone messenger RNA during oogenesis in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90188-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]