Abstract
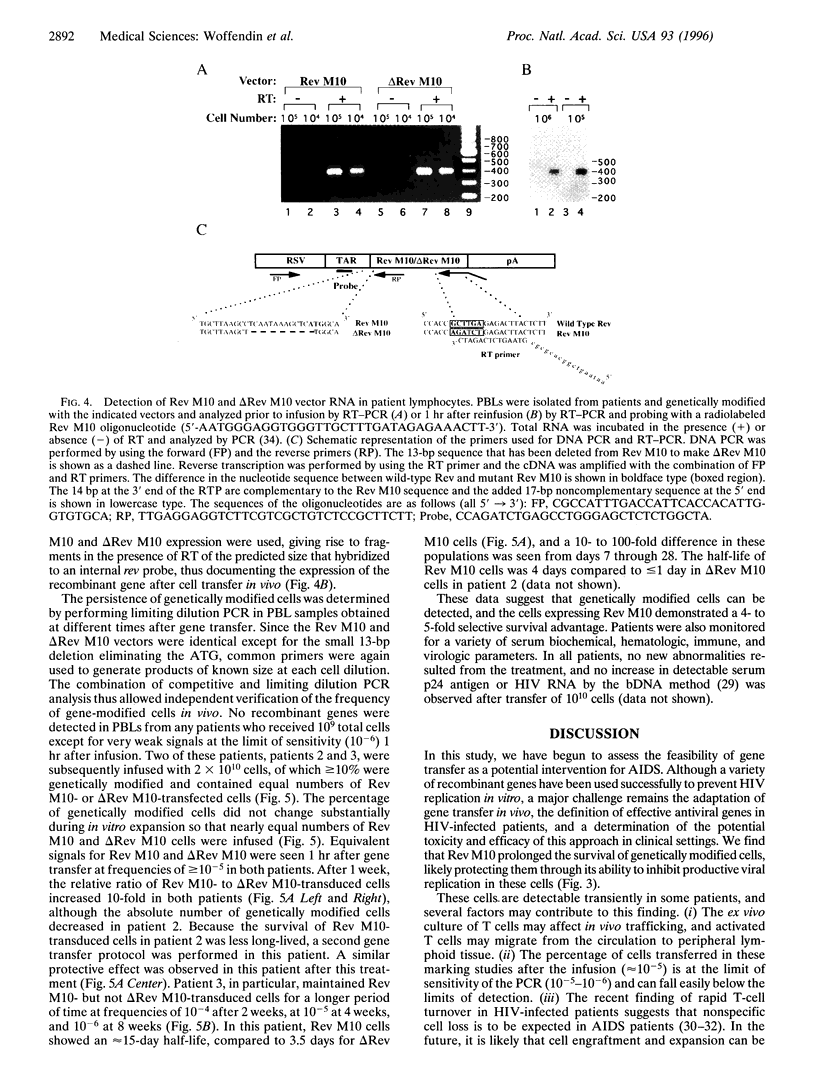
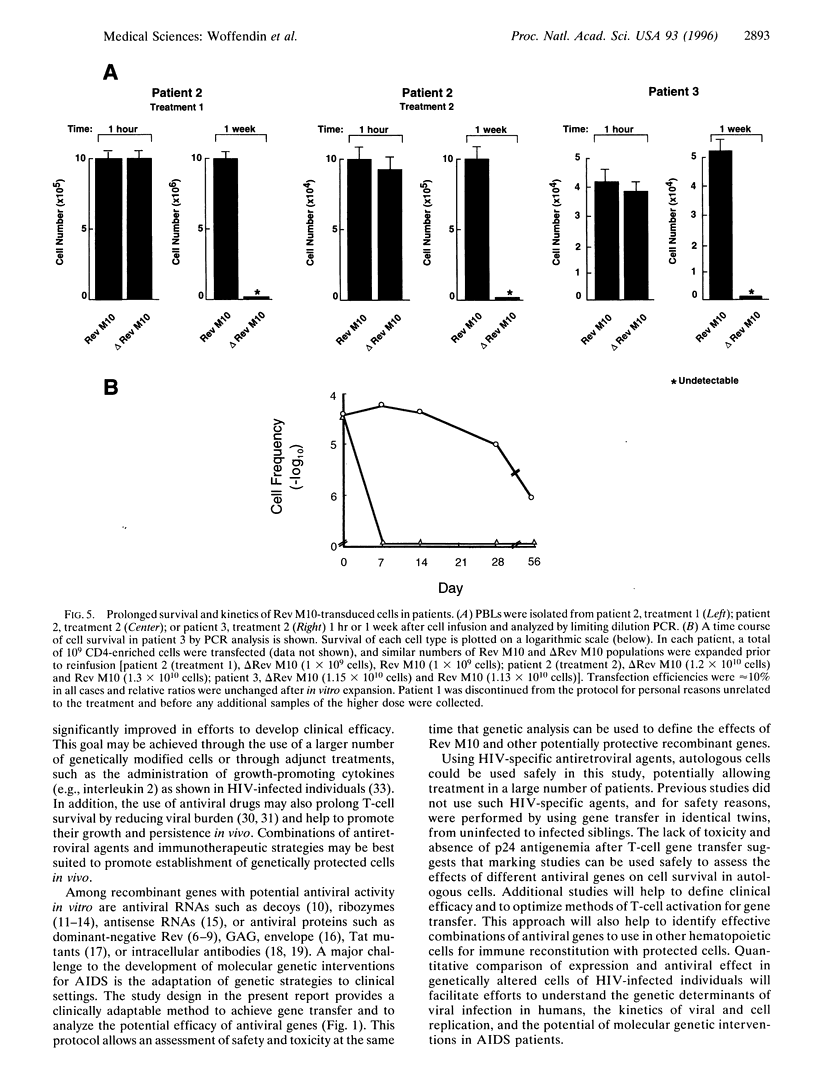
The resistance of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) to traditional drug therapy has prompted a search for alternative treatments for this disease. One potential approach is to provide genetic resistance to viral replication to prolong latency. This strategy requires the definition of effective antiviral genes that extend the survival of T cells in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected individuals. We report the results of a human study designed to determine whether a genetic intervention can prolong the survival of T cells in HIV-infected individuals. Gene transfer was performed in enriched CD4+ cells with plasmid expression vectors encoding an inhibitory Rev protein, Rev M10, or a deletion mutant control, deltaRev M10, delivered by gold microparticles. Autologous cells separately transfected with each of the vectors were returned to each patient, and toxicity, gene expression, and survival of genetically modified cells were assessed. Cells that expressed Rev M10 were more resistant to HIV infection than those with deltaRev M10 in vitro. In HIV-infected subjects, Rev M10-transduced cells showed preferential survival compared to deltaRev M10 controls. Rev M10 can therefore act as a specific intracellular inhibitor that can prolong T-cell survival in HIV-1-infected individuals and potentially serve as a molecular genetic intervention which can contribute to the treatment of AIDS.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahner I., Zhou C., Yu X. J., Hao Q. L., Guatelli J. C., Kohn D. B. Comparison of trans-dominant inhibitory mutant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genes expressed by retroviral vectors in human T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3199–3207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3199-3207.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Gene therapy. Intracellular immunization. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):395–396. doi: 10.1038/335395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevec D., Dobrovnik M., Hauber J., Böhnlein E. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in human T cells by retroviral-mediated gene transfer of a dominant-negative Rev trans-activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9870–9874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee S., Johnson P. R., Wong K. K., Jr Dual-target inhibition of HIV-1 in vitro by means of an adeno-associated virus antisense vector. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1485–1488. doi: 10.1126/science.1359646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., Mizukami T., Fuerst T. R., FitzGerald D. J., Moss B., Pastan I., Berger E. A. Selective killing of HIV-infected cells by recombinant human CD4-Pseudomonas exotoxin hybrid protein. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):369–372. doi: 10.1038/335369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M. HIV population dynamics in vivo: implications for genetic variation, pathogenesis, and therapy. Science. 1995 Jan 27;267(5197):483–489. doi: 10.1126/science.7824947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Hauber J., Campbell K., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A., Rosen C. A. Subcellular localization of the human immunodeficiency virus trans-acting art gene product. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2498–2501. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2498-2501.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan L., Bagasra O., Laughlin M. A., Oakes J. W., Pomerantz R. J. Potent inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by an intracellular anti-Rev single-chain antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5075–5079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Dueweke T. J., Poppe S. M., Romero D. L., Swaney S. M., So A. G., Downey K. M., Althaus I. W., Reusser F., Busso M., Resnick L. U-90152, a potent inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 May;37(5):1127–1131. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.5.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox B. A., Woffendin C., Yang Z. Y., San H., Ranga U., Gordon D., Osterholzer J., Nabel G. J. Genetic modification of human peripheral blood lymphocytes with a transdominant negative form of Rev: safety and toxicity. Hum Gene Ther. 1995 Aug;6(8):997–1004. doi: 10.1089/hum.1995.6.8-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Triezenberg S. J., McKnight S. L. Expression of a truncated viral trans-activator selectively impedes lytic infection by its cognate virus. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):452–454. doi: 10.1038/335452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Functional inactivation of genes by dominant negative mutations. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):219–222. doi: 10.1038/329219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Neumann A. U., Perelson A. S., Chen W., Leonard J. M., Markowitz M. Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):123–126. doi: 10.1038/373123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Baseler M., Dewar R. J., Vogel S., Davey R. T., Jr, Falloon J., Polis M. A., Walker R. E., Stevens R., Salzman N. P. Increases in CD4 T lymphocytes with intermittent courses of interleukin-2 in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. A preliminary study. N Engl J Med. 1995 Mar 2;332(9):567–575. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199503023320904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Woffendin C., Yang Z. Y., Nabel G. J. Regulated expression of a dominant negative form of Rev improves resistance to HIV replication in T cells. Gene Ther. 1994 Jan;1(1):32–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Böhnlein S., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Functional dissection of the HIV-1 Rev trans-activator--derivation of a trans-dominant repressor of Rev function. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Freimuth W. W., Liu J., Boyle T. J., Lyerly H. K., Cullen B. R., Nabel G. J. Stable expression of transdominant Rev protein in human T cells inhibits human immunodeficiency virus replication. J Exp Med. 1992 Oct 1;176(4):1197–1201. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.4.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., McCarn D. F., Tiley L. S., Cullen B. R. Mutational definition of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev activation domain. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4248–4254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4248-4254.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Haseltine W. A., Chen S. Y. Design, intracellular expression, and activity of a human anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 single-chain antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7889–7893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G. J., Fox B. A., Post L., Thompson C. B., Woffendin C. A molecular genetic intervention for AIDS--effects of a transdominant negative form of Rev. Hum Gene Ther. 1994 Jan;5(1):79–92. doi: 10.1089/hum.1994.5.1-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojwang J. O., Hampel A., Looney D. J., Wong-Staal F., Rappaport J. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expression by a hairpin ribozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10802–10806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson L., Garcia J., Wu F., Modesti N., Nelson J., Gaynor R. A transdominant tat mutant that inhibits tat-induced gene expression from the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5079–5083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz R. J., Trono D., Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D. Cells nonproductively infected with HIV-1 exhibit an aberrant pattern of viral RNA expression: a molecular model for latency. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1271–1276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Cantin E. M., Chang P. S., Zaia J. A., Ladne P. A., Stephens D. A., Rossi J. J. Ribozymes as potential anti-HIV-1 therapeutic agents. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1222–1225. doi: 10.1126/science.2107573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullenger B. A., Gallardo H. F., Ungers G. E., Gilboa E. Overexpression of TAR sequences renders cells resistant to human immunodeficiency virus replication. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90455-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D. HIV-1 Gag mutants can dominantly interfere with the replication of the wild-type virus. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90874-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udaykumar, Epstein J. S., Hewlett I. K. A novel method employing UNG to avoid carry-over contamination in RNA-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 11;21(16):3917–3918. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.16.3917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaishnav Y. N., Wong-Staal F. The biochemistry of AIDS. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:577–630. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei X., Ghosh S. K., Taylor M. E., Johnson V. A., Emini E. A., Deutsch P., Lifson J. D., Bonhoeffer S., Nowak M. A., Hahn B. H. Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):117–122. doi: 10.1038/373117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woffendin C., Yang Z. Y., Udaykumar, Xu L., Yang N. S., Sheehy M. J., Nabel G. J. Nonviral and viral delivery of a human immunodeficiency virus protective gene into primary human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 22;91(24):11581–11585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.24.11581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu M., Ojwang J., Yamada O., Hampel A., Rapapport J., Looney D., Wong-Staal F. A hairpin ribozyme inhibits expression of diverse strains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6340–6344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu M., Poeschla E., Wong-Staal F. Progress towards gene therapy for HIV infection. Gene Ther. 1994 Jan;1(1):13–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]