Abstract
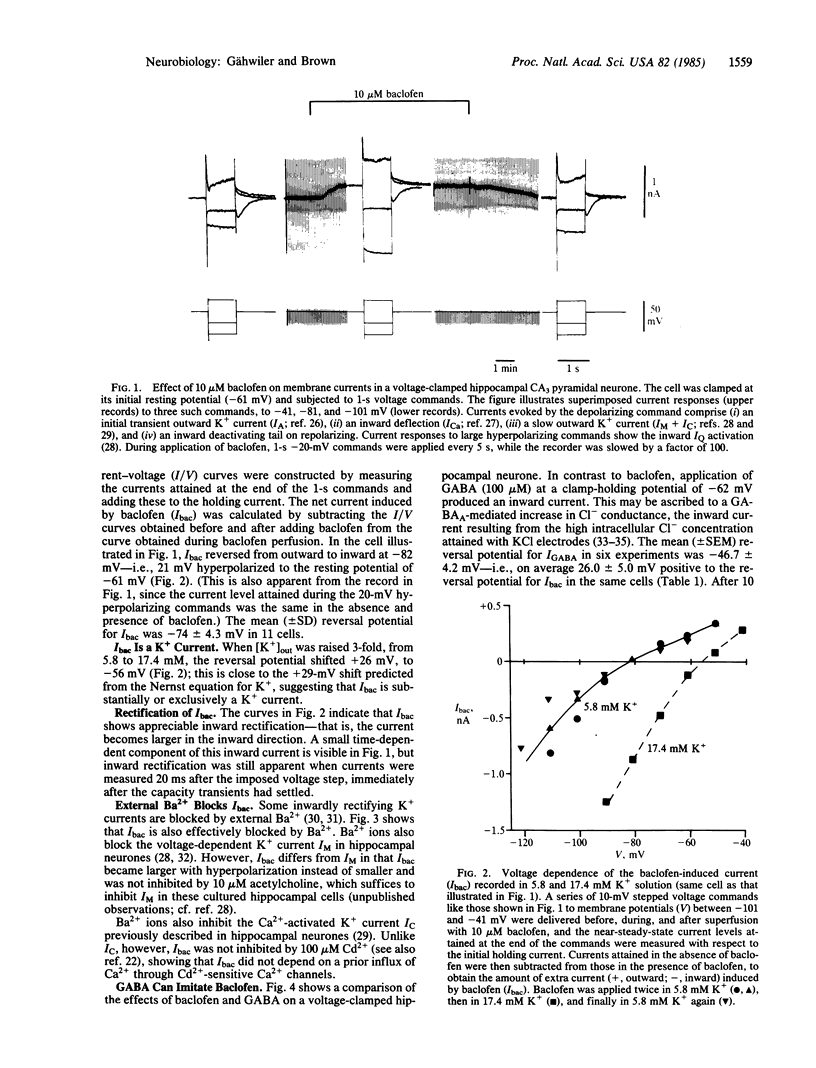
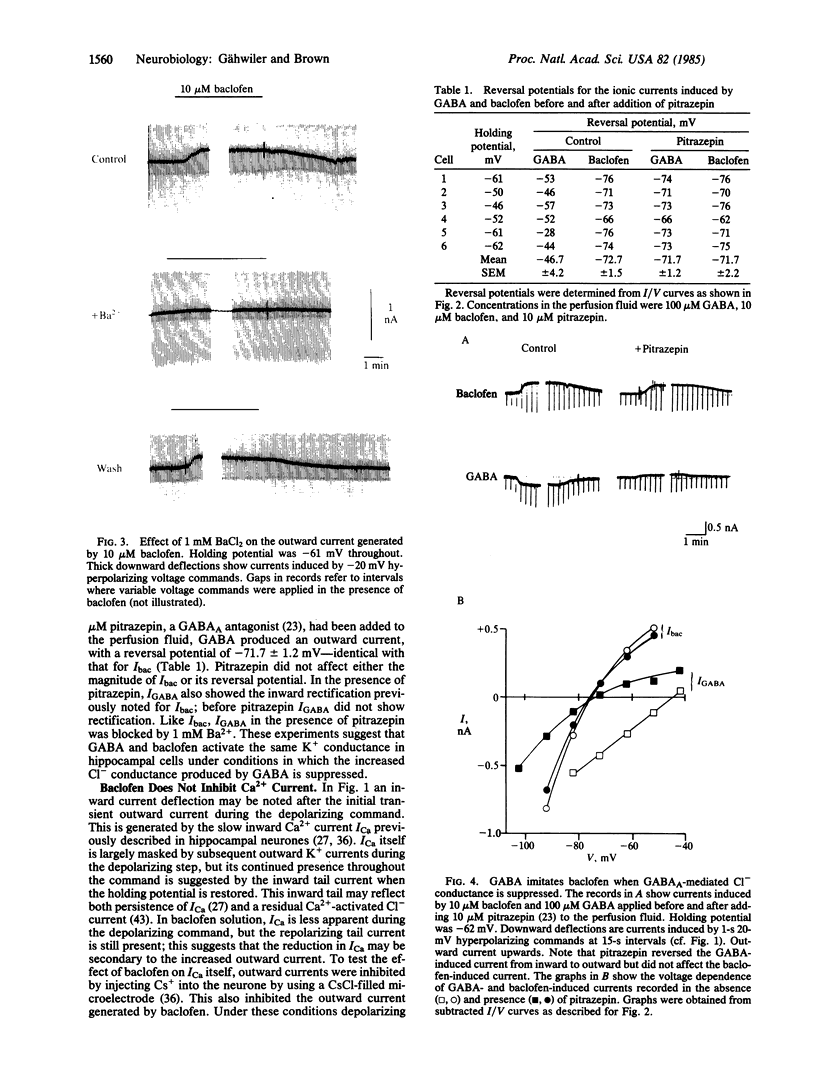
GABAB receptors are a subclass of receptors for gamma-amino-n-butyric acid (GABA) that are also activated by the antispastic drug beta-p-chlorophenyl-GABA (baclofen). One effect of baclofen is to inhibit excitatory transmission from CA3 to CA1 hippocampal pyramidal cells. To identify the ionic mechanism of GABAB-receptor-mediated depression, we have studied the effect of baclofen and GABA on ionic currents in voltage-clamped CA3 pyramidal cell somata in rat hippocampal slice cultures. Baclofen (10 microM) induced an inwardly rectifying outward current that reversed at -74 +/- 4.3 mV (mean +/- SD). This appeared to be a K+ current since (i) its reversal potential showed the expected shift when extracellular K+ concentration was changed and (ii) it was blocked by external Ba2+ or internal Cs+. The action of baclofen was closely imitated by GABA after the GABAA-mediated Cl- current had been abolished with pitrazepin (10 microM); under these conditions, GABA (100 microM) also produced an inwardly rectifying, Ba2+-sensitive current with a reversal potential identical to that of the baclofen-induced current. When outward currents were blocked with internal Cs+, the residual inward voltage-dependent Ca2+ current was not changed by baclofen. It is concluded that the primary effect of GABAB-receptor activation in these neurones is to increase K+ permeability rather than to reduce Ca2+ permeability.
Full text
PDF
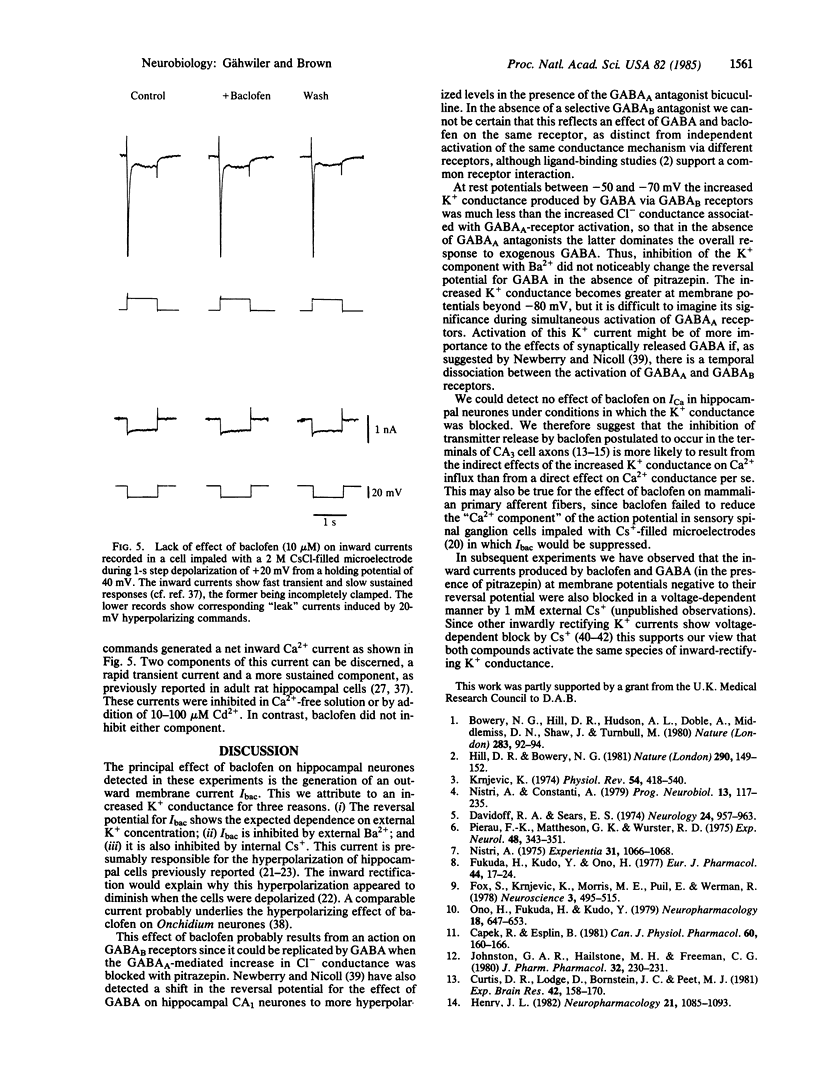

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alger B. E., Nicoll R. A. GABA-mediated biphasic inhibitory responses in hippocampus. Nature. 1979 Sep 27;281(5729):315–317. doi: 10.1038/281315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Dingledine R., Gjerstad L., Langmoen I. A., Laursen A. M. Two different responses of hippocampal pyramidal cells to application of gamma-amino butyric acid. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:279–296. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Nadler J. V. Baclofen selectively inhibits transmission at synapses made by axons of CA3 pyramidal cells in the hippocampal slice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):291–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Nadler J. V. Effects of baclofen on synaptically-induced cell firing in the rat hippocampal slice. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;80(1):211–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11068.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ari Y., Krnjević K., Reiffenstein R. J., Reinhardt W. Inhibitory conductance changes and action of gamma-aminobutyrate in rat hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2445–2463. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L., Doble A., Middlemiss D. N., Shaw J., Turnbull M. (-)Baclofen decreases neurotransmitter release in the mammalian CNS by an action at a novel GABA receptor. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):92–94. doi: 10.1038/283092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Griffith W. H. Calcium-activated outward current in voltage-clamped hippocampal neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:287–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Griffith W. H. Persistent slow inward calcium current in voltage-clamped hippocampal neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:303–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capek R., Esplin B. Baclofen-induced decrease of excitability of primary afferents and depression of monosynaptic transmission in cat spinal cord. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Feb;60(2):160–166. doi: 10.1139/y82-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Who do barium ions imitate acetylcholine? Brain Res. 1981 Feb 9;206(1):244–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Galvan M. Fast inward-rectifying current accounts for anomalous rectification in olfactory cortex neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:153–178. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Lodge D., Bornstein J. C., Peet M. J. Selective effects of (-)-baclofen on spinal synaptic transmission in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1981;42(2):158–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00236902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A., Sears E. S. The effects of Lioresal on synaptic activity in the isolated spinal cord. Neurology. 1974 Oct;24(10):957–963. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.10.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K. Two types of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor on embryonic sensory neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;74(3):579–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Désarmenien M., Feltz P., Occhipinti G., Santangelo F., Schlichter R. Coexistence of GABAA and GABAB receptors on A delta and C primary afferents. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Feb;81(2):327–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10082.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox S., Krnjević K., Morris M. E., Puil E., Werman R. Action of baclofen on mammalian synaptic transmission. Neuroscience. 1978;3(6):495–515. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda H., Kudo Y., Ono H. Effects of beta-(p-chlorophenyl)-GABA (baclofen) on spinal synaptic activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Jul 1;44(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay L. A., Stanfield P. R. Cs(+) causes a voltage-dependent block of inward K currents in resting skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1977 May 12;267(5607):169–170. doi: 10.1038/267169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Galvan M., Grafe P., Wigström H. A transient outward current in a mammalian central neurone blocked by 4-aminopyridine. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):252–254. doi: 10.1038/299252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H., Maurer R., Wüthrich H. J. Pitrazepin, a novel GABAA antagonist. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Apr 6;45(3):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90244-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H. Organotypic monolayer cultures of nervous tissue. J Neurosci Methods. 1981 Dec;4(4):329–342. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(81)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gähwiler B. H. Slice cultures of cerebellar, hippocampal and hypothalamic tissue. Experientia. 1984 Mar 15;40(3):235–243. doi: 10.1007/BF01947561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Moody W., Patlak J. Blocking effects of barium and hydrogen ions on the potassium current during anomalous rectification in the starfish egg. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:167–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Rosenthal N. P. Potassium current and the effect of cesium on this current during anomalous rectification of the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):621–638. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell J. V., Adams P. R. Voltage-clamp analysis of muscarinic excitation in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 28;250(1):71–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90954-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Bowery N. G. 3H-baclofen and 3H-GABA bind to bicuculline-insensitive GABA B sites in rat brain. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):149–152. doi: 10.1038/290149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D., Hablitz J. J., Wilson W. A. Voltage clamp discloses slow inward current in hippocampal burst-firing neurones. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):391–393. doi: 10.1038/286391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. A., Hailstone M. H., Freeman C. G. Baclofen: stereoselective inhibition of excitant amino acid release. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;32(3):230–231. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1980.tb12902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanthorn T. H., Cotman C. W. Baclofen selectively inhibits excitatory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 23;225(1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90326-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. Direct hyperpolarizing action of baclofen on hippocampal pyramidal cells. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):450–452. doi: 10.1038/308450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nistri A., Constanti A. Pharmacological characterization of different types of GABA and glutamate receptors in vertebrates and invertebrates. Prog Neurobiol. 1979;13(2):117–235. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(79)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nistri A. Further investigations into the effects of baclofen (Lioresal) on the isolated spinal cord. Experientia. 1975 Sep 15;31(9):1066–1068. doi: 10.1007/BF02326963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olpe H. R., Baudry M., Fagni L., Lynch G. The blocking action of baclofen on excitatory transmission in the rat hippocampal slice. J Neurosci. 1982 Jun;2(6):698–703. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-06-00698.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono H., Fukuda H., Kudo Y. Mechanisms of depressant action of baclofen on the spinal reflex in the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1979 Aug-Sep;18(8-9):647–653. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(79)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. G., Segal M., Barker J. L. A Ca-dependent Cl- conductance in cultured mouse spinal neurones. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):567–570. doi: 10.1038/311567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierau F. K., Matheson G. K., Wurster R. D. Presynaptic action of beta(4-chlorophenyl)-gaba. Exp Neurol. 1975 Aug;48(2):343–351. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(75)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu N., Akaike N., Oomura Y., Maruhashi J., Klee M. R. GABA and lioresal actions on the identified Onchidium neuron. Jpn J Physiol. 1983;33(3):459–467. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.33.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. A potential- and time-dependent blockade of inward rectification in frog skeletal muscle fibres by barium and strontium ions. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:169–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]