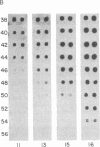
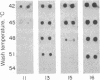
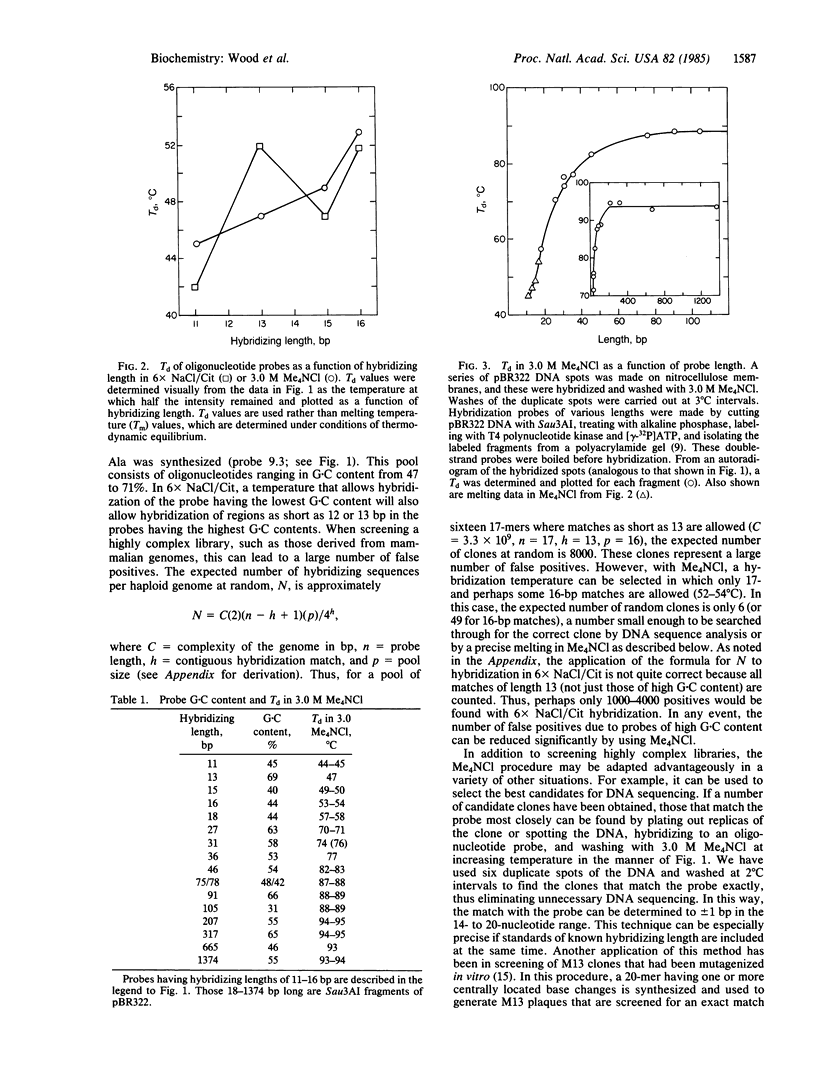
Abstract
An oligonucleotide hybridization procedure has been developed that eliminates the preferential melting of A X T versus G X C base pairs, allowing the stringency of the hybridization to be controlled as a function of probe length only. This technique, which uses tetramethylammonium chloride, is especially helpful whenever a highly complex library is screened with a pool of oligonucleotide probes, which usually vary widely in base composition. The procedure can also be applied advantageously whenever an exact match to an oligonucleotide probe is desired, such as in screening for clones having as little as a single-base alteration generated by in vitro mutagenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Britten R. J., Cetta A., Davidson E. H. The single-copy DNA sequence polymorphism of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1175–1186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. T., Hain T. C., Hutton J. R., Wetmur J. G. Effects of microscopic and macroscopic viscosity on the rate of renaturation of DNA. Biopolymers. 1974;13(9):1847–1858. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360130915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner B. J., Reyes A. A., Morin C., Itakura K., Teplitz R. L., Wallace R. B. Detection of sickle cell beta S-globin allele by hybridization with synthetic oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):278–282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crea R., Horn T. Synthesis of oligonucleotides on cellulose by a phosphotriester method. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2331–2348. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Yelverton E., Ullrich A., Heyneker H. L., Miozzari G., Holmes W., Seeburg P. H., Dull T., May L., Stebbing N. Human leukocyte interferon produced by E. coli is biologically active. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):411–416. doi: 10.1038/287411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior W. B., Jr, Von Hippel P. H. Alteration of the relative stability of dA-dT and dG-dC base pairs in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):298–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orosz J. M., Wetmur J. G. DNA melting temperatures and renaturation rates in concentrated alkylammonium salt solutions. Biopolymers. 1977 Jun;16(6):1183–1199. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Colby W. W., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Biological properties of human c-Ha-ras1 genes mutated at codon 12. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):71–75. doi: 10.1038/312071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. T., Stannard B. S., Felsenfeld G. The binding of small cations to deoxyribonucleic acid. Nucleotide specificity. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3233–3241. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs S. V., Wallace R. B., Hirose T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. Use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes: isolation of cloned cDNA sequences for human beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6613–6617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Stiles J. I., Tye B. K., Chiu P., Sherman F., Wu R. Hybridization with synthetic oligonucleotides. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:419–428. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Wood W. I., Hayflick J., Seeburg P. H. Isolation of a cDNA clone coding for the gamma-subunit of mouse nerve growth factor using a high-stringency selection procedure. DNA. 1984 Oct;3(5):387–392. doi: 10.1089/dna.1984.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Shaffer J., Murphy R. F., Bonner J., Hirose T., Itakura K. Hybridization of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides to phi chi 174 DNA: the effect of single base pair mismatch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3543–3557. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Capon D. J., Simonsen C. C., Eaton D. L., Gitschier J., Keyt B., Seeburg P. H., Smith D. H., Hollingshead P., Wion K. L. Expression of active human factor VIII from recombinant DNA clones. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):330–337. doi: 10.1038/312330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]