Abstract
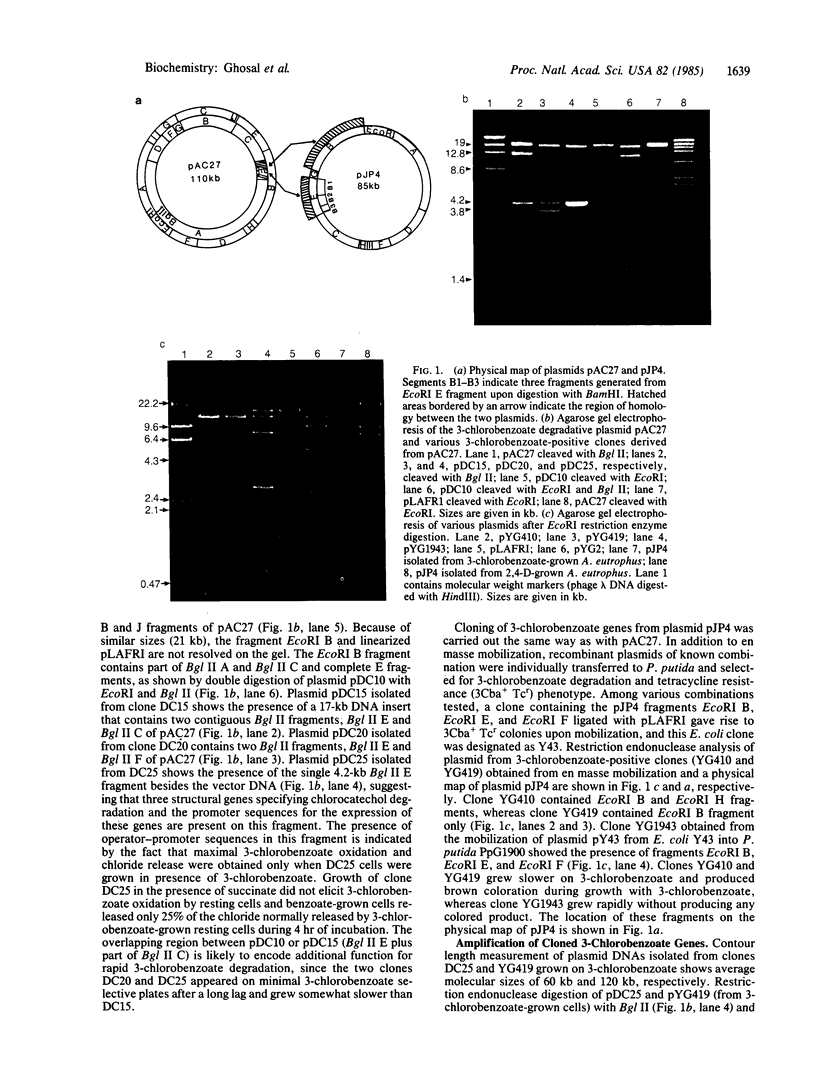
All of the structural genes for 3-chlorobenzoate degradation are clustered in a 4.2-kilobase (kb) region of plasmid pAC25 (or pAC27) in Pseudomonas putida. An approximate 10-kb DNA segment containing three structural genes for chlorocatechol metabolism present on plasmid pJP4 in Alcaligenes eutrophus shows homology with the above 4.2-kb region of pAC27. In spite of the detectable sequence homology in the structural genes present on both plasmids, the regulation of their expression seems quite different; unlike pAC27, structural rearrangements are prerequisite for efficient expression of the 3-chlorobenzoate genes on plasmid pJP4. Structural features such as stem-loop structures present on plasmid pJP4 are most likely the starting materials for such rearrangements.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Genetic homology between independently isolated chlorobenzoate-degradative plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):532–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.532-534.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzins A., Chakrabarty A. M. Cloning of genes controlling alginate biosynthesis from a mucoid cystic fibrosis isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):9–18. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.9-18.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Pemberton J. M. Properties of six pesticide degradation plasmids isolated from Alcaligenes paradoxus and Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.681-686.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., You I. S., Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Plasmids in the degradation of chlorinated aromatic compounds. Basic Life Sci. 1985;30:667–686. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2447-8_47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grund A. D., Gunsalus I. C. Cloning of genes for naphthalene metabolism in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):89–94. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.89-94.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffman G. A., Rownd R. H. Transition of deletion mutants of the composite resistance plasmid NR1 in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):488–498. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.488-498.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Molecular cloning of regulatory gene xylR and operator-promoter regions of the xylABC and xylDEGF operons of the TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1192–1199. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1192-1199.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. Isolation of inverted repeat sequences, including IS1, IS2, and IS3, in Escherichia coli plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2316–2320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisberg R. A., Adhya S. Illegitimate recombination in bacteria and bacteriophage. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:451–473. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]