Abstract
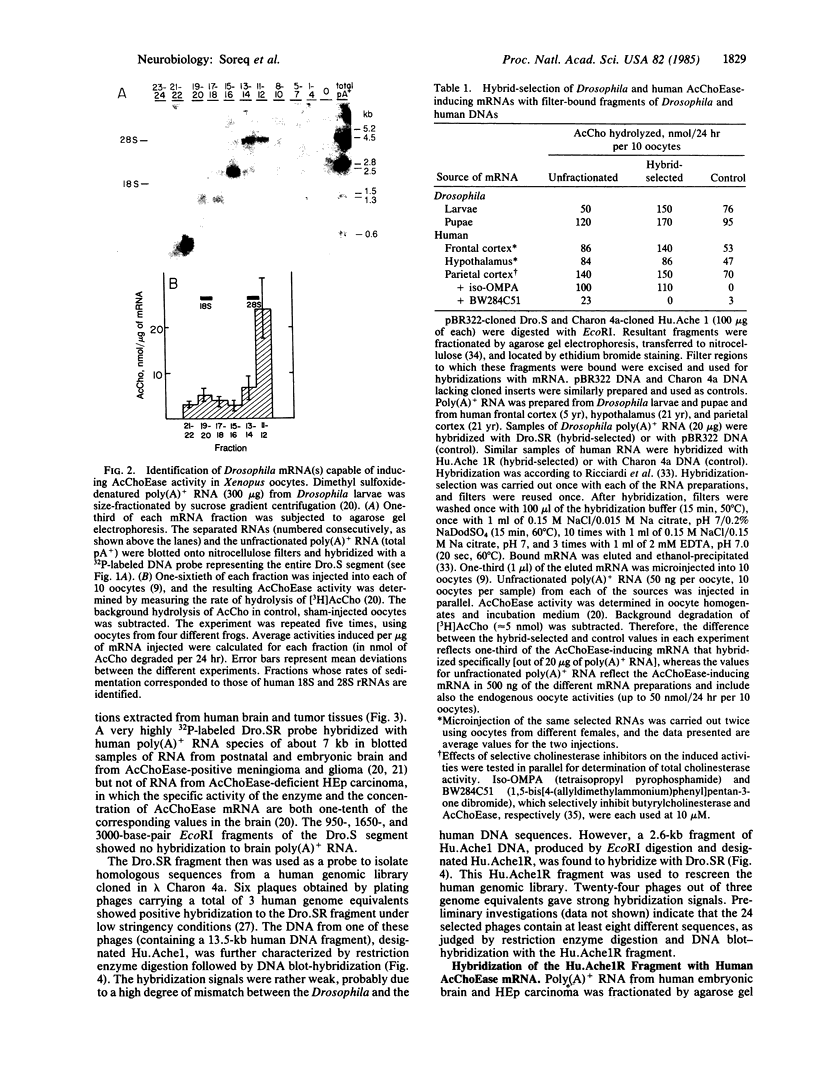
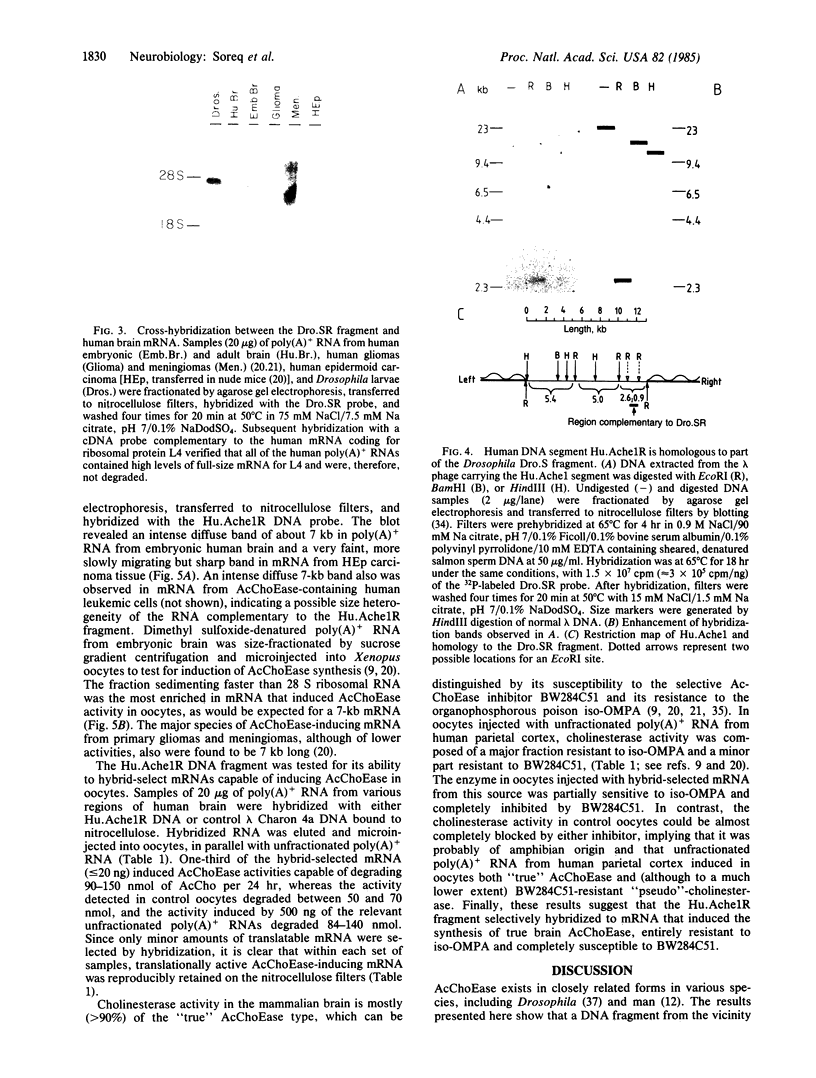
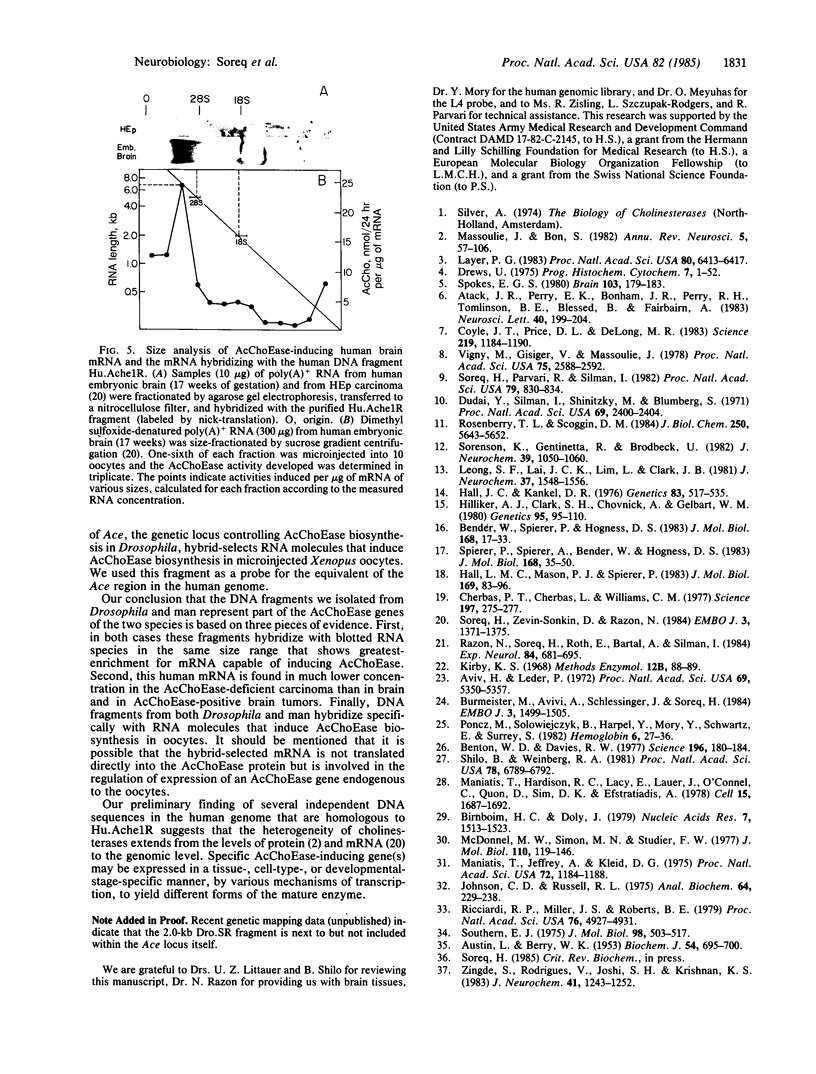
The Ace locus of the Drosophila genome controls biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter-hydrolyzing enzyme acetylcholinesterase (acetylcholine acetylhydrolase, EC 3.1.1.7). We injected the mRNA species hybridizing with DNA fragments from this region into Xenopus oocytes, in which acetylcholinesterase mRNA is translated into active acetylcholinesterase. A 2.0-kilobase (kb) fragment of DNA from this region selectively hybridizes with Drosophila mRNA capable of inducing the biosynthesis of acetylcholinesterase in oocytes. This Drosophila DNA fragment cross-hybridized with human brain poly(A)+ RNA. We therefore used this DNA fragment as a probe for homologous sequence(s) in a human genomic DNA library and thus selected a 13.5-kb human DNA segment. DNA blot-hybridization revealed that a 2.6-kb fragment of this human DNA segment hybridizes with the Drosophila 2.0-kb DNA fragment. Both Drosophila and human fragments hybridized with a human brain mRNA species of about 7.0-kb that was barely detectable in the acetylcholinesterase-deficient HEp carcinoma. A fraction containing mRNA of similar size, extracted from human brain, induced acetylcholinesterase biosynthesis in oocytes. The human DNA fragment also was used in hybridization-selection experiments. In oocytes, hybrid-selected human brain mRNA induced acetylcholinesterase activity that was completely inhibited by 1,5-bis[4-allyldimethylammonium)phenyl]pentan-3-one dibromide but not by tetraisopropyl pyrophosphamide, a differential response to these inhibitors characteristic of "true" human brain acetylcholinesterase. These findings strongly suggest that both the Drosophila and the human DNA fragments are directly involved in controlling acetylcholinesterase biosynthesis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUSTIN L., BERRY W. K. Two selective inhibitors of cholinesterase. Biochem J. 1953 Jul;54(4):695–700. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atack J. R., Perry E. K., Bonham J. R., Perry R. H., Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G., Fairbairn A. Molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase in senile dementia of Alzheimer type: selective loss of the intermediate (10S) form. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Sep 30;40(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90302-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W., Spierer P., Hogness D. S. Chromosomal walking and jumping to isolate DNA from the Ace and rosy loci and the bithorax complex in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister M., Avivi A., Schlessinger J., Soreq H. Production of EGF-containing polypeptides in Xenopus oocytes microinjected with submaxillary gland mRNA. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1499–1505. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02002.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherbas P., Cherbas L., Williams C. M. Induction of acetylcholinesterase activity by beta-ecdysone in a Drosophila cell line. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.877552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Price D. L., DeLong M. R. Alzheimer's disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1184–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.6338589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drews U. Cholinesterase in embryonic development. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 1975;7(3):1–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudai Y., Silman I., Shinitzky M., Blumberg S. Purification by affinity chromatography of the molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase present in fresh electric-organ tissue of electric eel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2400–2403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. C., Kankel D. R. Genetics of acetylcholinesterase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1976 Jul;83(3 PT2):517–535. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Mason P. J., Spierer P. Transcripts, genes and bands in 315,000 base-pairs of Drosophila DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 5;169(1):83–96. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliker A. J., Clark S. H., Chovnick A., Gelbart W. M. Cytogenetic analysis of the chromosomal region immediately adjacent to the rosy locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1980 May;95(1):95–110. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. D., Russell R. L. A rapid, simple radiometric assay for cholinesterase, suitable for multiple determinations. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layer P. G. Comparative localization of acetylcholinesterase and pseudocholinesterase during morphogenesis of the chicken brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6413–6417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong S. F., Lai J. C., Lim L., Clark J. B. Energy-metabolizing enzymes in brain regions of adult and aging rats. J Neurochem. 1981 Dec;37(6):1548–1556. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb06326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Bon S. The molecular forms of cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1982;5:57–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.05.030182.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Solowiejczyk D., Harpel B., Mory Y., Schwartz E., Surrey S. Construction of human gene libraries from small amounts of peripheral blood: analysis of beta-like globin genes. Hemoglobin. 1982;6(1):27–36. doi: 10.3109/03630268208996930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razon N., Soreq H., Roth E., Bartal A., Silman I. Characterization of activities and forms of cholinesterases in human primary brain tumors. Exp Neurol. 1984 Jun;84(3):681–695. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(84)90215-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L., Scoggin D. M. Structure of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Characterization of intersubunit disulfide bonding and detergent interaction. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5643–5652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilo B. Z., Weinberg R. A. DNA sequences homologous to vertebrate oncogenes are conserved in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6789–6792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Parvari R., Silman I. Biosynthesis and secretion of catalytically active acetylcholinesterase in Xenopus oocytes microinjected with mRNA from rat brain and from Torpedo electric organ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):830–834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Zevin-Sonkin D., Razon N. Expression of cholinesterase gene(s) in human brain tissues: translational evidence for multiple mRNA species. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1371–1375. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spierer P., Spierer A., Bender W., Hogness D. S. Molecular mapping of genetic and chromomeric units in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):35–50. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spokes E. G. Neurochemical alterations in Huntington's chorea: a study of post-mortem brain tissue. Brain. 1980 Mar;103(1):179–210. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen K., Gentinetta R., Brodbeck U. An amphiphile-dependent form of human brain caudate nucleus acetylcholinesterase: purification and properties. J Neurochem. 1982 Oct;39(4):1050–1060. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb11496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigny M., Gisiger V., Massoulié J. "Nonspecific" cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in rat tissues: molecular forms, structural and catalytic properties, and significance of the two enzyme systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2588–2592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zingde S., Rodrigues V., Joshi S. M., Krishnan K. S. Molecular properties of Drosophila acetylcholinesterase. J Neurochem. 1983 Nov;41(5):1243–1252. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb00818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]