Abstract
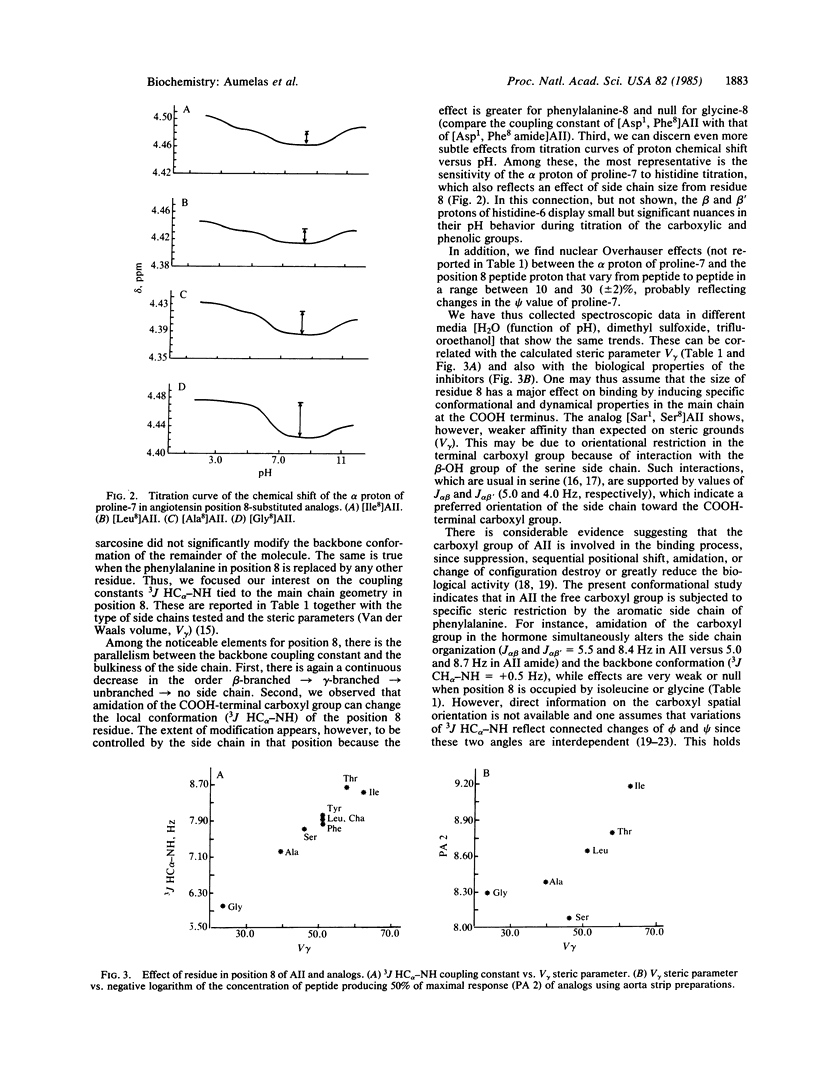
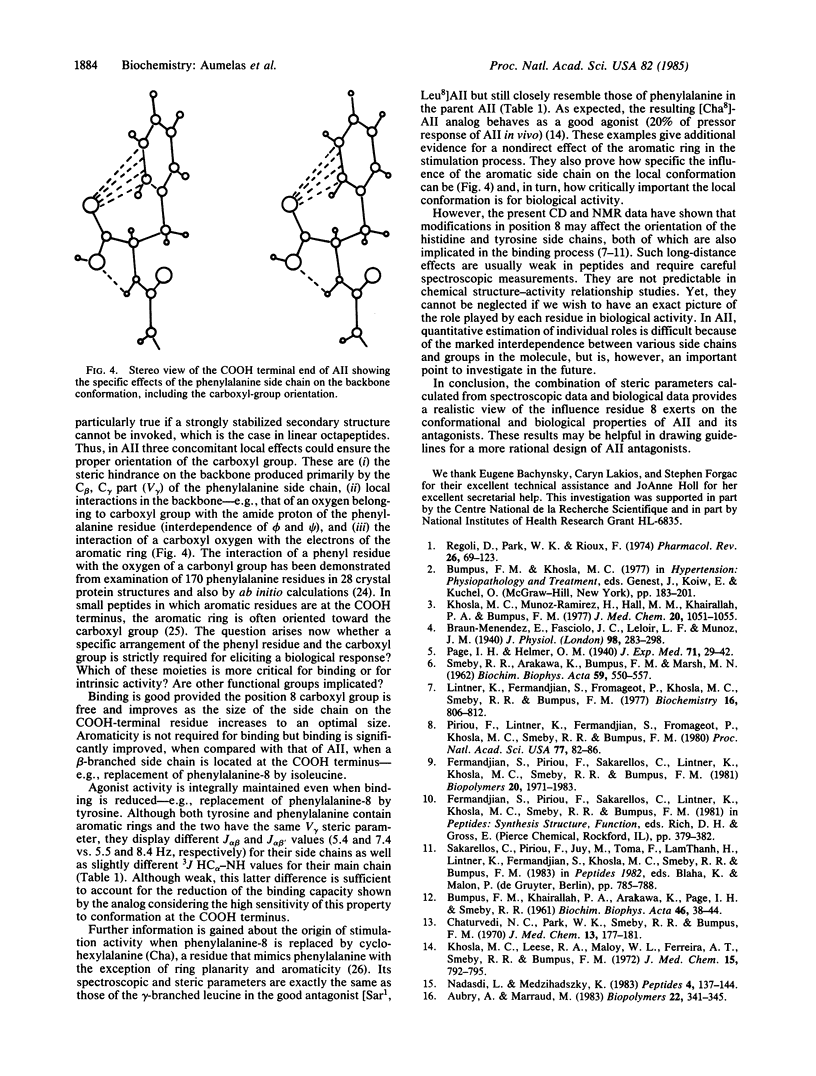
Affinity, residual agonist activity, and inhibitor properties of a series of angiotensin II analogs modified at the COOH-terminal position (X8-substituted peptides) have been probed for structure/conformation-biological activity relationships. The results emphasize (i) the large impact that subtle conformational variations caused by structural alterations in the position 8 side chain have on biological properties, (ii) the implication of the COOH-terminal carboxyl group in both affinity and intrinsic activity, and (iii) the influence that the bulkiness of the side chain in position 8 of antagonists has on the local conformation at the COOH terminus and thus on the inhibitory properties. In the hormone, the phenylalanine-8 ring is required for its steric influence and aromaticity to ensure a fully active conformation at the COOH terminus. Especially, correct orientation of the position 8 carboxyl group relative to the phenyl group of the phenylalanine residue may be necessary for agonistic activation of the angiotensin receptor complex. Replacement of the aromatic ring on the COOH-terminal residue by a nonaromatic group leads to incorrect orientation of the carboxyl group and causes the appearance of antagonist properties. Although the steric effects of the side chain can be modulated by specific interaction of its chemical groups (if any) with the peptide backbone, we found a good correlation between the size of the side chain-e.g., the steric parameter V gamma (the van der Waals volume consisting of the C alpha, C beta, and C gamma atoms), the conformational properties in the backbone (3J HC alpha-NH), and the binding capacities in all compounds tested.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun-Menendez E., Fasciolo J. C., Leloir L. F., Muñoz J. M. The substance causing renal hypertension. J Physiol. 1940 Jul 24;98(3):283–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1940.sp003850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi N. C., Park W. K., Smeby R. R., Bumpus F. M. Analogs of angiotensin II. I. Solid phase synthesis. J Med Chem. 1970 Mar;13(2):177–181. doi: 10.1021/jm00296a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fermandjian S., Piriou F., Sakarellos C., Lintner K., Khosla M. C., Smeby R. R., Bumpus M. Conformation and activity in angiotensin II peptides. Biopolymers. 1981 Sep;20(9):1971–1983. doi: 10.1002/bip.1981.360200919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gieren A., Dederer B., Schanda F. Some aspects concerning conformation of polypeptide chains in proteins. Z Naturforsch C. 1980 Sep-Oct;35(9-10):741–746. doi: 10.1515/znc-1980-9-1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosla M. C., Leese R. A., Maloy W. L., Ferreira A. T., Smeby R. R., Bumpus F. M. Synthesis of some analogs of angiotensin II as specific antagonists of the parent hormone. J Med Chem. 1972 Aug;15(8):792–795. doi: 10.1021/jm00278a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosla M. C., Muñoz-Ramírez H., Hall M. M., Khairallah P. A., Bumpus F. M. Synthesis of angiotensin II antagonists by incorporating alpha-methylalanine or O-methylthreonine residues in angiotension II analogues. J Med Chem. 1977 Aug;20(8):1051–1055. doi: 10.1021/jm00218a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lintner K., Fermandjian S., Fromageot P., Khosla M. C., Smeby R. R., Bumpus F. M. Circular dichroism studies of angiotensin II and analogues: effects of primary sequence, solvent, and pH on the side-chain conformation. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):806–812. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nádasdi L., Medzihradszky K. The use of a steric parameter (Y gamma) in QSAR calculations for peptide hormones. Peptides. 1983 Mar-Apr;4(2):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(83)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piriou F., Lintner K., Fermandjian S., Fromageot P., Khosla M. C., Smeby R. R., Bumpus F. M. Amino acid side chain conformation in angiotensin II and analogs: correlated results of circular dichroism and 1H nuclear magnetic resonance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):82–86. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl F. M. Empirical protein energy maps. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 29;234(52):277–279. doi: 10.1038/newbio234277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Park W. K., Rioux F. Pharmacology of angiotensin. Pharmacol Rev. 1974 Jun;26(2):69–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWYZER R., TURRIAN H. The chemistry and pharmacology of angiotensin. Vitam Horm. 1960;18:237–288. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60864-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMEBY R. R., ARAKAWA K., BUMPUS F. M., MARSH M. M. A proposed conformation of isoleucyl-5-angiotensin II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 23;58:550–557. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Smith G. M., Thomas T. B., Feldmann R. J. Electronic distributions within protein phenylalanine aromatic rings are reflected by the three-dimensional oxygen atom environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4843–4847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An attempt to evaluate the influence of neighboring amino acids (n-1) and (n+1) on the backbone conformation of amino acid (n) in proteins. Use in predicting the three-dimensional structure of the polypeptide backbone of other proteins. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 25;75(1):13–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90526-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. S., Pottle M. S., Némethy G., Scheraga H. A. Conformational analysis of the 20 naturally occurring amino acid residues using ECEPP. Macromolecules. 1977 Jan-Feb;10(1):1–9. doi: 10.1021/ma60055a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


