Abstract
Subcloned probes of the L1 family of repetitive elements were used to isolate L1-carrying clones from a plasmid library of HeLa cell extrachromosomal circular DNA. One clone was analyzed in detail by restriction mapping, cross-hybridization to L1 probes, and base sequence analysis. In addition to approximately the 3' half of a full-sized L1 element, this clone carried 390 base pairs of non-L1 sequence that is single copy in the HeLa genome. A HeLa genomic clone of this unique chromosomal region was isolated and the sequence organization of the circle clone was compared with the linear chromosomal region from which it was ultimately derived. We discuss possible mechanisms of circular DNA formation and propose homologous intrachromosomal recombination between 9-base-pair direct repeats to be most likely in this case.
Full text
PDF
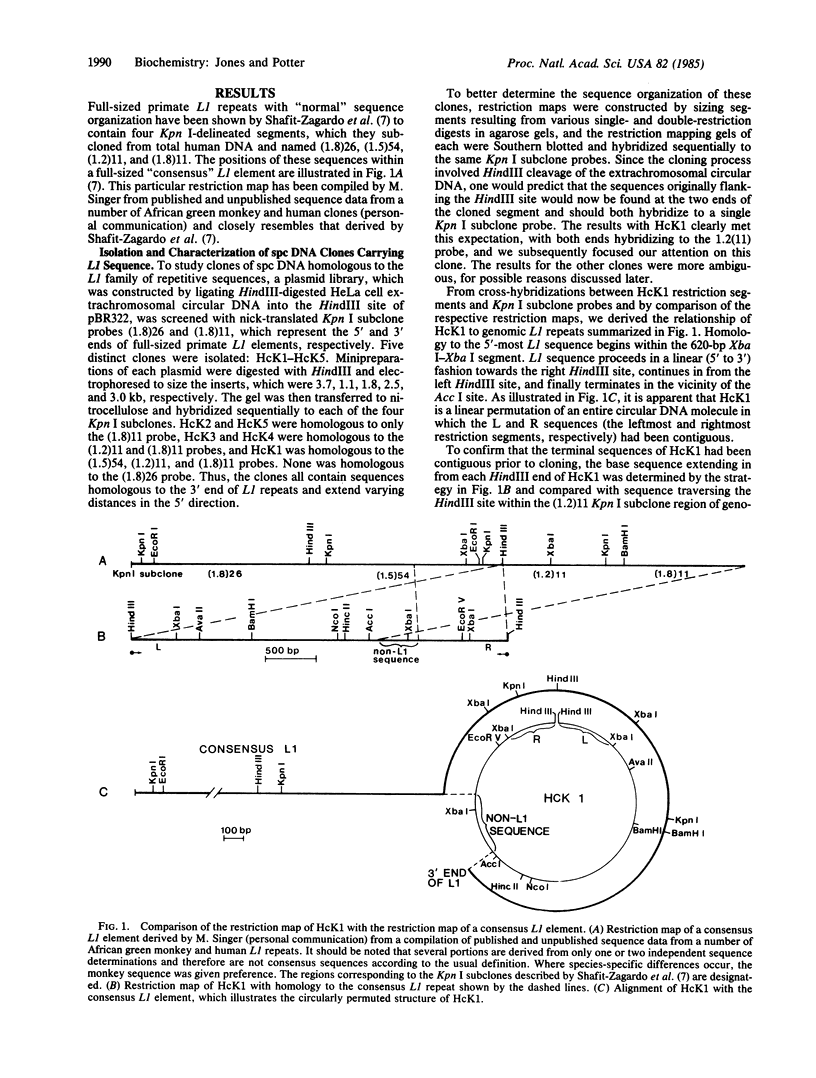


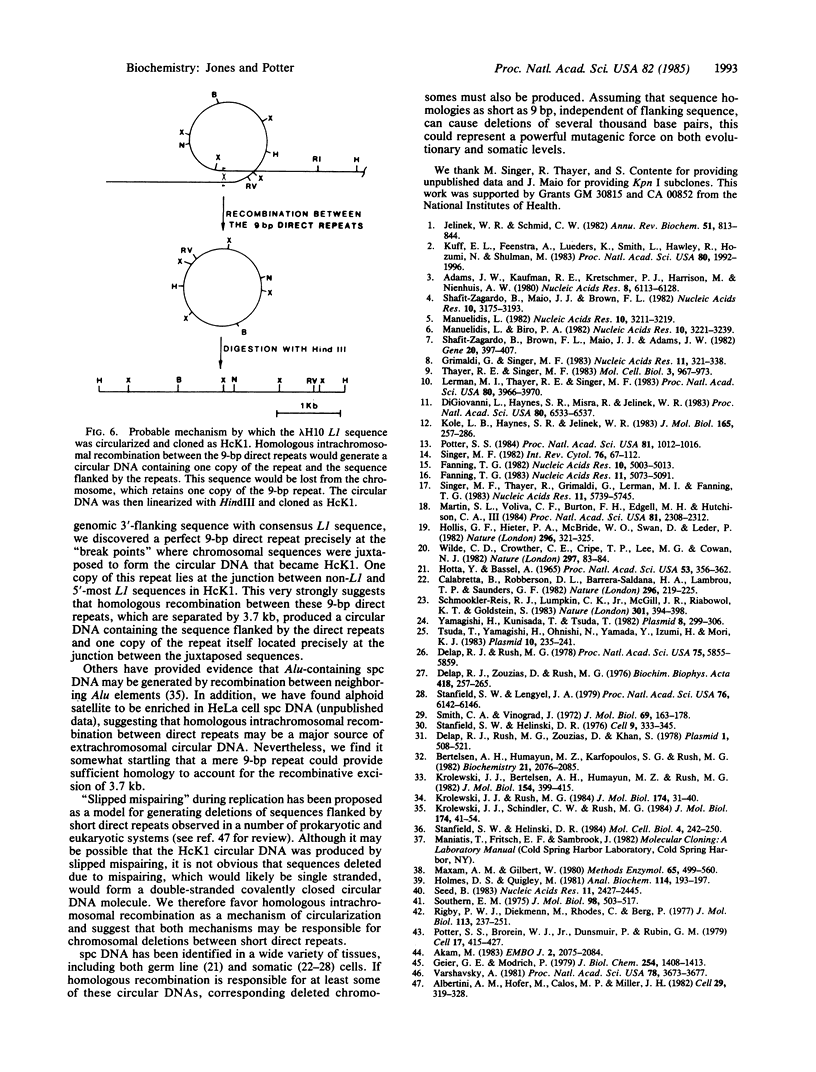
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. W., Kaufman R. E., Kretschmer P. J., Harrison M., Nienhuis A. W. A family of long reiterated DNA sequences, one copy of which is next to the human beta globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6113–6128. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akam M. E. The location of Ultrabithorax transcripts in Drosophila tissue sections. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2075–2084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01703.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albertini A. M., Hofer M., Calos M. P., Miller J. H. On the formation of spontaneous deletions: the importance of short sequence homologies in the generation of large deletions. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertelsen A. H., Humayun M. Z., Karfopoulos S. G., Rush M. G. Molecular characterization of small polydisperse circular deoxyribonucleic acid from an African green monkey cell line. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 27;21(9):2076–2085. doi: 10.1021/bi00538a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabretta B., Robberson D. L., Barrera-Saldaña H. A., Lambrou T. P., Saunders G. F. Genome instability in a region of human DNA enriched in Alu repeat sequences. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):219–225. doi: 10.1038/296219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLap R. J., Rush M. G. Change in quantity and size distribution of small circular DNAs during development of chicken bursa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5855–5859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLap R. J., Rush M. G., Zouzias D., Khan S. Isolation and preliminary characterization of the small circular DNA present in African green monkey kidney (BSC-1) cells. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):508–521. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delap R. J., Zouzias D., Rush M. G. Preparation of radioiodinated simian virus 40 DNA for use in DNA - DNA reassociation kinetics experiments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 5;418(3):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGiovanni L., Haynes S. R., Misra R., Jelinek W. R. Kpn I family of long-dispersed repeated DNA sequences of man: evidence for entry into genomic DNA of DNA copies of poly(A)-terminated Kpn I RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6533–6537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G. Characterization of a highly repetitive family of DNA sequences in the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):5003–5013. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.5003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G. Size and structure of the highly repetitive BAM HI element in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5073–5091. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geier G. E., Modrich P. Recognition sequence of the dam methylase of Escherichia coli K12 and mode of cleavage of Dpn I endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1408–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Singer M. F. Members of the KpnI family of long interspersed repeated sequences join and interrupt alpha-satellite in the monkey genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):321–338. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOTTA Y., BASSEL A. MOLECULAR SIZE AND CIRCULARITY OF DNA IN CELLS OF MAMMALS AND HIGHER PLANTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:356–362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis G. F., Hieter P. A., McBride O. W., Swan D., Leder P. Processed genes: a dispersed human immunoglobulin gene bearing evidence of RNA-type processing. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):321–325. doi: 10.1038/296321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole L. B., Haynes S. R., Jelinek W. R. Discrete and heterogeneous high molecular weight RNAs complementary to a long dispersed repeat family (a possible transposon) of human DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 5;165(2):257–286. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolewski J. J., Bertelsen A. H., Humayun M. Z., Rush M. G. Members of the Alu family of interspersed, repetitive DNA sequences are in the small circular DNA population of monkey cells grown in culture. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 25;154(3):399–415. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(82)80003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolewski J. J., Rush M. G. Some extrachromosomal circular DNAs containing the Alu family of dispersed repetitive sequences may be reverse transcripts. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90363-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolewski J. J., Schindler C. W., Rush M. G. Structure of extrachromosomal circular DNAs containing both the Alu family of dispersed repetitive sequences and other regions of chromosomal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):41–54. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90364-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Feenstra A., Lueders K., Smith L., Hawley R., Hozumi N., Shulman M. Intracisternal A-particle genes as movable elements in the mouse genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1992–1996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman M. I., Thayer R. E., Singer M. F. Kpn I family of long interspersed repeated DNA sequences in primates: polymorphism of family members and evidence for transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Biro P. A. Genomic representation of the Hind II 1.9 kb repeated DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3221–3239. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Nucleotide sequence definition of a major human repeated DNA, the Hind III 1.9 kb family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3211–3219. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. L., Voliva C. F., Burton F. H., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd A large interspersed repeat found in mouse DNA contains a long open reading frame that evolves as if it encodes a protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2308–2312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S., Brorein W. J., Jr, Dunsmuir P., Rubin G. M. Transposition of elements of the 412, copia and 297 dispersed repeated gene families in Drosophila. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):415–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S. Rearranged sequences of a human Kpn I element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1012–1016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. Purification of genomic sequences from bacteriophage libraries by recombination and selection in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2427–2445. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafit-Zagardo B., Brown F. L., Maio J. J., Adams J. W. KpnI families of long, interspersed repetitive DNAs associated with the human beta-globin gene cluster. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafit-Zagardo B., Maio J. J., Brown F. L. KpnI families of long, interspersed repetitive DNAs in human and other primate genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3175–3193. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmookler Reis R. J., Lumpkin C. K., Jr, McGill J. R., Riabowol K. T., Goldstein S. Extrachromosomal circular copies of an 'inter-Alu' unstable sequence in human DNA are amplified during in vitro and in vivo ageing. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):394–398. doi: 10.1038/301394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F., Thayer R. E., Grimaldi G., Lerman M. I., Fanning T. G. Homology between the KpnI primate and BamH1 (M1F-1) rodent families of long interspersed repeated sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5739–5745. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Vinograd J. Small polydisperse circular DNA of HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 21;69(2):163–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90222-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield S. W., Lengyel J. A. Small circular DNA of Drosophila melanogaster: chromosomal homology and kinetic complexity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6142–6146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield S., Helinski D. R. Small circular DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):333–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer R. E., Singer M. F. Interruption of an alpha-satellite array by a short member of the KpnI family of interspersed, highly repeated monkey DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):967–973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda T., Yamagishi H., Ohnishi N., Yamada Y., Izumi H., Mori K. J. Extrachromosomal circular DNAs from murine hemopoietic tissue cells. Plasmid. 1983 Nov;10(3):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. On the possibility of metabolic control of replicon "misfiring": relationship to emergence of malignant phenotypes in mammalian cell lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3673–3677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. D., Crowther C. E., Cripe T. P., Gwo-Shu Lee M., Cowan N. J. Evidence that a human beta-tubulin pseudogene is derived from its corresponding mRNA. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):83–84. doi: 10.1038/297083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi H., Kunisada T., Tsuda T. Small circular DNA complexes in eucaryotic cells. Plasmid. 1982 Nov;8(3):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


