Abstract
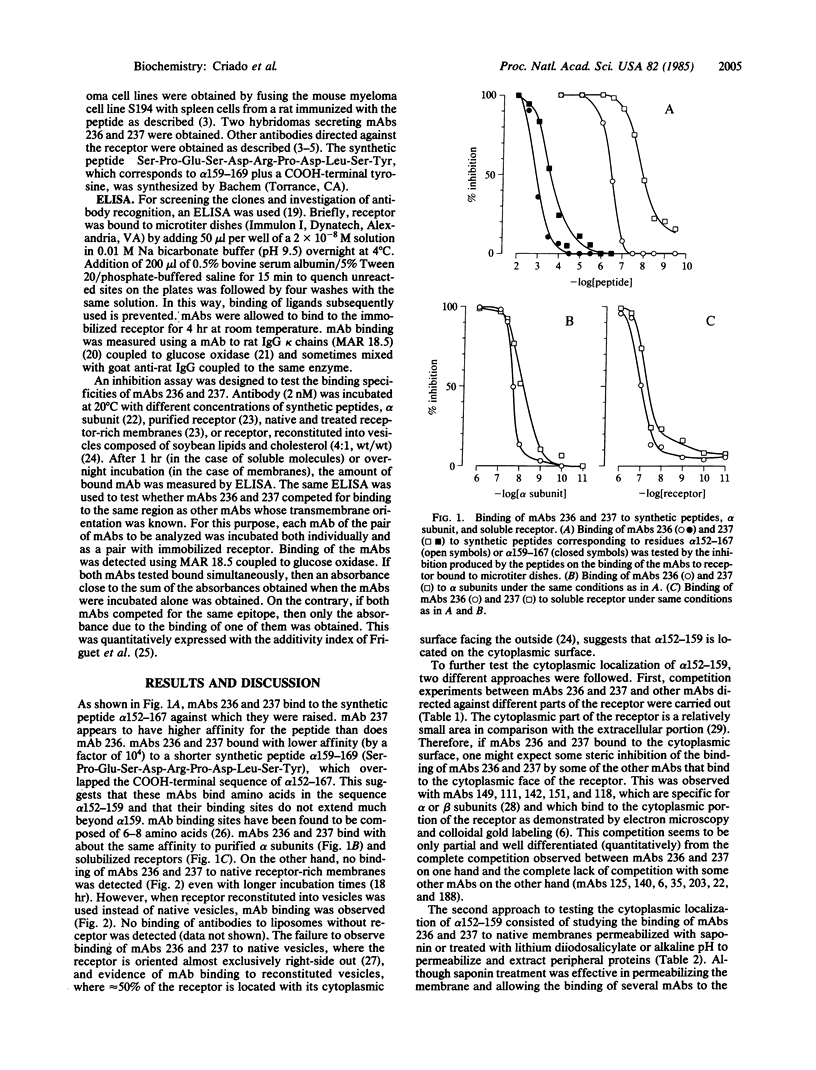
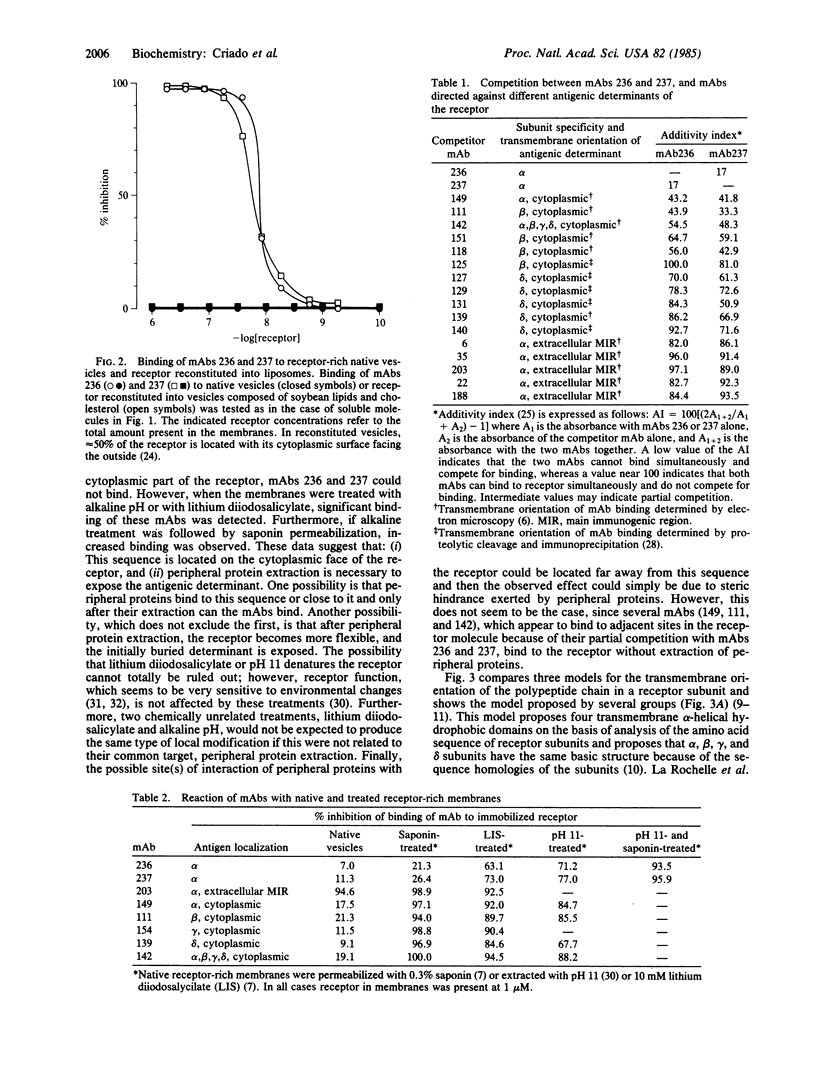
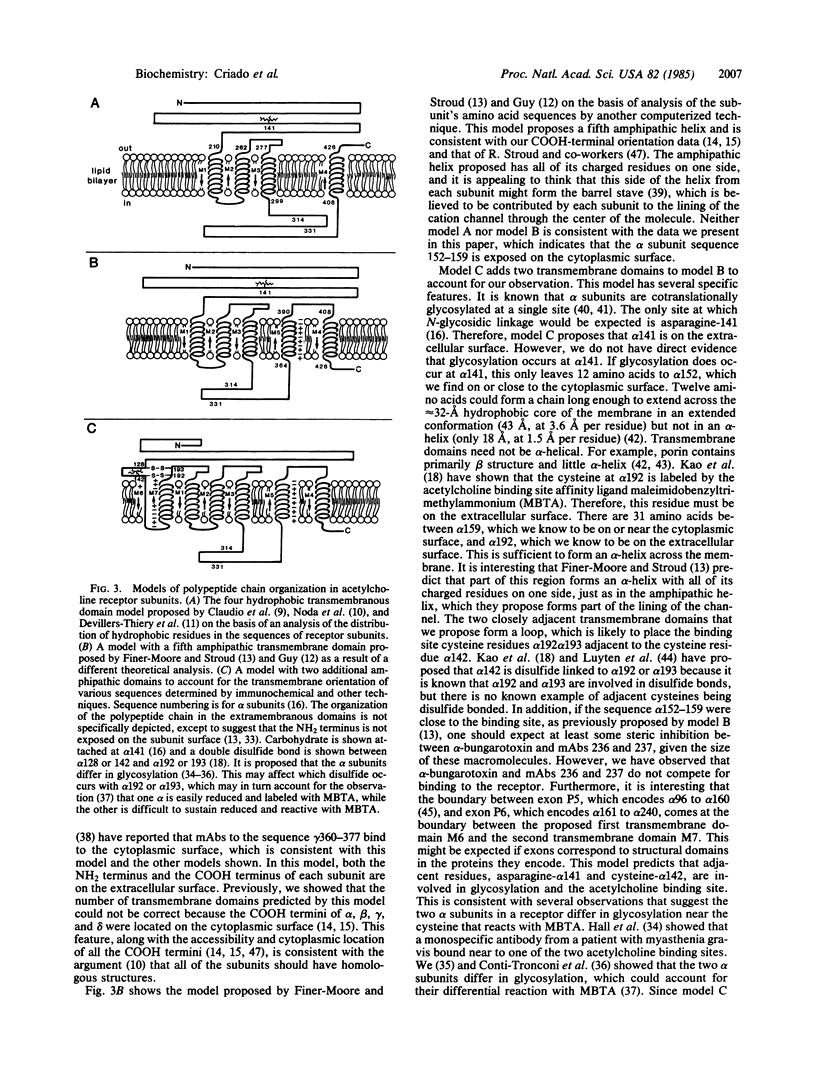
Two monoclonal antibodies (mAbs 236 and 237) against a synthetic peptide composed of the same amino acid residues as the sequence 152-167 of the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor were obtained, and their crossreaction with the synthetic peptide, alpha subunit, and solubilized receptor was demonstrated. Crossreaction with the synthetic peptide alpha 159-169 was less by a factor of 10(4), suggesting that the mAbs bind primarily to the sequence alpha 152-159. Cholinergic ligands did not inhibit mAb binding. No crossreaction was observed with the receptor in native membranes, but the mAbs could bind to receptor reconstituted into liposomes in which 50% of the receptors have their cytoplasmic surface oriented outside. When native membranes were permeabilized with saponin, mAbs directed against cytoplasmic determinants of the receptor could bind to them, but mAbs 236 and 237 could not. However, after treatments that removed peripheral proteins from the cytoplasmic surface, binding of both mAbs was observed. Further evidence for the cytoplasmic localization of this sequence was provided by observation of partial competition for binding between mAbs 236 and 237 and mAbs previously demonstrated to bind to the cytoplasmic surface of the receptor. To account for these findings, a model for the organization of the polypeptide chains in receptor subunits is proposed that has a total of seven transmembrane domains in each subunit, two of which are amphipathic and one of which is not alpha-helical.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G. In vitro synthesis, glycosylation, and membrane insertion of the four subunits of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5598–5602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G., Tzartos S., Gullick W., Lindstrom J. Transmembrane orientation of an early biosynthetic form of acetylcholine receptor delta subunit determined by proteolytic dissection in conjunction with monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci. 1983 Sep;3(9):1773–1784. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-09-01773.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anholt R., Fredkin D. R., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Montal M., Lindstrom J. Incorporation of acetylcholine receptors into liposomes. Vesicle structure and acetylcholine receptor function. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7122–7134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anholt R., Lindstrom J., Montal M. Stabilization of acetylcholine receptor channels by lipids in cholate solution and during reconstitution in vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4377–4387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Krämer C., Schmidmayr W., Henning U. Primary structure of major outer membrane protein I of Escherichia coli B/r. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5014–5017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T., Ballivet M., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor gamma subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Raftery M. A. Molecular weight and structural nonequivalence of the mature alpha subunits of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2631–2634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criado M., Eibl H., Barrantes F. J. Functional properties of the acetylcholine receptor incorporated in model lipid membranes. Differential effects of chain length and head group of phospholipids on receptor affinity states and receptor-mediated ion translocation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9188–9198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillers-Thiery A., Giraudat J., Bentaboulet M., Changeux J. P. Complete mRNA coding sequence of the acetylcholine binding alpha-subunit of Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor: a model for the transmembrane organization of the polypeptide chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2067–2071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D. Three-dimensional structure of membrane and surface proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:595–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer-Moore J., Stroud R. M. Amphipathic analysis and possible formation of the ion channel in an acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):155–159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Douville K., Klink S., Culp W. J. Monoclonal antibodies to cytoplasmic domains of the acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7112–7120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Lindstrom J. M. Mapping the binding of monoclonal antibodies to the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 5;22(14):3312–3320. doi: 10.1021/bi00283a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R. A structural model of the acetylcholine receptor channel based on partition energy and helix packing calculations. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):249–261. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84152-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W., Roisin M. P., Gu Y., Gorin P. D. A developmental change in the immunological properties of acetylcholine receptors at the rat neuromuscular junction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):101–108. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. R., Orengo A. The preparation of an immunoglobulin--amyloglucosidase conjugate and its quantitation by an enzyme-cycling assay. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 1;113(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartig P. R., Raftery M. A. Preparation of right-side-out, acetylcholine receptor enriched intact vesicles from Torpedo californica electroplaque membranes. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1146–1150. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juillerat M. A., Barkas T., Tzartos S. J. Antigenic sites of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor cannot be predicted from the hydrophilicity profile. FEBS Lett. 1984 Mar 12;168(1):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80224-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao P. N., Dwork A. J., Kaldany R. R., Silver M. L., Wideman J., Stein S., Karlin A. Identification of the alpha subunit half-cystine specifically labeled by an affinity reagent for the acetylcholine receptor binding site. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11662–11665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kistler J., Stroud R. M., Klymkowsky M. W., Lalancette R. A., Fairclough R. H. Structure and function of an acetylcholine receptor. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):371–383. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84685-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klymkowsky M. W., Stroud R. M. Immunospecific identification and three-dimensional structure of a membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 5;128(3):319–334. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Gutman G. A., Lewis D. E., Griswold S. T., Warner N. L. Monoclonal antibodies against rat immunoglobulin kappa chains. Hybridoma. 1982;1(2):125–131. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1.1982.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Anholt R., Einarson B., Engel A., Osame M., Montal M. Purification of acetylcholine receptors, reconstitution into lipid vesicles, and study of agonist-induced cation channel regulation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8340–8350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Criado M., Hochschwender S., Fox J. L., Sarin V. Immunochemical tests of acetylcholine receptor subunit models. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):573–575. doi: 10.1038/311573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Merlie J., Yogeeswaran G. Biochemical properties of acteylcholine receptor subunits from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4465–4470. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Tzartos S., Gullick W., Hochschwender S., Swanson L., Sargent P., Jacob M., Montal M. Use of monoclonal antibodies to study acetylcholine receptors from electric organs, muscle, and brain and the autoimmune response to receptor in myasthenia gravis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):89–99. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Lindstrom J. Assembly in vivo of mouse muscle acetylcholine receptor: identification of an alpha subunit species that may be an assembly intermediate. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):747–757. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90531-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Sebbane R., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. Inhibition of glycosylation with tunicamycin blocks assembly of newly synthesized acetylcholine receptor subunits in muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2694–2701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubig R. R., Krodel E. K., Boyd N. D., Cohen J. B. Acetylcholine and local anesthetic binding to Torpedo nicotinic postsynaptic membranes after removal of nonreceptor peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):690–694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann D., Fridkin M., Fuchs S. Anti-acetylcholine receptor response achieved by immunization with a synthetic peptide from the receptor sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):673–679. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90234-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Tanabe T., Shimizu S., Kikyotani S., Kayano T., Hirose T., Inayama S. Cloning and sequence analysis of calf cDNA and human genomic DNA encoding alpha-subunit precursor of muscle acetylcholine receptor. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):818–823. doi: 10.1038/305818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Miyata T., Numa S. Primary structure of alpha-subunit precursor of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):793–797. doi: 10.1038/299793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Structural homology of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor subunits. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):528–532. doi: 10.1038/302528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnam M., Lindstrom J. Structural features of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor revealed by antibodies to synthetic peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1225–1233. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91223-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent P. B., Hedges B. E., Tsavaler L., Clemmons L., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. M. Structure and transmembrane nature of the acetylcholine receptor in amphibian skeletal muscle as revealed by cross-reacting monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):609–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Lindstrom J. M. Monoclonal antibodies used to probe acetylcholine receptor structure: localization of the main immunogenic region and detection of similarities between subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Rand D. E., Einarson B. L., Lindstrom J. M. Mapping of surface structures of electrophorus acetylcholine receptor using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8635–8645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S., Langeberg L., Hochschwender S., Lindstrom J. Demonstration of a main immunogenic region on acetylcholine receptors from human muscle using monoclonal antibodies to human receptor. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 11;158(1):116–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80688-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosin J. M., Lyddiatt A., Dolly J. O., Barnard E. A. Stoichiometry of the ligand-binding sites in the acetylcholine-receptor oligomer from muscle and from electric organ. Measurement by affinity alkylation with bromoacetylcholine. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):495–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04821.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. F., Ralston E., Blake J., Ramachandran J., Hall Z. W., Stroud R. M. Topological mapping of acetylcholine receptor: evidence for a model with five transmembrane segments and a cytoplasmic COOH-terminal peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):626–630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


