Abstract
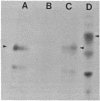
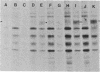
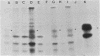
Recombinant plasmids were constructed in which genes coding for either the entire or the signal-minus (amino acid residues 2-17 deleted) hemagglutinin (HA) of WSN influenza virus were placed under the control of the alcohol dehydrogenase I gene promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Both recombinant plasmids were shown to direct the synthesis of HA-specific polypeptides that were detected by immunoprecipitation with antiviral antibodies. The complete HA produced in yeast had an approximate Mr of 70,000 and was glycosylated, as determined by the endoglycosidase H sensitivity, and was bound to membrane. Therefore, the complete HA polypeptide possessing the signal sequence probably traversed the yeast secretory pathways. Signal-minus HA, on the other hand, had a lower molecular weight and was nonglycosylated. The specific binding of yeast HA with antiviral antibodies could be competitively inhibited by influenza viral HA, demonstrating that the HA produced in yeast contained antigenic determinants of the native viral HA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso-Caplen F. V., Compans R. W. Modulation of glycosylation and transport of viral membrane glycoproteins by a sodium ionophore. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):659–668. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Davis A. R., Nayak D. P. NH2-terminal hydrophobic region of influenza virus neuraminidase provides the signal function in translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2327–2331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd J. C., Tarentino A. L., Maley F., Atkinson P. H., Trimble R. B. Glycoprotein synthesis in yeast. Identification of Man8GlcNAc2 as an essential intermediate in oligosaccharide processing. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14657–14666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. R., Bos T., Ueda M., Nayak D. P., Dowbenko D., Compans R. W. Immune response to human influenza virus hemagglutinin expressed in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Mar;21(3):273–284. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. R., Hiti A. L., Nayak D. P. Construction and characterization of a bacterial clone containing the hemagglutinin gene of the WSN strain (HON1) of influenza virus. Gene. 1980 Aug;10(3):205–218. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. R., Nayak D. P., Ueda M., Hiti A. L., Dowbenko D., Kleid D. G. Expression of antigenic determinants of the hemagglutinin gene of a human influenza virus in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5376–5380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Singh A., Goeddel D. V. Expression of the human interferon-gamma cDNA in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1819–1837. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edens L., Bom I., Ledeboer A. M., Maat J., Toonen M. Y., Visser C., Verrips C. T. Synthesis and processing of the plant protein thaumatin in yeast. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):629–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90394-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard W., Yewdell J., Frankel M. E., Webster R. Antigenic structure of influenza virus haemagglutinin defined by hybridoma antibodies. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):713–717. doi: 10.1038/290713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff C. G., Moir D. T., Kohno T., Gravius T. C., Smith R. A., Yamasaki E., Taunton-Rigby A. Expression of calf prochymosin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1984 Jan;27(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90236-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiti A. L., Davis A. R., Nayak D. P. Complete sequence analysis shows that the hemagglutinins of the H0 and H2 subtypes of human influenza virus are closely related. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90658-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzeman R. A., Hagie F. E., Levine H. L., Goeddel D. V., Ammerer G., Hall B. D. Expression of a human gene for interferon in yeast. Nature. 1981 Oct 29;293(5835):717–722. doi: 10.1038/293717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzeman R. A., Leung D. W., Perry L. J., Kohr W. J., Levine H. L., Goeddel D. V. Secretion of human interferons by yeast. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):620–625. doi: 10.1126/science.6186023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Schekman R., Thorner J. Glycosylation and processing of prepro-alpha-factor through the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. A., DeChiara T. M., Schaber M. D., Hilliker S. Regulated expression of a human interferon gene in yeast: control by phosphate concentration or temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):367–370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott M. S. Isolation and chemical characterization of plasma membranes from the yeast and mycelial forms of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):115–132. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Dobson M. J., Roberts N. A., Tuite M. F., Emtage J. S., White S., Lowe P. A., Patel T., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Efficient synthesis of enzymatically active calf chymosin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1983 Sep;24(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak D. P., Tobita K., Janda J. M., Davis A. R., De B. K. Homologous interference mediated by defective interfering influenza virus derived from a temperature-sensitive mutant of influenza virus. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):375–386. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.375-386.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Plummer T. H., Jr, Maley F. The release of intact oligosaccharides from specific glycoproteins by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):818–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuite M. F., Dobson M. J., Roberts N. A., King R. M., Burke D. C., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. Regulated high efficiency expression of human interferon-alpha in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):603–608. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01215.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Medina A., Rutter W. J., Ammerer G., Hall B. D. Synthesis and assembly of hepatitis B virus surface antigen particles in yeast. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):347–350. doi: 10.1038/298347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Laver W. G., Air G. M., Schild G. C. Molecular mechanisms of variation in influenza viruses. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):115–121. doi: 10.1038/296115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]