Abstract
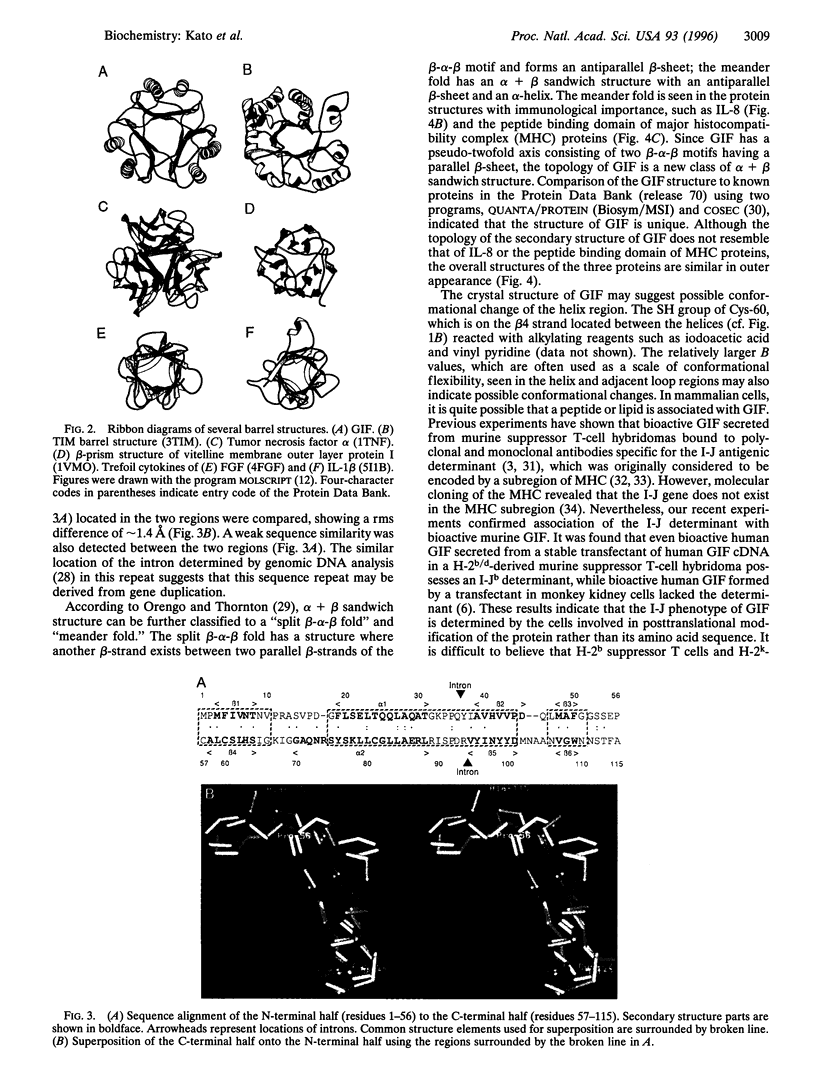
Glycosylation-inhibiting factor (GIF) is a cytokine that is involved in the regulation of IgE synthesis. The crystal structure of recombinant human GIF was determined by the multiple isomorphous replacement method. The structure was refined to an R factor of 0.168 at 1.9 angstrom resolution. The overall structure is seen to consist of three interconnected subunits forming a barrel with three 6-stranded beta-sheets on the inside and six alpha-helices on the outside. There is a 5-angstrom-diameter "hole" through the middle of the barrel. The barrel structure of GIF in part resembles other "trefoil" cytokines such as interleukin 1 and fibroblast growth factor. Each subunit has a new class of alpha + beta sandwich structure consisting of two beta-alpha-beta motifs. These beta-alpha-beta motifs are related by a pseudo-twofold axis and resemble both interleukin 8 and the peptide binding domain of major histocompatibility complex protein, although the topology of the polypeptide chain is quite different.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ago H., Kitagawa Y., Fujishima A., Matsuura Y., Katsube Y. Crystal structure of basic fibroblast growth factor at 1.6 A resolution. J Biochem. 1991 Sep;110(3):360–363. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner D. W., Bloomer A. C., Petsko G. A., Phillips D. C., Pogson C. I., Wilson I. A., Corran P. H., Furth A. J., Milman J. D., Offord R. E. Structure of chicken muscle triose phosphate isomerase determined crystallographically at 2.5 angstrom resolution using amino acid sequence data. Nature. 1975 Jun 19;255(5510):609–614. doi: 10.1038/255609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Y., Pettersson R. F. Release and subcellular localization of acidic fibroblast growth factor expressed to high levels in HeLa cells. Growth Factors. 1993;8(4):277–290. doi: 10.3109/08977199308991573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah E., Carr P. D., Suffolk P. M., Vasudevan S. G., Dixon N. E., Ollis D. L. Structure of the Escherichia coli signal transducing protein PII. Structure. 1994 Oct 15;2(10):981–990. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(94)00100-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eck M. J., Sprang S. R. The structure of tumor necrosis factor-alpha at 2.6 A resolution. Implications for receptor binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17595–17605. doi: 10.2210/pdb1tnf/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson A. E., Cousens L. S., Weaver L. H., Matthews B. W. Three-dimensional structure of human basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3441–3445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finzel B. C., Clancy L. L., Holland D. R., Muchmore S. W., Watenpaugh K. D., Einspahr H. M. Crystal structure of recombinant human interleukin-1 beta at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 20;209(4):779–791. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90606-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K. Regulation of IgE synthesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:159–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Ishizaka K. Construction of antigen-specific suppressor T cell hybridomas from spleen cells of mice primed for the persistent IgE antibody formation. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3270–3277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardieu P., Akasaki M., Ishizaka K. Carrier-specific suppression of antibody responses by antigen-specific glycosylation-inhibiting factors. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1494–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessop J. J., Hoffman T. Production and release of IL-1 beta by human peripheral blood monocytes in response to diverse stimuli: possible role of "microdamage" to account for unregulated release. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1993 Feb;12(1):51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. Y., Stuart D. I., Walker N. P. Structure of tumour necrosis factor. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):225–228. doi: 10.1038/338225a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg M., Steinmetz M., Kobori J., Kraig E., Kapp J. A., Pierce C. W., Sorensen C. M., Suzuki G., Tada T., Hood L. RNA transcripts for I-J polypeptides are apparently not encoded between the I-A and I-E subregions of the murine major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5704–5708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M., Chothia C. Structural patterns in globular proteins. Nature. 1976 Jun 17;261(5561):552–558. doi: 10.1038/261552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. D., Carroll J., Ellar D. J. Crystal structure of insecticidal delta-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis at 2.5 A resolution. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):815–821. doi: 10.1038/353815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. C., Nakano T., Elly C., Ishizaka K. Requirement of posttranslational modifications for the generation of biologic activity of glycosylation-inhibiting factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11227–11231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikayama T., Nakano T., Gomi H., Nakagawa Y., Liu Y. C., Sato M., Iwamatsu A., Ishii Y., Weiser W. Y., Ishizaka K. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a cDNA encoding glycosylation-inhibiting factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10056–10060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuguchi K., Go N. Comparison of spatial arrangements of secondary structural elements in proteins. Protein Eng. 1995 Apr;8(4):353–362. doi: 10.1093/protein/8.4.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Herzenberg L. A., Okumura K., Herzenberg L. A., McDevitt H. O. A new I subregion (I-J) marked by a locus (Ia-4) controlling surface determinants on suppressor T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):699–712. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Liu Y. C., Mikayama T., Watarai H., Taniguchi M., Ishizaka K. Association of the "major histocompatibility complex subregion" I-J determinant with bioactive glycosylation-inhibiting factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9196–9200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orengo C. A., Thornton J. M. Alpha plus beta folds revisited: some favoured motifs. Structure. 1993 Oct 15;1(2):105–120. doi: 10.1016/0969-2126(93)90026-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paralkar V., Wistow G. Cloning the human gene for macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Genomics. 1994 Jan 1;19(1):48–51. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priestle J. P., Schär H. P., Grütter M. G. Crystallographic refinement of interleukin 1 beta at 2.0 A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9667–9671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S. T., Rossmann M. G. Comparison of super-secondary structures in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 15;76(2):241–256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Vassylyev D. G., Kido S., Doi Y., Morikawa K. Crystal structure of vitelline membrane outer layer protein I (VMO-I): a folding motif with homologous Greek key structures related by an internal three-fold symmetry. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 1;13(5):1003–1010. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06348.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele J. K., Kuchroo V. K., Kawasaki H., Jayaraman S., Iwata M., Ishizaka K., Dorf M. E. A monoclonal antibody raised to lipomodulin recognizes T suppressor factors in two independent hapten-specific suppressor networks. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2213–2220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Taniguchi M., David C. S. Properties of the antigen-specific suppressive T-cell factor in the regulation of antibody response of the mouse. IV. Special subregion assignment of the gene(s) that codes for the suppressive T-cell factor in the H-2 histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):713–725. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veerapandian B., Gilliland G. L., Raag R., Svensson A. L., Masui Y., Hirai Y., Poulos T. L. Functional implications of interleukin-1 beta based on the three-dimensional structure. Proteins. 1992 Jan;12(1):10–23. doi: 10.1002/prot.340120103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:90–112. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. D., Cousens L. S., Barr P. J., Sprang S. R. Three-dimensional structure of human basic fibroblast growth factor, a structural homolog of interleukin 1 beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3446–3450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X., Komiya H., Chirino A., Faham S., Fox G. M., Arakawa T., Hsu B. T., Rees D. C. Three-dimensional structures of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):90–93. doi: 10.1126/science.1702556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]