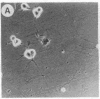
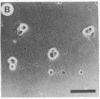
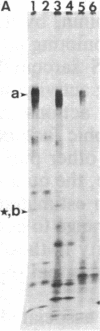
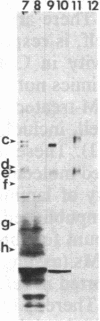
Abstract
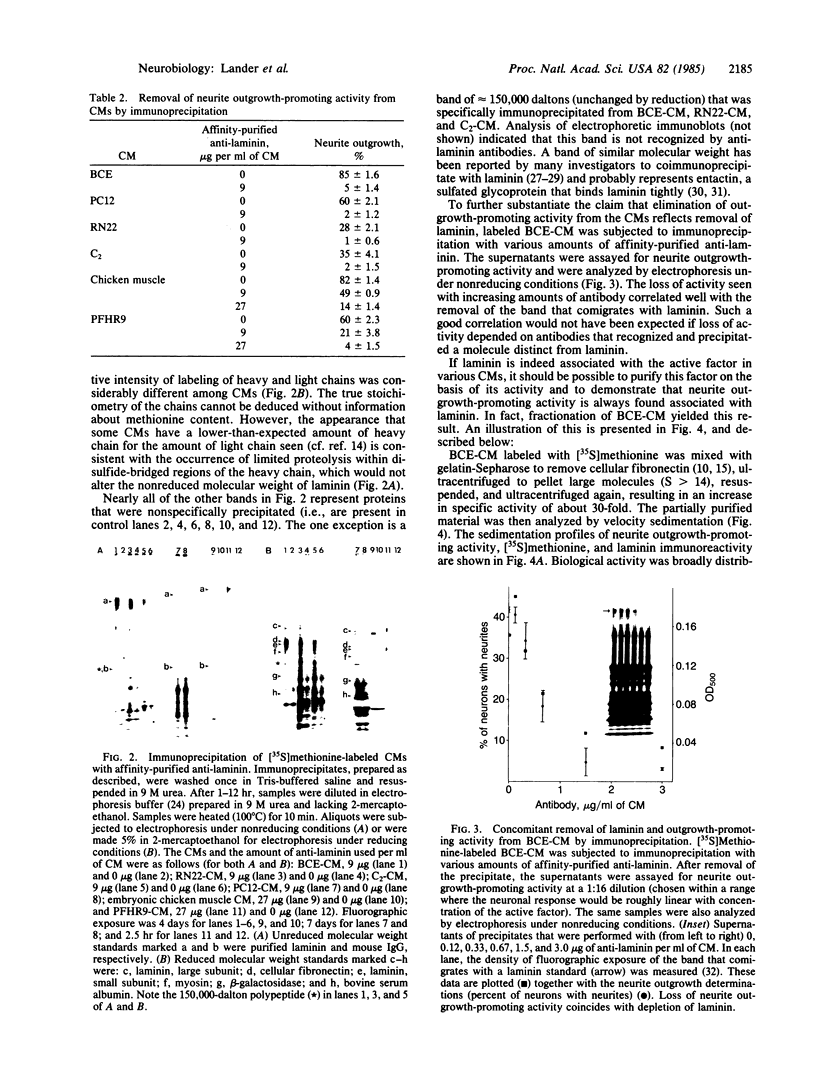
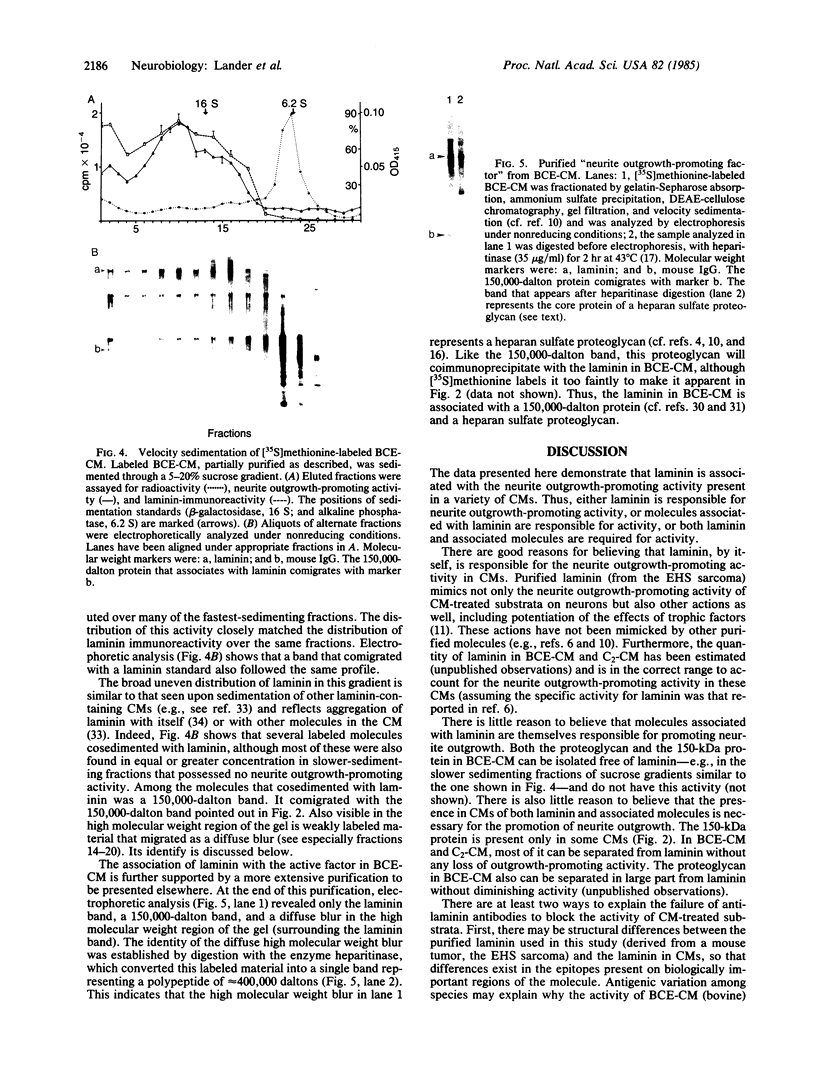
Conditioned media (CMs) from many cell types contain a factor that can adsorb to a polycationic substratum and cause neurons plated on that substratum to extend neurites rapidly and profusely. The extracellular matrix glycoprotein laminin, when bound to a substratum, elicits a similar response by neurons. In this report, six CMs that contain a "neurite outgrowth-promoting factor" were studied. Immunoprecipitation with affinity-purified anti-laminin antibodies demonstrated that laminin is present in all of them, and when it was selectively removed, there was a corresponding loss of neurite outgrowth-promoting activity in each CM. Antibodies to purified laminin failed, however, to block the outgrowth-promoting activity of five of the CMs tested, even though these antibodies blocked the outgrowth-promoting activity of purified laminin in the same assay. This result could reflect differences in amino acid sequence or protein modification between CM-derived laminin and the purified laminin used in generating antibodies. Alternatively, it could reflect the fact that other molecules bind to laminin in CMs and could interfere with the binding of antibodies to sites on laminin that are important for biological activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler R., Manthorpe M., Skaper S. D., Varon S. Polyornithine-attached neurite-promoting factors (PNPFs). Culture sources and responsive neurons. Brain Res. 1981 Feb 9;206(1):129–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron-Van Evercooren A., Kleinman H. K., Ohno S., Marangos P., Schwartz J. P., Dubois-Dalcq M. E. Nerve growth factor, laminin, and fibronectin promote neurite growth in human fetal sensory ganglia cultures. J Neurosci Res. 1982;8(2-3):179–193. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490080208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bächinger H. P., Fessler L. I., Fessler J. H. Mouse procollagen IV. Characterization and supramolecular association. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9796–9803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAVEN G. R., STEERS E., Jr, ANFINSEN C. B. PURIFICATION, COMPOSITION, AND MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF THE BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2468–2477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calof A. L., Reichardt L. F. Motoneurons purified by cell sorting respond to two distinct activities in myotube-conditioned medium. Dev Biol. 1984 Nov;106(1):194–210. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin B. E., Durkin M. E., Bender B., Jaffe R., Chung A. E. Synthesis of laminin and entactin by F9 cells induced with retinoic acid and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7729–7737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. Induction of neurite outgrowth by a conditioned-medium factor bound to the culture substratum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5210–5213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. Neurite outgrowth induced by the substrate associated material from nonneuronal cells. Dev Biol. 1980 Sep;79(1):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. R., Kurkinen M., Taylor A., Hogan B. L. Studies on the biosynthesis of laminin by murine parietal endoderm cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep;119(1):189–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornbrooks C. J., Carey D. J., McDonald J. A., Timpl R., Bunge R. P. In vivo and in vitro observations on laminin production by Schwann cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3850–3854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin M. D., Bloom E. M., Black I. B. Characterization of a neuronal growth factor from mouse heart-cell-conditioned medium. Dev Biol. 1981 Feb;82(1):56–68. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90428-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin M. D., Kessler J. A. Antiserum to a new neuronal growth factor: effects on neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci Res. 1982;8(2-3):289–302. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490080219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D., Timpl R., Thoenen H. The heparin-binding domain of laminin is responsible for its effects on neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1463–1468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Odermatt E., Engel A., Madri J. A., Furthmayr H., Rohde H., Timpl R. Shapes, domain organizations and flexibility of laminin and fibronectin, two multifunctional proteins of the extracellular matrix. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Krusius T., Wewer U., Ruoslahti E. Laminin from rat yolk sac tumor: isolation, partial characterization, and comparison with mouse laminin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Apr 15;222(2):649–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90562-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan B. L., Taylor A., Kurkinen M., Couchman J. R. Synthesis and localization of two sulphated glycoproteins associated with basement membranes and the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):197–204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., McGarvey M. L., Liotta L. A., Robey P. G., Tryggvason K., Martin G. R. Isolation and characterization of type IV procollagen, laminin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycan from the EHS sarcoma. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6188–6193. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühl U., Timpl R., von der Mark K. Synthesis of type IV collagen and laminin in cultures of skeletal muscle cells and their assembly on the surface of myotubes. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):344–354. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander A. D., Fujii D. K., Gospodarowicz D., Reichardt L. F. Characterization of a factor that promotes neurite outgrowth: evidence linking activity to a heparan sulfate proteoglycan. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):574–585. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander A. D., Tomaselli K., Calof A. L., Reichardt L. F. Studies on extracellular matrix components that promote neurite outgrowth. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):611–623. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liesi P., Dahl D., Vaheri A. Laminin is produced by early rat astrocytes in primary culture. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):920–924. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manthorpe M., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E., Longo F. M., Davis G. E., Varon S. Laminin promotes neuritic regeneration from cultured peripheral and central neurons. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1882–1890. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manthorpe M., Varon S., Adler R. Neurite-promoting factor in conditioned medium from RN22 Schwannoma cultures: bioassay, fractionation, and properties. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):759–767. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb12552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C. L. Theory and methods for immunization in culture and monoclonal antibody production. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Sep 30;53(3):261–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohde H., Bächinger H. P., Timpl R. Characterization of pepsin fragments of laminin in a tumor basement membrane. Evidence for the existence of related proteins. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980 Nov;361(11):1651–1660. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1980.361.2.1651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M., Engvall E. Fibronectin: purification, immunochemical properties, and biological activities. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):803–831. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Barrett K. The reversible dissociation of the alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli. I. Formation and reactivation of subunits. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4284–4292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suissa M. Spectrophotometric quantitation of silver grains eluted from autoradiograms. Anal Biochem. 1983 Sep;133(2):511–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Risteli L., Ott U., Robey P. G., Martin G. R. Laminin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):831–838. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):725–727. doi: 10.1038/270725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]