Abstract
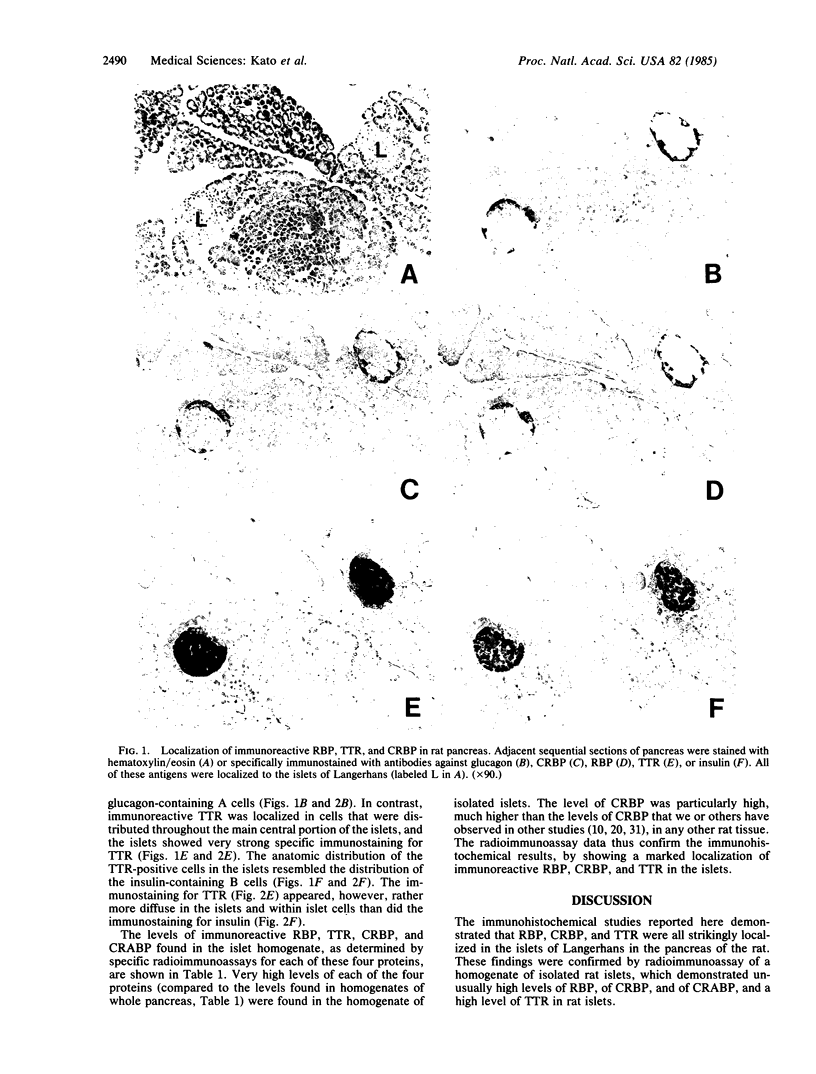
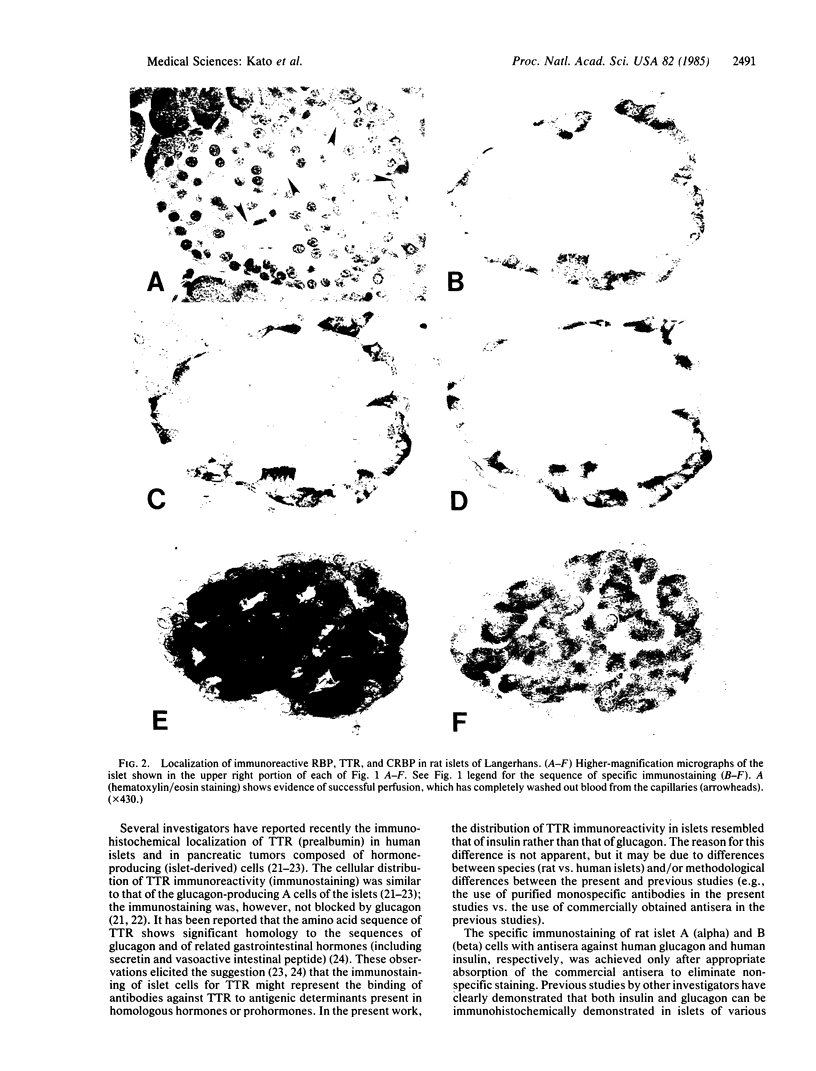
The immunohistochemical localization of plasma retinol-binding protein (RBP), cellular retinol-binding protein (CRBP), and transthyretin (TTR) was studied in rat pancreas. The studies employed antibodies purified by immunosorbent affinity chromatography, permitting the specific staining and localization of each antigen by the unlabeled peroxidase-antiperoxidase method. Specific immunostaining for each of these three proteins was found localized to the islets of Langerhans. Both RBP and CRBP were localized in cells that were peripherally distributed within the islets, with an anatomic distribution that resembled that of the glucagon-containing A cells. Immunoreactive TTR was localized in cells that were more centrally distributed in the islets, with an anatomic distribution that resembled that of the insulin-containing B cells. These findings were confirmed by radioimmunoassay of a homogenate of isolated rat islets. By using sensitive and specific radioimmunoassays for each antigen, unusually high levels of CRBP, RBP, TTR, and cellular retinoic acid-binding protein (CRABP) were found in rat islets. The physiological significance of the localization of RBP, CRBP, CRABP, and TTR in the islets is not known. The findings suggest that retinoids and their binding proteins may play important metabolic roles within islet cells, and hence that they may be involved in some way in the biological, endocrine, function of the islets.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi N., Smith J. E., Sklan D., Goodman D. S. Radioimmunoassay studies of the tissue distribution and subcellular localization of cellular retinol-binding protein in rats. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9471–9476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolati G., Papotti M., Sapino A. Binding of antibodies against human prealbumin to intestinal and bronchial carcinoids and to pancreatic endocrine tumours. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1984;45(1):15–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02889848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Heller J. Uptake of retinol and retinoic acid from serum retinol-binding protein by retinal pigment epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5216–5221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chertow B. S., Baker G. R. The effects of vitamin A on insulin release and glucose oxidation in isolated rat islets. Endocrinology. 1978 Nov;103(5):1562–1572. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-5-1562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chertow B. S., Baranetsky N. G., Sivitz W. I., Meda P., Webb M. D., Shih J. C. Cellular mechanisms of insulin release. Effects of retinoids on rat islet cell-to-cell adhesion, reaggregation, and insulin release. Diabetes. 1983 Jun;32(6):568–574. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.6.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chertow B. S., Buschmann R. J., Kaplan R. L. Cellular mechanisms of insulin release. Effects of retinol on insulin release and islet ultrastructure. Diabetes. 1979 Aug;28(8):754–761. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.8.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb J. W., Saari J. C. N-terminal sequence homology among retinoid-binding proteins from bovine retina. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jul 20;130(1):15–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80655-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Carlström A., Pettersson T., Jacobsson B., Persson M., Mutt V. Structural homologies between prealbumin, gastrointestinal prohormones and other proteins. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):261–263. doi: 10.1038/291261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda Y., Goodman D. S. Partial amino acid sequence of human plasma retinol-binding protein. Isolation and alignment of the five cyanogen bromide fragments and the amino acid sequences of four of the fragments. J Lipid Res. 1979 Sep;20(7):865–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato M., Kato K., Goodman D. S. Immunocytochemical studies on the localization of plasma and of cellular retinol-binding proteins and of transthyretin (prealbumin) in rat liver and kidney. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1696–1704. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato M., Sung W. K., Kato K., Goodman D. S. Immunohistochemical studies on the localization of cellular retinol-binding protein in rat testis and epididymis. Biol Reprod. 1985 Feb;32(1):173–189. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod32.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange R. H., Ali S. S., Klein C., Trandaburu T. Immunohistological demonstration of insulin and glucagon in islet tissue of reptiles, amphibians and teleosts using epoxy-embedded material and antiporcine hormone sera. Acta Histochem. 1975;52(1):71–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misugi K., Howell S. L., Greider M. H., Lacy P. E., Sorenson G. D. The pancreatic beta cell. Demonstration with peroxidase-labeled antibody technique. Arch Pathol. 1970 Feb;89(2):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto Y., Smith J. E., Milch P. O., Goodman D. S. Regulation of retinol-binding protein metabolism by vitamin A status in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2542–2550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navab M., Smith J. E., Goodman D. S. Rat plasma prealbumin. Metabolic studies on effects of vitamin A status and on tissue distribution. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5107–5114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong D. E., Crow J. A., Chytil F. Radioimmunochemical determination of cellular retinol- and cellular retinoic acid-binding proteins in cytosols of rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13385–13389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter S. B., Fraker L. D., Chytil F., Ong D. E. Localization of cellular retinol-binding protein in several rat tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6586–6590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rask L., Anundi H., Böhme J., Eriksson U., Ronne H., Sege K., Peterson P. A. Structural and functional studies of vitamin A-binding proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981 Feb 27;359:79–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb12739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rask L., Peterson P. A. In vitro uptake of vitamin A from the retinol-binding plasma protein to mucosal epithelial cells from the monkey's small intestine. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6360–6366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. E., Deen D. D., Jr, Sklan D., Goodman D. S. Colchicine inhibition of retinol-binding protein secretion by rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1980 Feb;21(2):229–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. E., Muto Y., Goodman D. S. Tissue distribution and subcellular localization of retinol-binding protein in normal and vitamin A-deficient rats. J Lipid Res. 1975 Jul;16(4):318–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Odani S., Ono T. A close structural relationship of rat liver Z-protein to cellular retinoid binding proteins and peripheral nerve myelin P2 protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 30;106(4):1099–1105. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91225-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald G. Molecular basis of visual excitation. Science. 1968 Oct 11;162(3850):230–239. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3850.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]