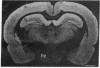
Abstract
The vertebrate central nervous system contains very high concentrations of protein kinase C, a calcium- and phospholipid-stimulated phosphorylating enzyme. Phorbol esters, compounds with inflammatory and tumor-promoting properties, bind to and activate this enzyme. To clarify the role of protein kinase C in neuronal function, we have localized phorbol ester receptors in the rat hippocampus by autoradiography and examined the electrophysiological effects of phorbol esters on hippocampal pyramidal neurons in vitro. Phorbol esters blocked a calcium-dependent potassium conductance. In addition, phorbol esters blocked the late hyperpolarization elicited by synaptic stimulation even though other synaptic potentials were not affected. The potencies of several phorbol esters in exerting these actions paralleled their affinities for protein kinase C, suggesting that protein kinase C regulates membrane ionic conductance.
Full text
PDF
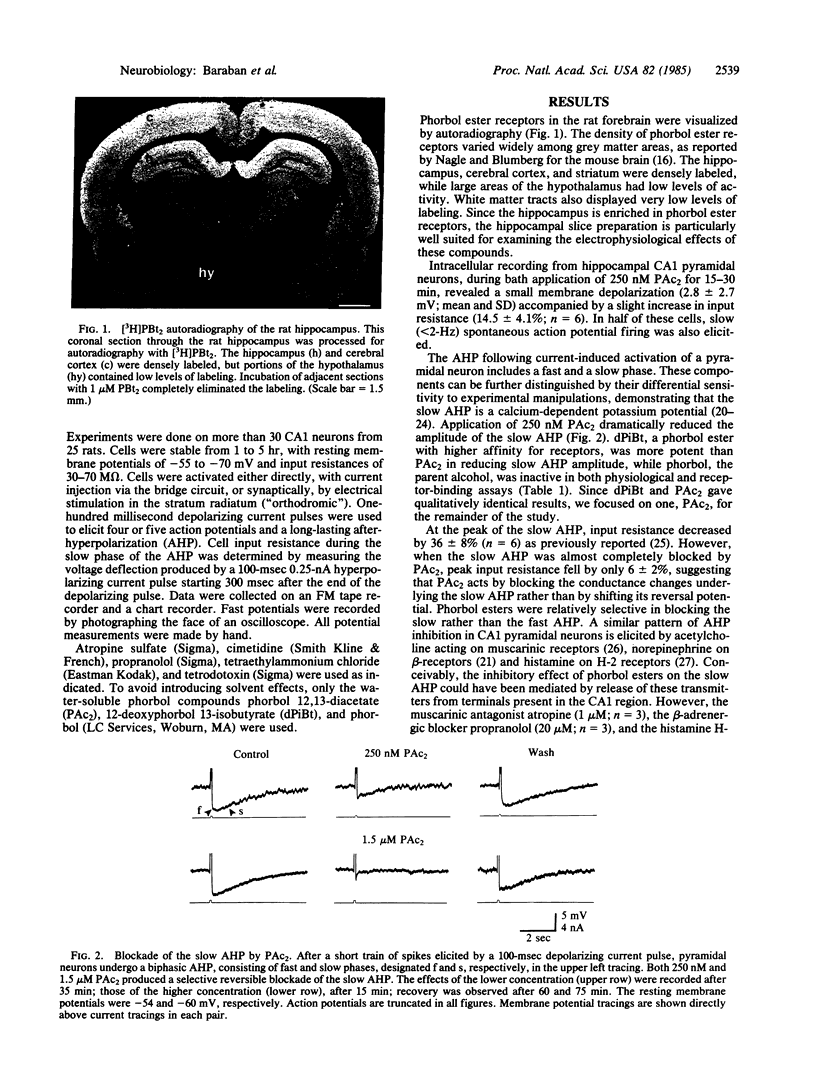
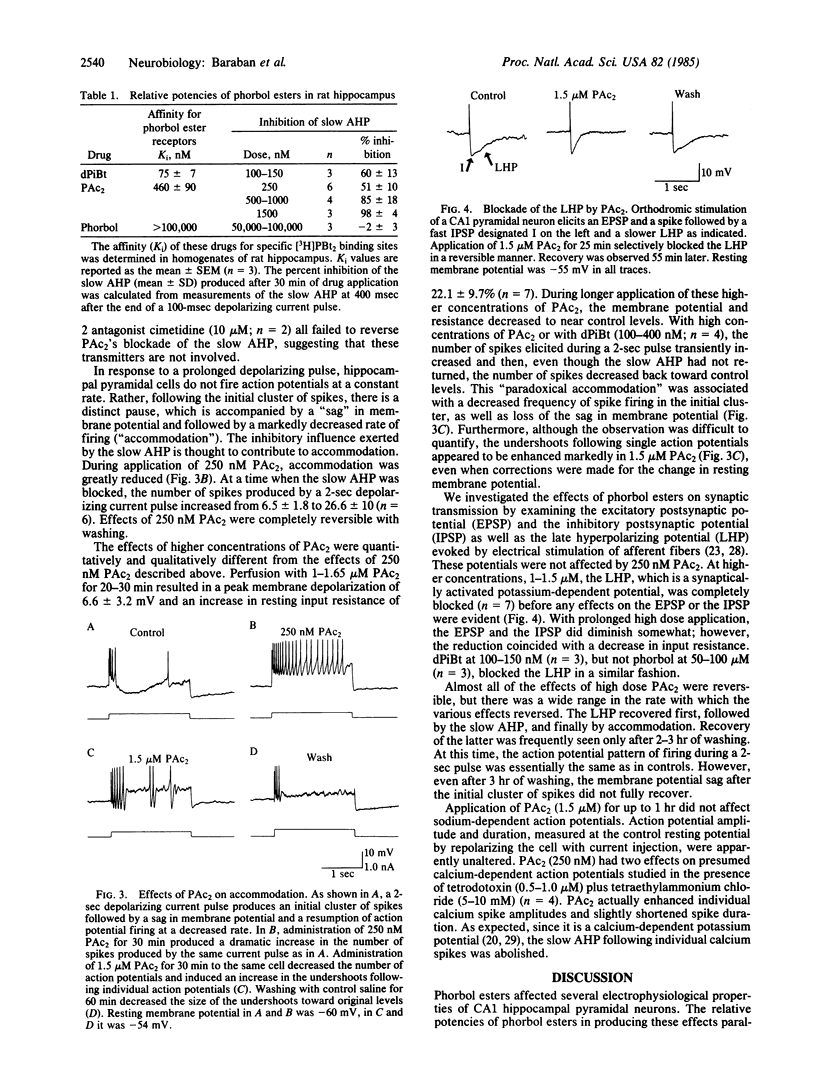


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alger B. E. Characteristics of a slow hyperpolarizing synaptic potential in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Nov;52(5):892–910. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.52.5.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alger B. E., Nicoll R. A. Epileptiform burst afterhyperolarization: calcium-dependent potassium potential in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. Science. 1980 Dec 5;210(4474):1122–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.7444438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alger B. E., Nicoll R. A. Feed-forward dendritic inhibition in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells studied in vitro. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:105–123. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraban J. M., Gould R. J., Peroutka S. J., Snyder S. H. Phorbol ester effects on neurotransmission: interaction with neurotransmitters and calcium in smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):604–607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M., Jaken S., König B., Sharkey N. A., Leach K. L., Jeng A. Y., Yeh E. Mechanism of action of the phorbol ester tumor promoters: specific receptors for lipophilic ligands. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 15;33(6):933–940. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Gill G. N., Meisenhelder J., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. C-kinase phosphorylates the epidermal growth factor receptor and reduces its epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2553–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. E., Nicoll R. A. Acetylcholine mediates a slow synaptic potential in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Science. 1983 Sep 23;221(4617):1299–1301. doi: 10.1126/science.6612345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRiemer S. A., Strong J. A., Albert K. A., Greengard P., Kaczmarek L. K. Enhancement of calcium current in Aplysia neurones by phorbol ester and protein kinase C. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):313–316. doi: 10.1038/313313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driedger P. E., Blumberg P. M. Specific binding of phorbol ester tumor promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):567–571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. A., Blumberg P. M. Specific binding of [20-3H]12-deoxyphorbol 13-isobutyrate to phorbol ester receptor subclasses in mouse skin particulate preparations. Cancer Res. 1983 Oct;43(10):4632–4637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman B., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Ross A. H., Connors J. M., Fujiki H., Sugimura T., Rosner M. R. Tumor promoters block tyrosine-specific phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3034–3038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Wigström H. Evidence for two types of afterhyperpolarization in CA1 pyramidal cells in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1981 Feb 16;206(2):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90548-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Konnerth A. Histamine and noradrenaline decrease calcium-activated potassium conductance in hippocampal pyramidal cells. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):432–434. doi: 10.1038/302432a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell J. V., Adams P. R. Voltage-clamp analysis of muscarinic excitation in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 28;250(1):71–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90954-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotson J. R., Prince D. A. A calcium-activated hyperpolarization follows repetitive firing in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Feb;43(2):409–419. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.43.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Studies on a cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinase and its proenzyme in mammalian tissues. II. Proenzyme and its activation by calcium-dependent protease from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7610–7616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Sahyoun N. E., Saltiel A. R., Cuatrecasas P. Phorbol esters stimulate the phosphorylation of receptors for insulin and somatomedin C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6211–6213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janowsky A., Labarca R., Paul S. M. Characterization of neurotransmitter receptor-mediated phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis in the rat hippocampus. Life Sci. 1984 Nov 5;35(19):1953–1961. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90476-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher D. J., Pessin J. E., Ruoho A. E., Johnson G. L. Phorbol ester induces desensitization of adenylate cyclase and phosphorylation of the beta-adrenergic receptor in turkey erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4316–4320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Tanaka Y., Miyake R., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C as a possible receptor protein of tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11442–11445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. The phorbol ester TPA increases the affinity of exocytosis for calcium in 'leaky' adrenal medullary cells. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 22;160(1-2):98–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80944-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Andersson R. G., Wise B. C., Mackerlova L., Salomonsson I., Brackett N. L., Katoh N., Shoji M., Wrenn R. W. Calcium-dependent protein kinase: widespread occurrence in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom and comparison of effects of phospholipid, calmodulin, and trifluoperazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7039–7043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Control of the repetitive discharge of rat CA 1 pyramidal neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:319–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Noradrenaline blocks accommodation of pyramidal cell discharge in the hippocampus. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):636–638. doi: 10.1038/299636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle D. S., Blumberg P. M. Regional localization by light microscopic autoradiography of receptors in mouse brain for phorbol ester tumor promoters. Cancer Lett. 1983 Feb;18(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(83)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. A bicuculline-resistant inhibitory post-synaptic potential in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:239–254. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Alger B. E. A simple chamber for recording from submerged brain slices. J Neurosci Methods. 1981 Aug;4(2):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(81)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Niehoff D. L., Kuhar M. J. Receptor autoradiography with tritium-sensitive film: potential for computerized densitometry. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Sep 1;25(2):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90315-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzan T., Gatti G., Dozio N., Vicentini L. M., Meldolesi J. Ca2+-dependent and -independent release of neurotransmitters from PC12 cells: a role for protein kinase C activation? J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):628–638. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Prince D. A. Effects of TEA on hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1980 Mar 3;185(1):169–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90680-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Nambi P., Peters J. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Phorbol diesters promote beta-adrenergic receptor phosphorylation and adenylate cyclase desensitization in duck erythrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 29;121(3):973–979. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Inoue M., Nishizuka Y. Studies on a cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinase and its proenzyme in mammalian tissues. I. Purification and characterization of an active enzyme from bovine cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7603–7609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A. Afterpotential generation in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jan;45(1):86–97. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]