Abstract
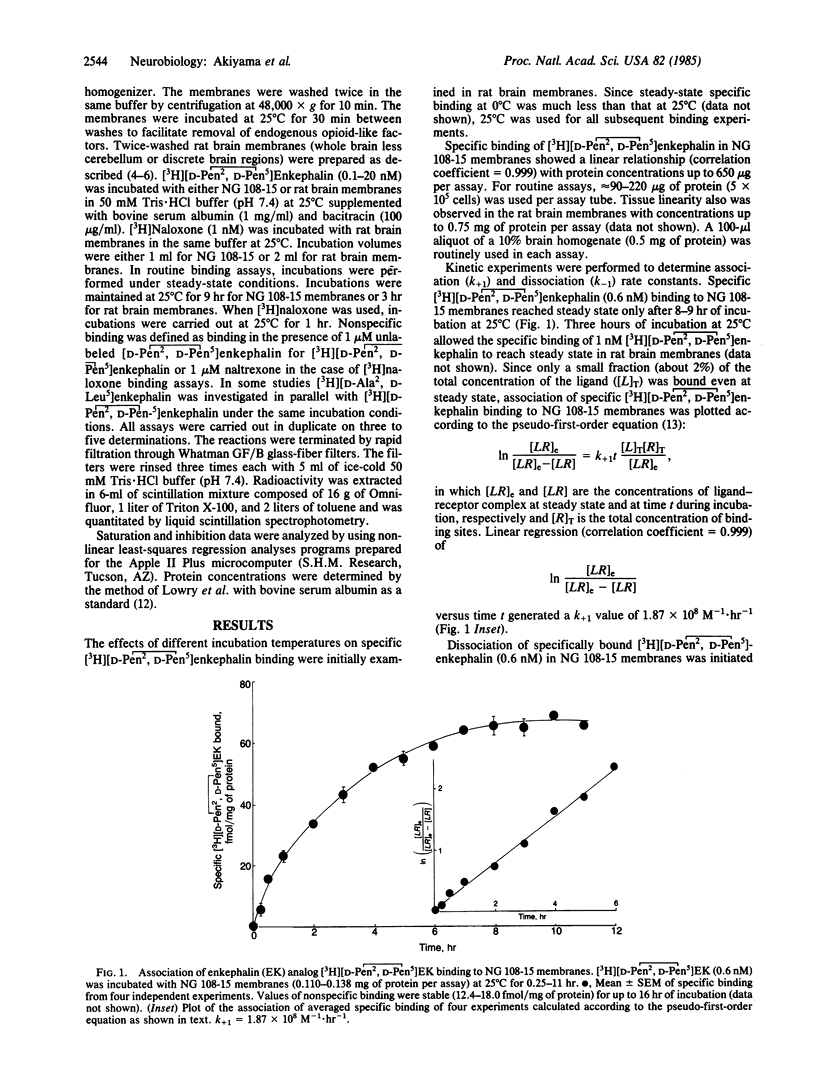
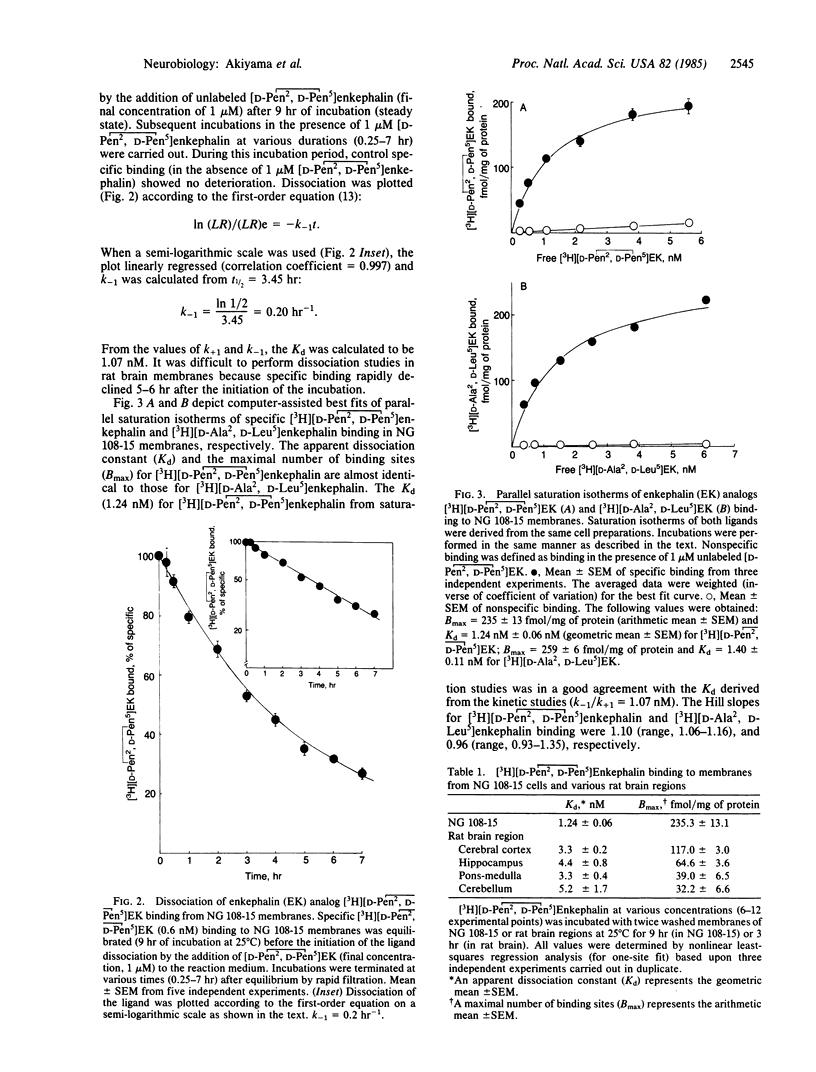
Specific binding properties of the tritium-labeled delta opiate receptor agonist [3H][2-D-penicillamine, 5-D-penicillamine]enkephalin [( 3H][D-Pen2, D-Pen5]enkephalin) were characterized in the rat brain and in a mouse neuroblastoma-rat glioma hybrid cell line (NG 108-15). Saturation isotherms of [3H][D-Pen2, D-Pen5]enkephalin binding to rat brain and NG 108-15 membranes gave apparent Kd values of 1-6 nM. These values are in good agreement with the Kd value obtained from the kinetic studies. The Bmax value in NG 108-15 membranes was 235.3 fmol/mg of protein. An apparent regional distribution of [3H][D-Pen2, D-Pen5]enkephalin binding was observed in the rat brain. A number of enkephalin analogues inhibited [3H][D-Pen2, D-Pen5]enkephalin binding with high affinity (IC50 values of 0.5-5.0 nM) in both NG 108-15 and rat brain membranes. However, putative mu receptor-selective ligands such as morphine, [D-Ala2, MePhe4, Gly5-ol]enkephalin, [MePhe3, D-Pro4]morphiceptin, and naloxone were less effective inhibitors of [3H][D-Pen2, D-Pen5]enkephalin binding in both systems tested. These data suggest that [3H][D-Pen2, D-Pen5]enkephalin is a potent and selective ligand for the delta opioid receptor.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama K., Watson M., Roeske W. R., Yamamura H. I. High-affinity [3H]pirenzepine binding to putative M1 muscarinic sites in the neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cell line (NG 108-15). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91650-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Multiple opiate receptors. Enkephalins and morphine bind to receptors of different specificity. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2610–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Wei E. T., Killian A., Chang J. K. Potent morphiceptin analogs: structure activity relationships and morphine-like activities. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Nov;227(2):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields J. Z., Roeske W. R., Morkin E., Yamamura H. I. Cardiac muscarinic cholinergic receptors. Biochemical identification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3251–3258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gacel G., Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. D-Tyr--Ser-Gly--Phe--Leu--Thr, a highly preferential ligand for delta-opiate receptors. FEBS Lett. 1980 Sep 8;118(2):245–247. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80229-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James I. F., Goldstein A. Site-directed alkylation of multiple opioid receptors. I. Binding selectivity. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 May;25(3):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Galligan J. J., Burks T. F., Gee K., Yamamura H. I. Conformationally constrained cyclic enkephalin analogs with pronounced delta opioid receptor agonist selectivity. Life Sci. 1983 May 30;32(22):2565–2569. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90239-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Galligan J. J., Burks T. F., Gee K., Yamamura H. I. [D-Pen2, L-Cys5]enkephalinamide and[D-Pen2, D-Cys5] enkephalinamide, conformationally constrained cyclic enkephalinamide analogs with delta receptor specificity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):506–512. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91139-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Gee K., Akiyama K., Yamamura H. I., Galligan J. J., Burks T. F. Cyclic penicillamine containing enkephalin analogs display profound delta receptor selectivities. Life Sci. 1983;33 (Suppl 1):447–450. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90538-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Gee K., Yamamura H. I., Galligan J. J., Burks T. F. Bis-penicillamine enkephalins possess highly improved specificity toward delta opioid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5871–5874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolozin B. L., Pasternak G. W. Classification of multiple morphine and enkephalin binding sites in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6181–6185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajac J. M., Gacel G., Petit F., Dodey P., Rossignol P., Roques B. P. Deltakephalin, Tyr-D-Thr-Gly-Phe-Leu-Thr: a new highly potent and fully specific agonist for opiate delta-receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):390–397. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90318-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


