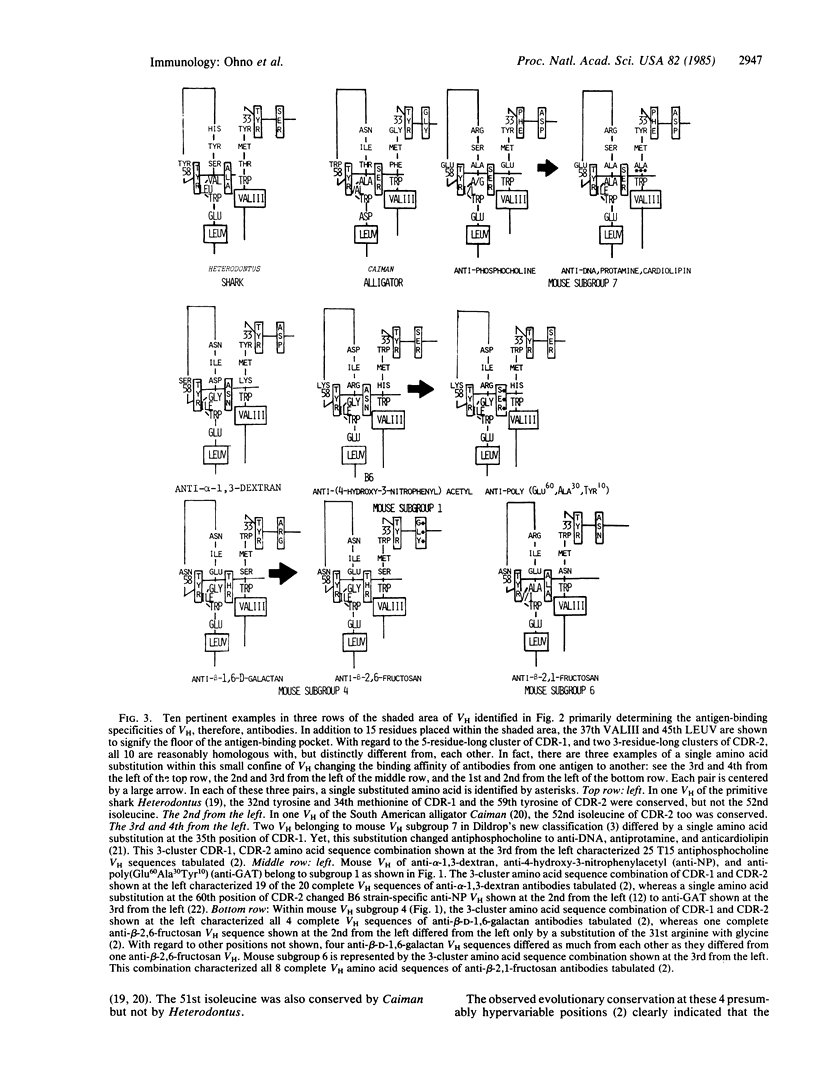
Abstract
Although the antigen-binding pocket of all antibodies consists of VL + VH dimers (where VL and VH represent immunoglobulin light and heavy chain regions, respectively), subgroups of their VH largely determine their antigen-binding specificities. This VH subgroup dependence automatically relegates subsidiary roles to VL as a whole and to the complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR-3) of VH encoded by independent diversity (D) and joining (J) coding segments in determining antigen-binding specificities of individual antibodies. As a sequel to our previous paper, which emphasized the role conserved residues in CDR-1 and CDR-2 of VH play in general shaping of the primordial antigen-binding cavity, here we propose that the three short clusters of amino acid sequences in CDR-1 and CDR-2 that are placed in the immediate vicinity of the tryptophan loop primarily determine subgroup-dependent antigen preference of individual VH, therefore, antibodies. The three clusters are the 31st to 35th positions of CDR-1 and the 50th to 52nd and 58th to 60th positions of CDR-2. Of those, the 32nd, 34th, 51st, and 59th positions tend to be occupied by tyrosine, methionine, isoleucine, and tyrosine, respectively. Nevertheless, free amino acid substitutions at the remaining seven sites can generate 20(7) or 1.28 X 10(9) varieties of amino acid sequence combinations. Some of these astronomically numerous sequence combinations no doubt contribute to the maintenance of the vast repertoire of antigen-combining diversity, which might be as large as 10(7), whereas others serve to vary binding affinities toward the same antigen. Ironically, but not surprisingly, a single nonconservative amino acid substitution at one of these sites often suffices to change the antigen preference of VH from one to another, whereas more substitutions affecting two or more clusters are apparently required to change the binding affinity toward the same antigen. In the case of mouse anti-p-azophenylarsonate antibodies, the principle of VH subgroup dependence is violated, their VH belonging to either subgroup 1 or 3. It appears that the mouse genome lacks anti-p-azophenylarsonate germ line VH, residues of CDR-3 derived from one particular JH coding segment coming to rescue to cope with this unnatural man-made antigen.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bothwell A. L., Paskind M., Reth M., Imanishi-Kari T., Rajewsky K., Baltimore D. Heavy chain variable region contribution to the NPb family of antibodies: somatic mutation evident in a gamma 2a variable region. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):625–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Effron K., Rechavi G., Ben-Neriah Y., Zakut R., Givol D. Simple DNA sequences in homologous flanking regions near immunoglobulin VH genes: a role in gene interaction? Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 11;10(11):3353–3370. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.11.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. D., Rudikoff S., Giusti A. M., Scharff M. D. Somatic mutation in a cultured mouse myeloma cell affects antigen binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1240–1244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews S., Griffin J., Huang H., Calame K., Hood L. A single VH gene segment encodes the immune response to phosphorylcholine: somatic mutation is correlated with the class of the antibody. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90231-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Scharff M. D. Somatic mutation of the T15 heavy chain gives rise to an antibody with autoantibody specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5841–5844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Huang H., Davis M., Calame K., Hood L. An immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene is generated from three segments of DNA: VH, D and JH. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):981–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilat D., Hochberg M., Pumphrey J., Rudikoff S. Monoclonal antibodies to DNA and RNA from NZB/NZW F1 mice: antigenic specificities and NH2 terminal amino acid sequences. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):489–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Givol D., Zakut R., Effron K., Rechavi G., Ram D., Cohen J. B. Diversity of germ-line immunoglobulin VH genes. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):426–430. doi: 10.1038/292426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazim A. L., Atassi M. Z. Antibody combining sites can be mimicked synthetically. Surface-simulation synthesis of the phosphorylcholine-combining site of myeloma protein M-603. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):661–666. doi: 10.1042/bj1870661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Davis M., Sinn E., Patten P., Hood L. Antibody diversity: somatic hypermutation of rearranged VH genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90399-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman G. W., Berger L., Murphy K., Litman R., Hinds K., Jahn C. L., Erickson B. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of an immunoglobulin VH gene homologue from Caiman, a phylogenetically ancient reptile. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):349–352. doi: 10.1038/303349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman G. W., Murphy K., Berger L., Litman R., Hinds K., Erickson B. W. Complete nucleotide sequences of three VH genes in Caiman, a phylogenetically ancient reptile: evolutionary diversification in coding segments and variation in the structure and organization of recombination elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):844–848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Matsunaga T., Lee A. D. The invariably present tryptophan loop as the core of all divergent antigen-binding pockets. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Nov;20(5):377–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb01017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollo R., Auffray C., Sikorav J. L., Rougeon F. Mouse heavy chain variable regions: nucleotide sequence of a germ-line VH gene segment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4099–4109. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechavi G., Bienz B., Ram D., Ben-Neriah Y., Cohen J. B., Zakut R., Givol D. Organization and evolution of immunoglobulin VH gene subgroups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4405–4409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechavi G., Ram D., Glazer L., Zakut R., Givol D. Evolutionary aspects of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (VH) gene subgroups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):855–859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocca-Serra J., Tonnelle C., Fougereau M. Two monoclonal antibodies against different antigens using the same VH germ-line gene. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):353–355. doi: 10.1038/304353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Maki R., Kurosawa Y., Roeder W., Tonegawa S. Two types of somatic recombination are necessary for the generation of complete immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):676–683. doi: 10.1038/286676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul F. A., Amzel L. M., Poljak R. J. Preliminary refinement and structural analysis of the Fab fragment from human immunoglobulin new at 2.0 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):585–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz M., Huang S. Y., Gefter M. L. The genetic basis of antibody production: a single heavy chain variable region gene encodes all molecules bearing the dominant anti-arsonate idiotype in the strain A mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Feb;13(2):123–132. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twining S. S., Atassi M. Z. Antibody-combining sites can be mimicked synthetically. Surface-simulation synthesis of the immunoglobulin new combining site to the gamma-hydroxyl derivative of vitamin K1. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5259–5262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


