Abstract
An integrated map of the genome of the tubercle bacillus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, was constructed by using a twin-pronged approach. Pulsed-field gel electrophoretic analysis enabled cleavage sites for Asn I and Dra I to be positioned on the 4.4-Mb circular chromosome, while, in parallel, clones from two cosmid libraries were ordered into contigs by means of fingerprinting and hybridization mapping. The resultant contig map was readily correlated with the physical map of the genome via the landmarked restriction sites. Over 165 genes and markers were localized on the integrated map, thus enabling comparisons with the leprosy bacillus, Mycobacterium leprae, to be undertaken. Mycobacterial genomes appear to have evolved as mosaic structures since extended segments with conserved gene order and organization are interspersed with different flanking regions. Repetitive sequences and insertion elements are highly abundant in M. tuberculosis, but the distribution of IS6110 is apparently nonrandom.
Full text
PDF

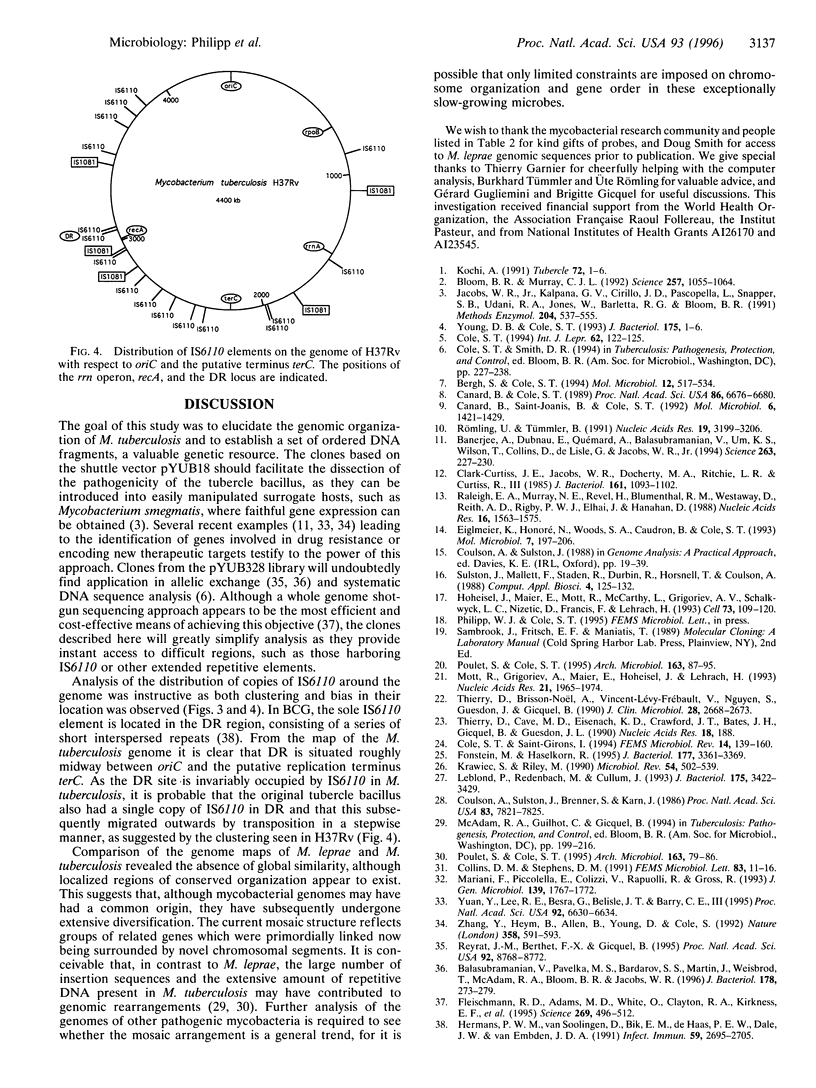
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balasubramanian V., Pavelka M. S., Jr, Bardarov S. S., Martin J., Weisbrod T. R., McAdam R. A., Bloom B. R., Jacobs W. R., Jr Allelic exchange in Mycobacterium tuberculosis with long linear recombination substrates. J Bacteriol. 1996 Jan;178(1):273–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.1.273-279.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A., Dubnau E., Quemard A., Balasubramanian V., Um K. S., Wilson T., Collins D., de Lisle G., Jacobs W. R., Jr inhA, a gene encoding a target for isoniazid and ethionamide in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science. 1994 Jan 14;263(5144):227–230. doi: 10.1126/science.8284673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canard B., Saint-Joanis B., Cole S. T. Genomic diversity and organization of virulence genes in the pathogenic anaerobe Clostridium perfringens. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(11):1421–1429. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E., Jacobs W. R., Docherty M. A., Ritchie L. R., Curtiss R., 3rd Molecular analysis of DNA and construction of genomic libraries of Mycobacterium leprae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1093–1102. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1093-1102.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T., Saint Girons I. Bacterial genomics. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1994 Jun;14(2):139–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1994.tb00084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T. The genome of Mycobacterium leprae. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1994 Mar;62(1):122–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Sulston J., Brenner S., Karn J. Toward a physical map of the genome of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7821–7825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiglmeier K., Honoré N., Woods S. A., Caudron B., Cole S. T. Use of an ordered cosmid library to deduce the genomic organization of Mycobacterium leprae. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(2):197–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann R. D., Adams M. D., White O., Clayton R. A., Kirkness E. F., Kerlavage A. R., Bult C. J., Tomb J. F., Dougherty B. A., Merrick J. M. Whole-genome random sequencing and assembly of Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):496–512. doi: 10.1126/science.7542800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonstein M., Haselkorn R. Physical mapping of bacterial genomes. J Bacteriol. 1995 Jun;177(12):3361–3369. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.12.3361-3369.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P. W., van Soolingen D., Bik E. M., de Haas P. E., Dale J. W., van Embden J. D. Insertion element IS987 from Mycobacterium bovis BCG is located in a hot-spot integration region for insertion elements in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2695–2705. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2695-2705.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoheisel J. D., Maier E., Mott R., McCarthy L., Grigoriev A. V., Schalkwyk L. C., Nizetic D., Francis F., Lehrach H. High resolution cosmid and P1 maps spanning the 14 Mb genome of the fission yeast S. pombe. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):109–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90164-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs W. R., Jr, Kalpana G. V., Cirillo J. D., Pascopella L., Snapper S. B., Udani R. A., Jones W., Barletta R. G., Bloom B. R. Genetic systems for mycobacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:537–555. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04027-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochi A. The global tuberculosis situation and the new control strategy of the World Health Organization. Tubercle. 1991 Mar;72(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(91)90017-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawiec S., Riley M. Organization of the bacterial chromosome. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):502–539. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.502-539.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblond P., Redenbach M., Cullum J. Physical map of the Streptomyces lividans 66 genome and comparison with that of the related strain Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3422–3429. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3422-3429.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani F., Piccolella E., Colizzi V., Rappuoli R., Gross R. Characterization of an IS-like element from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Aug;139(8):1767–1772. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-8-1767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott R., Grigoriev A., Maier E., Hoheisel J., Lehrach H. Algorithms and software tools for ordering clone libraries: application to the mapping of the genome of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1965–1974. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulet S., Cole S. T. Repeated DNA sequences in mycobacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1995 Feb;163(2):79–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00381780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh E. A., Murray N. E., Revel H., Blumenthal R. M., Westaway D., Reith A. D., Rigby P. W., Elhai J., Hanahan D. McrA and McrB restriction phenotypes of some E. coli strains and implications for gene cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1563–1575. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyrat J. M., Berthet F. X., Gicquel B. The urease locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its utilization for the demonstration of allelic exchange in Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8768–8772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römling U., Tümmler B. The impact of two-dimensional pulsed-field gel electrophoresis techniques for the consistent and complete mapping of bacterial genomes: refined physical map of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3199–3206. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J., Mallett F., Staden R., Durbin R., Horsnell T., Coulson A. Software for genome mapping by fingerprinting techniques. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):125–132. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry D., Brisson-Noël A., Vincent-Lévy-Frébault V., Nguyen S., Guesdon J. L., Gicquel B. Characterization of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis insertion sequence, IS6110, and its application in diagnosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2668–2673. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2668-2673.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry D., Cave M. D., Eisenach K. D., Crawford J. T., Bates J. H., Gicquel B., Guesdon J. L. IS6110, an IS-like element of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):188–188. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Y., Lee R. E., Besra G. S., Belisle J. T., Barry C. E., 3rd Identification of a gene involved in the biosynthesis of cyclopropanated mycolic acids in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 3;92(14):6630–6634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.14.6630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Heym B., Allen B., Young D., Cole S. The catalase-peroxidase gene and isoniazid resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):591–593. doi: 10.1038/358591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]