Abstract
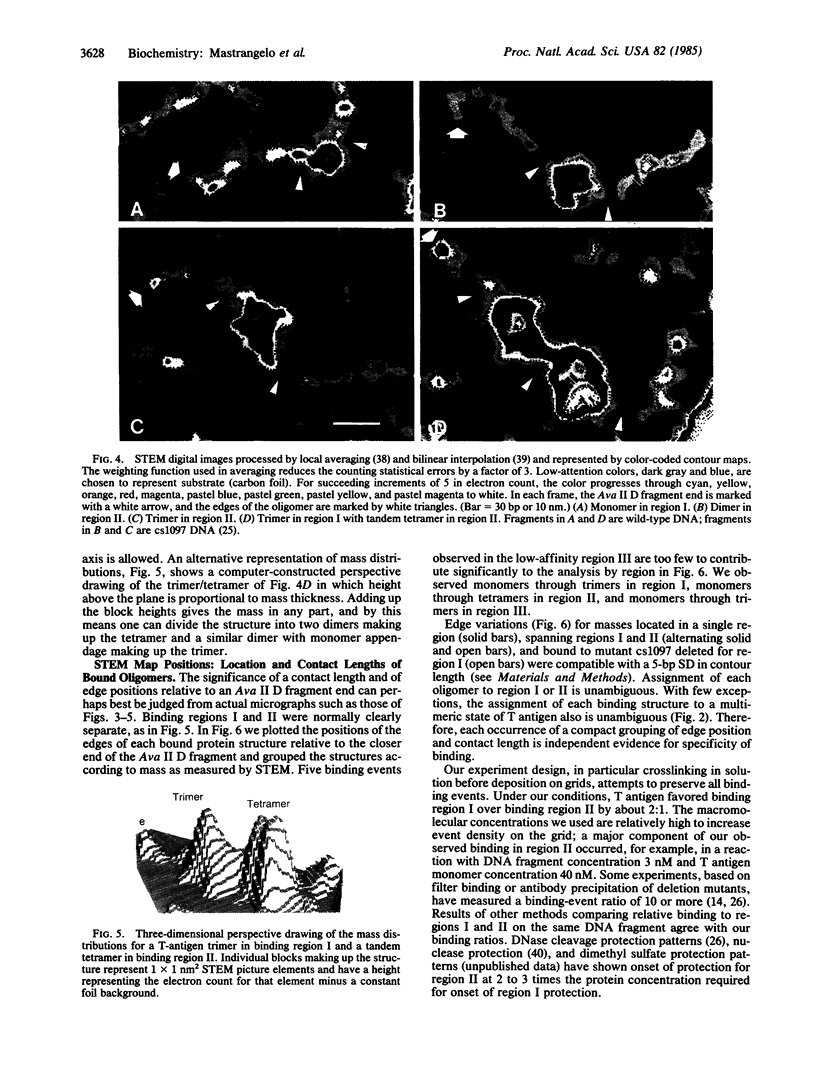
Large tumor (T) antigen and its bound multimeric states are positioned by scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) within a few base pairs at control sequences of the simian virus 40 DNA origin of replication region. Proximal and distal edge positions for each multimer group match the end positions of previously mapped fragments protected from DNase cleavage. Since chance correspondence is shown to be extremely unlikely, STEM mass measurements, obtained concurrently with STEM map positions, indicate that the DNase fragments arise from bound monomers, dimers, trimers, and tetramers in binding region II and monomers, dimers, and trimers in binding region I. Simultaneous binding of seven monomer-equivalent masses is observed, three in region I and four in region II, with an ordered and interpretable mass distribution in the plane of the foil. Although this observation does not prove that the six G-A-G-G-C and one T-A-G-G-C sequences, similarly distributed, function as recognition sequences for T-antigen monomer, it provides strong support for such a model. The stable existence in solution of low-and intermediate-mass structures, observed at lower T-antigen concentrations, suggests a role as assembly intermediates.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. K., Griffin J. D., Livingston D. M. Relationship of oligomerization to enzymatic and DNA-binding properties of the SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Lewton B. A., Tjian R., Tegtmeyer P. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of pentanucleotide interaction sites at the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):143–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.143-150.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Nathans D. Regulatory mutants of simian virus 40. Effect of mutations at a T antigen binding site on DNA replication and expression of viral genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):531–548. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A., Baumeister W., Saxton W. O. Mass mapping of a protein complex with the scanning transmission electron microscope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4050–4054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Westphal K. H., Brauer D., Cörlin D. Subclasses of simian virus 40 large T antigen: differential binding of two subclasses of T antigen from productively infected cells to viral and cellular DNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1023–1028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01290.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Scheller A., Barnet B., Hantzopoulos P., Oren M., Prives C. Different forms of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen varying in their affinities for DNA. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):456–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.456-466.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Tenen D. G., Livingston D. M., Sharp P. A. T antigen repression of SV40 early transcription from two promoters. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough P. V., Mastrangelo I. A., Wall J. S., Hainfeld J. F., Simon M. N., Manley J. L. DNA-protein complexes spread on N2-discharged carbon film and characterized by molecular weight and its projected distribution. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Tjian R. Essential contact residues within SV40 large T antigen binding sites I and II identified by alkylation-interference. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Hainfeld J., Wall J., Haschemeyer R. H. Identification and mass analysis of human fibrinogen molecules and their domains by scanning transmission electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):695–718. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Rio D. C., Robbins A. K., Tjian R. SV40 gene expression is modulated by the cooperative binding of T antigen to DNA. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tjian R. Construction and analysis of simian virus 40 origins defective in tumor antigen binding and DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6491–6495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Williams R. C., Tjian R. Oligomeric structure of a simian virus 40 T antigen in free form and bound to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Stark G. R., Alwine J. C. Autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A by T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Tjian R. SV40 T antigen binding site mutations that affect autoregulation. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1227–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. Transforming genes and gene products of polyoma and SV40. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;13(3):215–286. doi: 10.3109/10409238209114230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Kleinberger T., Livingston D. M. Mapping of SV40 DNA replication origin region binding sites for the SV40 T antigen by protection against exonuclease III digestion. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D. R., Margolskee R. F., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of the simian virus 40 replicon: pseudorevertants of mutants with a defective replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Andersen B. Partial purification of SV40 A protein and a related cellular protein from permissive cells. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Andersen B., Shaw S. B., Wilson V. G. Alternative interactions of the SV40 A protein with DNA. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Function of simian virus 40 gene A in transforming infection. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.613-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Lewton B. A., DeLucia A. L., Wilson V. G., Ryder K. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of protein bound to the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):151–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.151-161.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen D. G., Haines L. L., Livingston D. M. Binding of an analog of the simian virus 40 T antigen to wild-type and mutant viral replication origins. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 25;157(3):473–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90472-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen D. G., Taylor T. S., Haines L. L., Bradley M. K., Martin R. G., Livingston D. M. Binding of simian virus 40 large T antigen from virus-infected monkey cells to wild-type and mutant viral replication origins. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 25;168(4):791–808. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. Protein-DNA interactions at the origin of simian virus 40 DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):655–661. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. Regulation of viral transcription and DNA replication by the SV40 large T antigen. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:5–24. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V. G., Tevethia M. J., Lewton B. A., Tegtmeyer P. DNA binding properties of simian virus 40 temperature-sensitive A proteins. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):458–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.458-466.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]