Abstract
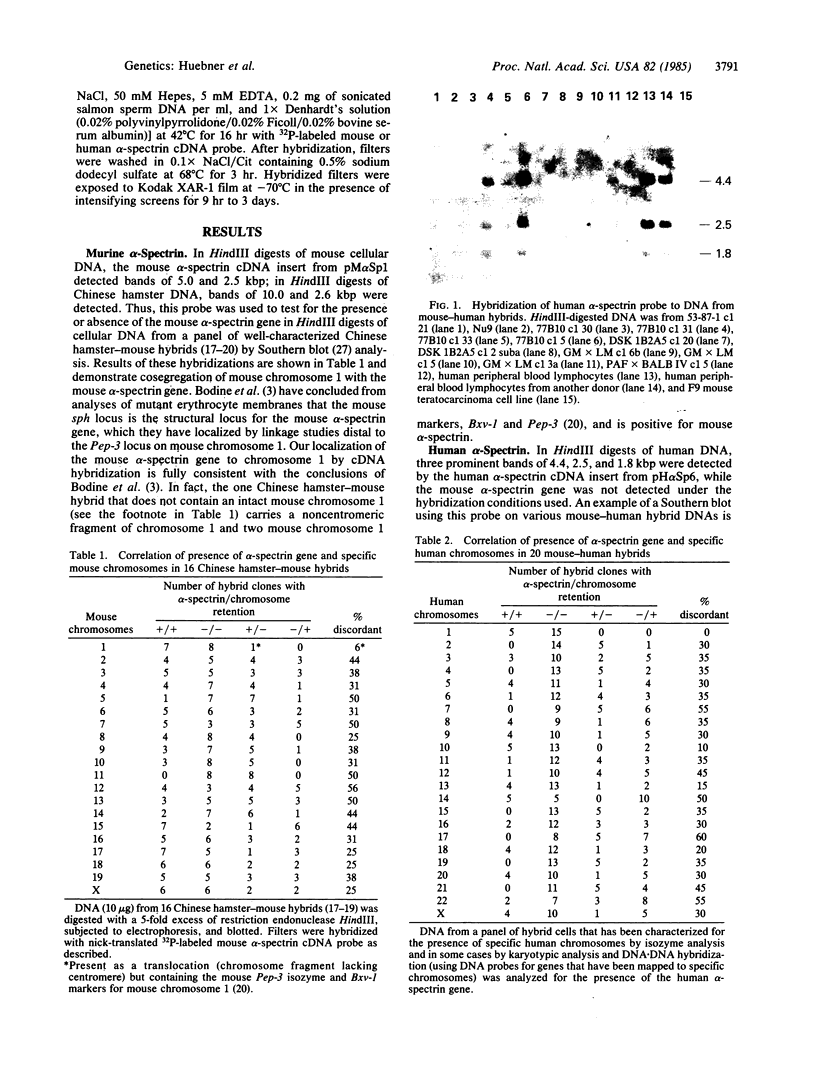
By using alpha-spectrin cDNA clones of murine and human origin and somatic cell hybrids segregating either mouse or human chromosomes, the gene for alpha-spectrin has been mapped to chromosome 1 in both species. This assignment of the mouse alpha-spectrin gene to mouse chromosome 1 by DNA hybridization strengthens the previous identification of the alpha-spectrin locus in mouse with the sph locus, which previously was mapped by linkage analysis to mouse chromosome 1, distal to the Pep-3 locus. By in situ hybridization to human metaphase chromosomes, the human alpha-spectrin gene has been localized to 1q22-1q25; interestingly, the locus for a non-Rh-linked form of elliptocytosis has been provisionally mapped to band 1q2 by family linkage studies.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agre P., Orringer E. P., Bennett V. Deficient red-cell spectrin in severe, recessively inherited spherocytosis. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 13;306(19):1155–1161. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205133061906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass E. B., Smith S. W., Jr, Stevenson R. E., Rosse W. F. Further evidence for location of the spherocytosis gene on chromosome 8. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Aug;99(2):192–193. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-2-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein S. E. Inherited hemolytic disease in mice: a review and update. Lab Anim Sci. 1980 Apr;30(2 Pt 1):197–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodine D. M., 4th, Birkenmeier C. S., Barker J. E. Spectrin deficient inherited hemolytic anemias in the mouse: characterization by spectrin synthesis and mRNA activity in reticulocytes. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90408-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgerhout W., van Someren H., Bootsma D. Cytological mapping of the genes assigned to the human A 1 chromosome by use of radiation-induced chromosome breakage in a human-Chinese hamster hybrid cell line. Humangenetik. 1973;20(2):159–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00284852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman V. M., Ruddle F. H., Roderick T. H. Linkage of isozyyme loci in the mouse: phosphoglucomutase-2 (Pgm-2), mitochondrial NADP malate dehydrogenase (Mod-2), and dipeptidase-1 (Dip-1). Biochem Genet. 1971 Apr;5(2):101–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00485638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Schaefer I. M., Diaz J. A., Lalley P. A. Mouse kidney renin gene is on chromosome one. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Nov;10(6):633–637. doi: 10.1007/BF01535229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cioe L., Curtis P. Detection and characterization of a mouse alpha-spectrin cDNA clone by its expression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1367–1371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. S., Park M., Blair D. G., Tainsky M. A., Huebner K., Croce C. M., Vande Woude G. F. Molecular cloning of a new transforming gene from a chemically transformed human cell line. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):29–33. doi: 10.1038/311029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Bregni M., Erikson J., Patterson D., Gallo R. C., Croce C. M. Human c-myc onc gene is located on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7824–7827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. R., Shiffer K. A., Casoria L. A., Eyster M. E. Identification of the molecular defect in the erythrocyte membrane skeleton of some kindreds with hereditary spherocytosis. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):772–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. R., Shiffer K. The spectrin membrane skeleton of normal and abnormal human erythrocytes: a review. Am J Physiol. 1983 Mar;244(3):C121–C141. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.244.3.C121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L., Van Antwerpen R., Stein J., Stein G., Tripputi P., Emanuel B., Selden J., Croce C. A major human histone gene cluster on the long arm of chromosome 1. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):838–840. doi: 10.1126/science.6494913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Saunders G. F. Localization of single copy DNA sequences of G-banded human chromosomes by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1981;83(3):431–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00327364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B. J. Another elliptocytosis locus on chromosome 1? Hum Genet. 1979 Sep;50(3):227–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00399385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberling W. J., Fulbeck T., Dixon L., Lubs H. A. Localization of spherocytosis to chromosome 8 or 12 and report of a family with spherocytosis and a reciprocal translocation. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Sep;27(5):586–594. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberling W. J., Taylor R. A., Chapman R. G., Lubs H. A. Linkage and gene localization of hereditary spherocytosis (HS). Blood. 1978 Nov;52(5):859–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A. Genetic mapping of a mouse chromosomal locus required for mink cell focus-forming virus replication. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):300–303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.300-303.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Rowe W. P. Genetic mapping of the ecotropic murine leukemia virus-inducing locus of BALB/c mouse to chromosome 5. Science. 1979 Apr 6;204(4388):69–71. doi: 10.1126/science.219475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Rowe W. P. Genetic mapping of the ecotropic virus-inducing locus Akv-2 of the AKR mouse. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1419–1423. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C., Nichols E., Ruddle F. H. Gene linkage analysis in the mouse by somatic cell hybridization: assignment of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase to chromosome 8 and alpha-galactosidase to the X chromosome. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Oct;1(4):371–382. doi: 10.1007/BF01538668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnenbach A., Huebner K., Croce C. M. DNA-transformed murine teratocarcinoma cells: regulation of expression of simian virus 40 tumor antigen in stem versus differentiated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4875–4879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., Pease B., Tomaselli M. B., John K. M., Bernstein S. E. Hemolytic anemias associated with deficient or dysfunctional spectrin. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1979;30:463–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E. Spectrin-actin membrane skeleton of normal and abnormal red blood cells. Semin Hematol. 1979 Jan;16(1):21–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. The detection and estimation of linkage between the genes for elliptocytosis and the Rh blood type. Am J Hum Genet. 1956 Jun;8(2):80–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T. The red cell membrane skeleton: recent progress. Blood. 1983 Jan;61(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repasky E. A., Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Widespread occurrence of avian spectrin in nonerythroid cells. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):821–833. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90444-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle F., Ricciuti F., McMorris F. A., Darlington G., Chen T. Somatic cell genetic assignment of peptidase C and the Rh linkage group to chromosome A-1 in man. Science. 1972 Jun 30;176(4042):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4042.1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchernia G., Mohandas N., Shohet S. B. Deficiency of skeletal membrane protein band 4.1 in homozygous hereditary elliptocytosis. Implications for erythrocyte membrane stability. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):454–460. doi: 10.1172/JCI110275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger A. E., Harris M. J., Bernstein S. E., Falcone J. C., Lux S. E. Hemolytic anemia in the mouse. Report of a new mutation and clarification of its genetics. J Hered. 1983 Mar-Apr;74(2):88–92. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a109747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Erdös E. G., Wilson J. D., Taylor B. A. Location on chromosome 1 of Rnr, a gene that regulates renin in the submaxillary gland of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5623–5626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]