Abstract
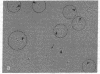
The C1q subunit of complement component C1 is known to bind to immune complexes, which often are deposited in basement membrane. We investigated the possibility that this deposition is a result of binding to laminin, a large basement membrane glycoprotein. C1q showed saturable binding to immobilized laminin; this binding was increased at reduced ionic strength. Intact C1 did not bind laminin. A ternary complex was formed by laminin, C1q, and aggregated IgG. This complex formation was dependent on and proportional to the amount of C1q bound to the aggregated IgG. Binding of laminin to C1q occurred with a Kd of 2 nM and was stronger than the binding of C1q to fibronectin. Preliminary data, including electron micrographs of rotary-shadowed preparations, suggest that laminin binds to the collagen-like tail of C1q. Electron microscopy localized the site of interaction with C1q to a short arm of laminin. Since laminin is found only in basement membranes, the interaction between laminin and C1q could be involved in the deposition and retention of immune complexes in these structures.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel G. B., Silva F. G., Pirani C. L., Meltzer J. I., Estes D. Renal involvement in systemic lupud erythematosus (SLE): a study of 56 patients emphasizing histologic classification. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 Sep;57(5):371–410. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197809000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bing D. H., Almeda S., Isliker H., Lahav J., Hynes R. O. Fibronectin binds to the C1q component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4198–4201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Bekisz J. Neoantigens appear in human IgG upon antigen binding: detection by antibodies that react specifically with antigen-bound IgG. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1346–1352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Porter R. R., Sim R. B. The unactivated form of the first component of human complement, C1. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):541–548. doi: 10.1042/bj1570541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill G. S., Hinglais N., Tron F., Bach J. F. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Morphologic correlations with immunologic and clinical data at the time of biopsy. Am J Med. 1978 Jan;64(1):61–79. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes-Jones N. C., Gardner B. Reaction between the isolated globular sub-units of the complement component C1q and IgG-complexes. Mol Immunol. 1979 Sep;16(9):697–701. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Yamada K. M. Fibronectins: multifunctional modular glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):369–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham K. C., Brew S. A., Miekka S. I. Interaction of plasma fibronectin with gelatin and complement C1q. Mol Immunol. 1983 Mar;20(3):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., McGarvey M. L., Liotta L. A., Robey P. G., Tryggvason K., Martin G. R. Isolation and characterization of type IV procollagen, laminin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycan from the EHS sarcoma. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6188–6193. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie G. W., Leblond C. P., Martin G. R. Light microscopic immunolocalization of type IV collagen, laminin, heparan sulfate proteoglycan, and fibronectin in the basement membranes of a variety of rat organs. Am J Anat. 1983 May;167(1):71–82. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001670107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstein E., Sorvillo J., Gigli I. The interaction of human plasma fibronectin with a subunit of the first component of complement, C1q. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2036–2039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier C. G., Inada S., Fries L. F., Takahashi T., Frank M. M., Brown E. J. Plasma fibronectin enhances phagocytosis of opsonized particles by human peripheral blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1844–1854. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. N., Margulies I. M., Tralka T. S., Terranova V. P., Madri J. A., Liotta L. A. Isolation of a subunit of laminin and its role in molecular structure and tumor cell attachment. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9740–9744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B. Proteins involved in the activation and control of the two pathways of human complement. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Jan;11(1):1–12. doi: 10.1042/bst0110001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Sim R. B., Faiers A. P. Inhibition of the reconstitution of the haemolytic activity of the first component of human complement by a pepsin-derived fragment of subcomponent C1q. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 1;161(2):239–245. doi: 10.1042/bj1610239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Burke B. E., Branton D. The molecular structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. Biophysical and electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):303–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Lesavre P. H., Cooper N. R. Purification and radiolabeling of human C1q. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):648–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley D. T., Rao C. N., Hassell J. R., Liotta L. A., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K. Interactions of basement membrane components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 27;761(3):278–283. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. J., McAdams A. J., Forristal J., Snyder J., West C. D. Glomerular deposition of complement-control proteins in acute and chronic glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1979 Oct;16(4):505–512. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J., Cooper N. R. Active disassembly of the first complement component, C-1, by C-1 inactivator. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):788–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]