Abstract
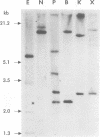
The vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP), a substrate for cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinases in vitro and in intact cells, is associated with actin filaments, focal adhesions and dynamic membrane regions. VASP, cloned here from human HL-60 and canine MDCK cells, is organized into three distinct domains. A central proline-rich domain contains a GPPPPP motif as a single copy and as a 3-fold tandem repeat, as well as three conserved phosphorylation sites for cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. A C-terminal domain contains a repetitive mixed-charge cluster which is predicted to form an alpha-helix. The hydrodynamic properties of purified human VASP together with the calculated molecular mass of cloned VASP suggest that the native protein is a homotetramer with an elongated structure. VASP over-expressed in transiently transfected BHK21 cells was predominantly detected at stress fibres, at focal adhesions and in F-actin-containing cell surface protrusions, whereas truncated VASP lacking the C-terminal domain was no longer concentrated at focal adhesions. These data indicate that the C-terminal domain is required for anchoring VASP at focal adhesion sites, whereas the central domain is suggested to mediate VASP interaction with profilin. Our results provide evidence for the structural basis by which VASP, both a target of the cAMP and cGMP signal transduction pathways and a component of the actin-based cytoskeleton, including the cytoskeleton-membrane interface, may be able to exchange signals between these networks.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adzhubei A. A., Sternberg M. J. Left-handed polyproline II helices commonly occur in globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 20;229(2):472–493. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Bucher P., Nourbakhsh I. R., Blaisdell B. E., Karlin S. Methods and algorithms for statistical analysis of protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2002–2006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt E., Abel K., Krieger M., Palm D., Hoppe V., Hoppe J., Walter U. cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation sites of the focal adhesion vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) in vitro and in intact human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14509–14517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damsky C. H., Werb Z. Signal transduction by integrin receptors for extracellular matrix: cooperative processing of extracellular information. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;4(5):772–781. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90100-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domann E., Wehland J., Rohde M., Pistor S., Hartl M., Goebel W., Leimeister-Wächter M., Wuenscher M., Chakraborty T. A novel bacterial virulence gene in Listeria monocytogenes required for host cell microfilament interaction with homology to the proline-rich region of vinculin. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1981–1990. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05252.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly S. F., Pocklington M. J., Pallotta D., Orr E. A proline-rich protein, verprolin, involved in cytoskeletal organization and cellular growth in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Nov;10(3):585–596. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Miller K. G., Botstein D. Yeast actin-binding proteins: evidence for a role in morphogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2551–2561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigenthaler M., Nolte C., Halbrügge M., Walter U. Concentration and regulation of cyclic nucleotides, cyclic-nucleotide-dependent protein kinases and one of their major substrates in human platelets. Estimating the rate of cAMP-regulated and cGMP-regulated protein phosphorylation in intact cells. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Apr 15;205(2):471–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett T. W., Bartlett G. An effective method for eliminating "artifact banding" when sequencing double-stranded DNA templates. Biotechniques. 1990 Jul;9(1):46–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funayama N., Nagafuchi A., Sato N., Tsukita S., Tsukita S. Radixin is a novel member of the band 4.1 family. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):1039–1048. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B. A 130K protein from chicken gizzard: its localization at the termini of microfilament bundles in cultured chicken cells. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):193–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Bretscher A., Esch F. S., Hunter T. cDNA cloning and sequencing of the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate, ezrin, reveals homology to band 4.1. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4133–4142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbrügge M., Friedrich C., Eigenthaler M., Schanzenbächer P., Walter U. Stoichiometric and reversible phosphorylation of a 46-kDa protein in human platelets in response to cGMP- and cAMP-elevating vasodilators. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3088–3093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbrügge M., Walter U. Purification of a vasodilator-regulated phosphoprotein from human platelets. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Oct 20;185(1):41–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Henikoff J. G. Amino acid substitution matrices from protein blocks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10915–10919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B. G., Frischauf A. M. Isolation of genomic DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:180–183. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstrup K., Jablonka B., Hönig-Liedl P., Just M., Kochsiek K., Walter U. Phosphorylation of focal adhesion vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein at Ser157 in intact human platelets correlates with fibrinogen receptor inhibition. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Oct 1;225(1):21–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.00021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Blaisdell B. E., Brendel V. Identification of significant sequence patterns in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:388–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Bucher P., Brendel V., Altschul S. F. Statistical methods and insights for protein and DNA sequences. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:175–203. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Gouin E., Tabouret M., Berche P., Ohayon H., Cossart P. L. monocytogenes-induced actin assembly requires the actA gene product, a surface protein. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):521–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90188-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luna E. J., Hitt A. L. Cytoskeleton--plasma membrane interactions. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):955–964. doi: 10.1126/science.1439807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacArthur M. W., Thornton J. M. Influence of proline residues on protein conformation. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 20;218(2):397–412. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90721-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machesky L. M., Poland T. D. Profilin as a potential mediator of membrane-cytoskeleton communication. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;3(11):381–385. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90087-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matviw H., Yu G., Young D. Identification of a human cDNA encoding a protein that is structurally and functionally related to the yeast adenylyl cyclase-associated CAP proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5033–5040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton C. J., Campbell I. D. SH3 domains. Molecular 'Velcro'. Curr Biol. 1994 Jul 1;4(7):615–617. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A. A., Gerisch G., Lottspeich F., Schleicher M. A protein with homology to the C-terminal repeat sequence of Octopus rhodopsin and synaptophysin is a member of a multigene family in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):118–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81521-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolte C., Eigenthaler M., Schanzenbächer P., Walter U. Endothelial cell-dependent phosphorylation of a platelet protein mediated by cAMP- and cGMP-elevating factors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14808–14812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price G. J., Jones P., Davison M. D., Patel B., Eperon I. C., Critchley D. R. Isolation and characterization of a vinculin cDNA from chick-embryo fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):595–603. doi: 10.1042/bj2450595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard M., Halbrügge M., Scheer U., Wiegand C., Jockusch B. M., Walter U. The 46/50 kDa phosphoprotein VASP purified from human platelets is a novel protein associated with actin filaments and focal contacts. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2063–2070. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R., Mayer B. J., Cicchetti P., Baltimore D. Identification of a ten-amino acid proline-rich SH3 binding site. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.8438166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach P. J. Multisite and hierarchal protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14139–14142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler I., Crawford A. W., Michelsen J. W., Beckerle M. C. Zyxin and cCRP: two interactive LIM domain proteins associated with the cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1573–1587. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann R., Nieberding M., Walter U. Vasodilator-stimulated protein phosphorylation in platelets is mediated by cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinases. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 15;167(3):441–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J. A., Heistad D. D. Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. Platelet-endothelium interactions. N Engl J Med. 1993 Mar 4;328(9):628–635. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199303043280907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson M. P. The structure and function of proline-rich regions in proteins. Biochem J. 1994 Jan 15;297(Pt 2):249–260. doi: 10.1042/bj2970249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Chen J. K., Feng S., Dalgarno D. C., Brauer A. W., Schreiber S. L. Structural basis for the binding of proline-rich peptides to SH3 domains. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):933–945. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]