Abstract
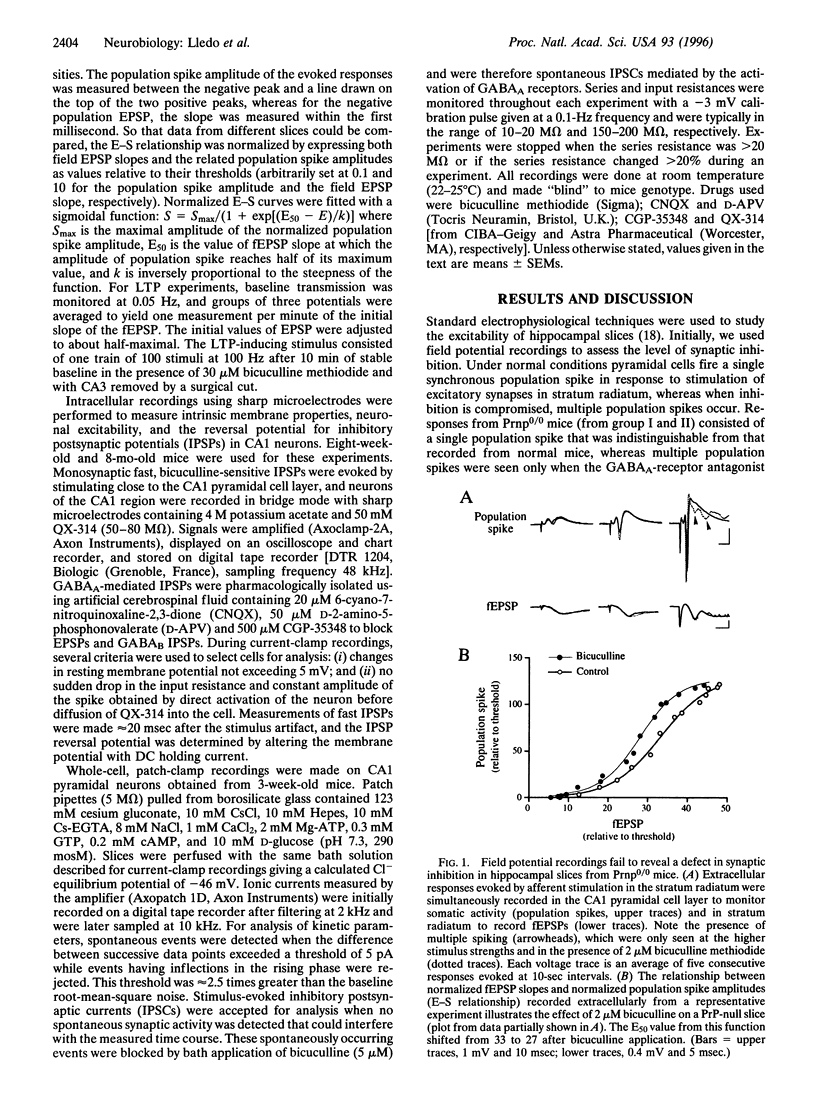
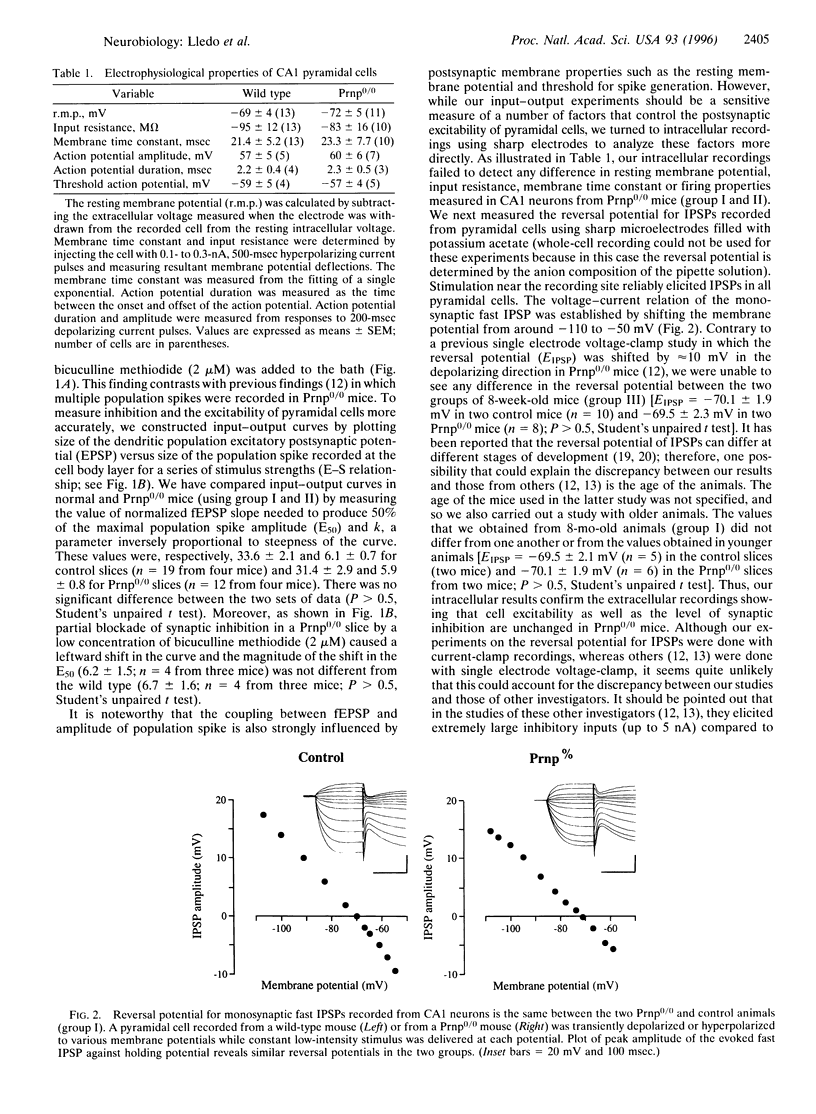
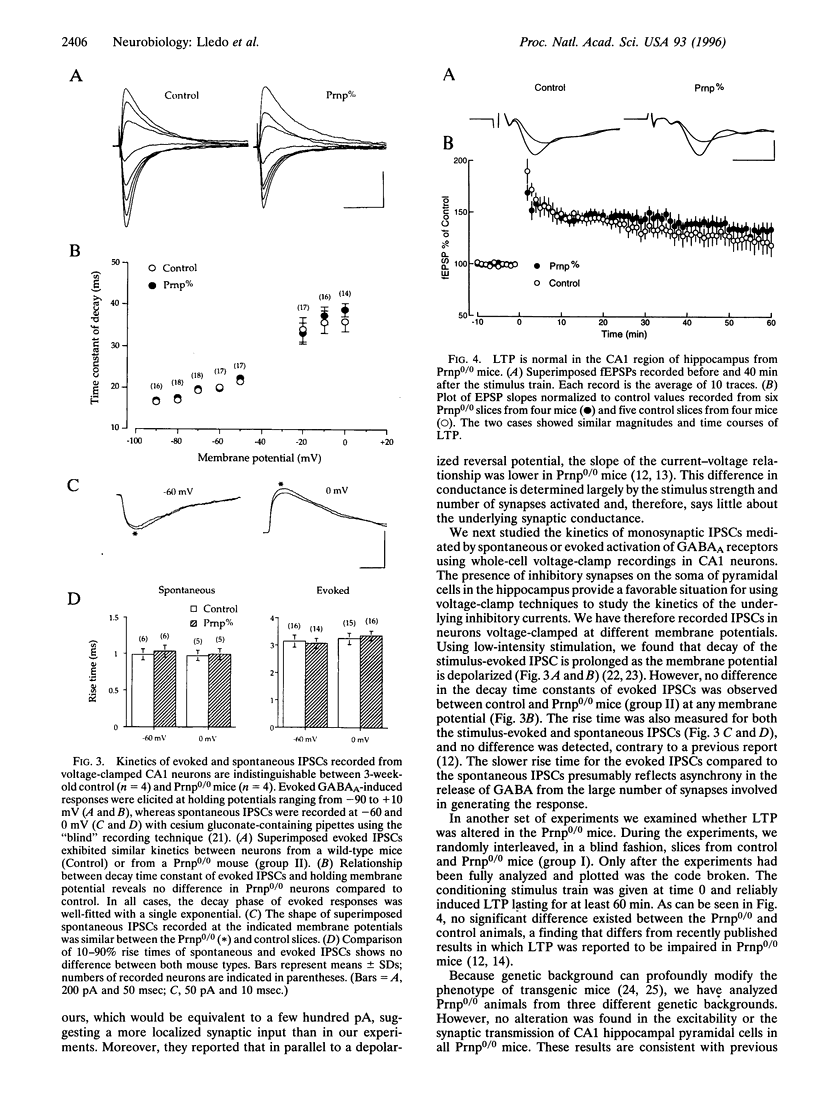
We recorded in the CA1 region from hippocampal slices of prion protein (PrP) gene knockout mice to investigate whether the loss of the normal form of prion protein (PrPC) affects neuronal excitability as well as synaptic transmission in the central nervous system. No deficit in synaptic inhibition was found using field potential recordings because (i) responses induced by stimulation in stratum radiatum consisted of a single population spike in PrP gene knockout mice similar to that recorded from control mice and (ii) the plot of field excitatory postsynaptic potential slope versus the population spike amplitude showed no difference between the two groups of mice. Intracellular recordings also failed to detect any difference in cell excitability and the reversal potential for inhibitory postsynaptic potentials. Analysis of the kinetics of inhibitory postsynaptic current revealed no modification. Finally, we examined whether synaptic plasticity was altered and found no difference in long-term potentiation between control and PrP gene knockout mice. On the basis of our findings, we propose that the loss of the normal form of prion protein does not alter the physiology of the CA1 region of the hippocampus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Ari Y., Cherubini E., Corradetti R., Gaiarsa J. L. Giant synaptic potentials in immature rat CA3 hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:303–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton M. G., Lo Turco J. J., Kriegstein A. R. Whole cell recording from neurons in slices of reptilian and mammalian cerebral cortex. J Neurosci Methods. 1989 Dec;30(3):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(89)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borchelt D. R., Scott M., Taraboulos A., Stahl N., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie and cellular prion proteins differ in their kinetics of synthesis and topology in cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):743–752. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers B. J., Christensen S. C., Pauley J. R., Paylor R., Yuva L., Dunbar S. E., Wehner J. M. Protein and molecular characterization of hippocampal protein kinase C in C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice. J Neurochem. 1995 Jun;64(6):2737–2746. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.64062737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner H. R., Herczeg A., Oesch B. Normal development of nerve-muscle synapses in mice lacking the prion protein gene. Proc Biol Sci. 1992 Nov 23;250(1328):151–155. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büeler H., Aguzzi A., Sailer A., Greiner R. A., Autenried P., Aguet M., Weissmann C. Mice devoid of PrP are resistant to scrapie. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1339–1347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büeler H., Fischer M., Lang Y., Bluethmann H., Lipp H. P., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B., Aguet M., Weissmann C. Normal development and behaviour of mice lacking the neuronal cell-surface PrP protein. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):577–582. doi: 10.1038/356577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. The new mouse genetics: altering the genome by gene targeting. Trends Genet. 1989 Mar;5(3):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B., Raymond G. J. The scrapie-associated form of PrP is made from a cell surface precursor that is both protease- and phospholipase-sensitive. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18217–18223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinge J., Whittington M. A., Sidle K. C., Smith C. J., Palmer M. S., Clarke A. R., Jefferys J. G. Prion protein is necessary for normal synaptic function. Nature. 1994 Jul 28;370(6487):295–297. doi: 10.1038/370295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Gage P. W., Robertson B. Inhibitory post-synaptic currents in rat hippocampal CA1 neurones. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:551–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeArmond S. J., Mobley W. C., DeMott D. L., Barry R. A., Beckstead J. H., Prusiner S. B. Changes in the localization of brain prion proteins during scrapie infection. Neurology. 1987 Aug;37(8):1271–1280. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.8.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T., Maeda N., Smithies O. Targeted mutation of the Hprt gene in mouse embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8583–8587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabizon R., McKinley M. P., Groth D., Prusiner S. B. Immunoaffinity purification and neutralization of scrapie prion infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6617–6621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek D. C. Unconventional viruses and the origin and disappearance of kuru. Science. 1977 Sep 2;197(4307):943–960. doi: 10.1126/science.142303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R., Johnston D. Rectification of single GABA-gated chloride channels in adult hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Jul;54(1):134–142. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.1.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herms J. W., Kretzchmar H. A., Titz S., Keller B. U. Patch-clamp analysis of synaptic transmission to cerebellar purkinje cells of prion protein knockout mice. Eur J Neurosci. 1995 Dec 1;7(12):2508–2512. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb01049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson J. C., Hope J., Clarke A. R., Johnston A., Black C., MacLeod N. PrP gene dosage and long term potentiation. Neurodegeneration. 1995 Mar;4(1):113–114. doi: 10.1006/neur.1995.0014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Alger B. E. A simple chamber for recording from submerged brain slices. J Neurosci Methods. 1981 Aug;4(2):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(81)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan K. M., Baldwin M., Nguyen J., Gasset M., Serban A., Groth D., Mehlhorn I., Huang Z., Fletterick R. J., Cohen F. E. Conversion of alpha-helices into beta-sheets features in the formation of the scrapie prion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):10962–10966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.10962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Biology and genetics of prion diseases. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1994;48:655–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.48.100194.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., DeArmond S. J. Prion diseases and neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:311–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D., Serban A., Koehler R., Foster D., Torchia M., Burton D., Yang S. L., DeArmond S. J. Ablation of the prion protein (PrP) gene in mice prevents scrapie and facilitates production of anti-PrP antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10608–10612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D., Serban A., Stahl N., Gabizon R. Attempts to restore scrapie prion infectivity after exposure to protein denaturants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2793–2797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1515–1522. doi: 10.1126/science.1675487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibilia M., Wagner E. F. Strain-dependent epithelial defects in mice lacking the EGF receptor. Science. 1995 Jul 14;269(5221):234–238. doi: 10.1126/science.7618085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threadgill D. W., Dlugosz A. A., Hansen L. A., Tennenbaum T., Lichti U., Yee D., LaMantia C., Mourton T., Herrup K., Harris R. C. Targeted disruption of mouse EGF receptor: effect of genetic background on mutant phenotype. Science. 1995 Jul 14;269(5221):230–234. doi: 10.1126/science.7618084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittington M. A., Sidle K. C., Gowland I., Meads J., Hill A. F., Palmer M. S., Jefferys J. G., Collinge J. Rescue of neurophysiological phenotype seen in PrP null mice by transgene encoding human prion protein. Nat Genet. 1995 Feb;9(2):197–201. doi: 10.1038/ng0295-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Spigelman I., Carlen P. L. Development of GABA-mediated, chloride-dependent inhibition in CA1 pyramidal neurones of immature rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:25–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


