Abstract
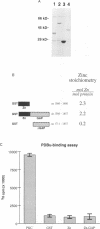
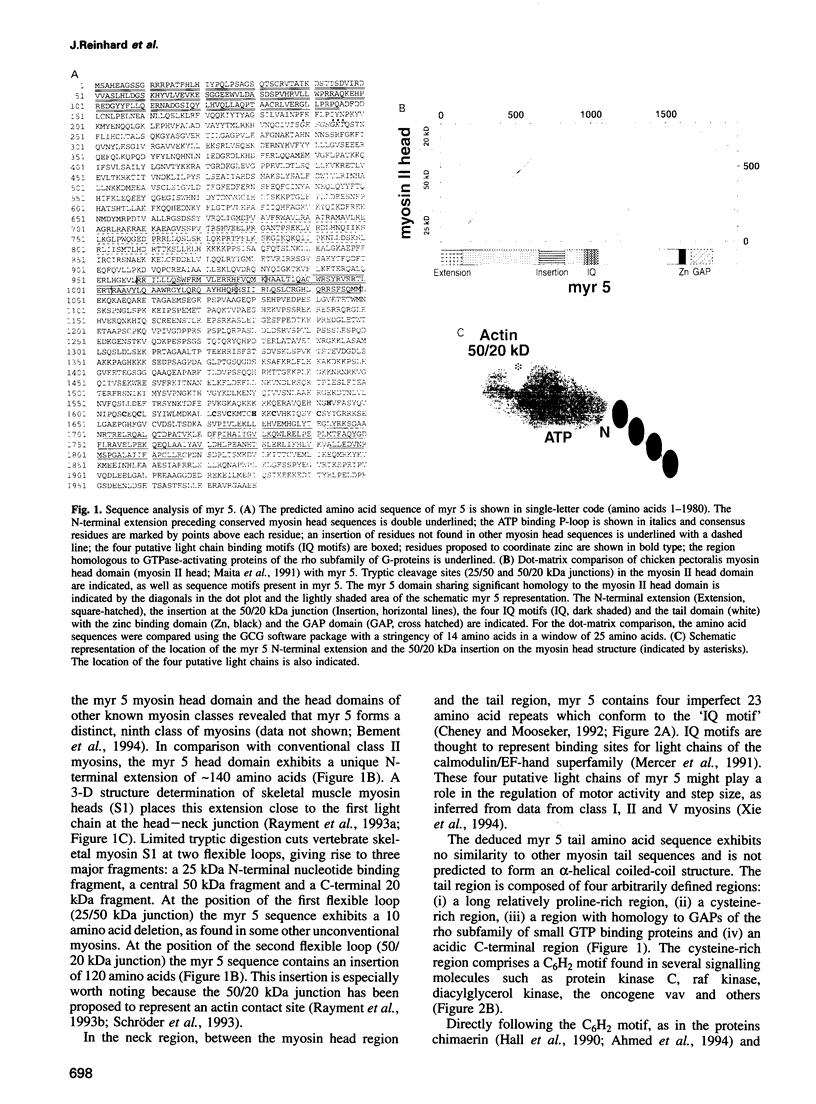
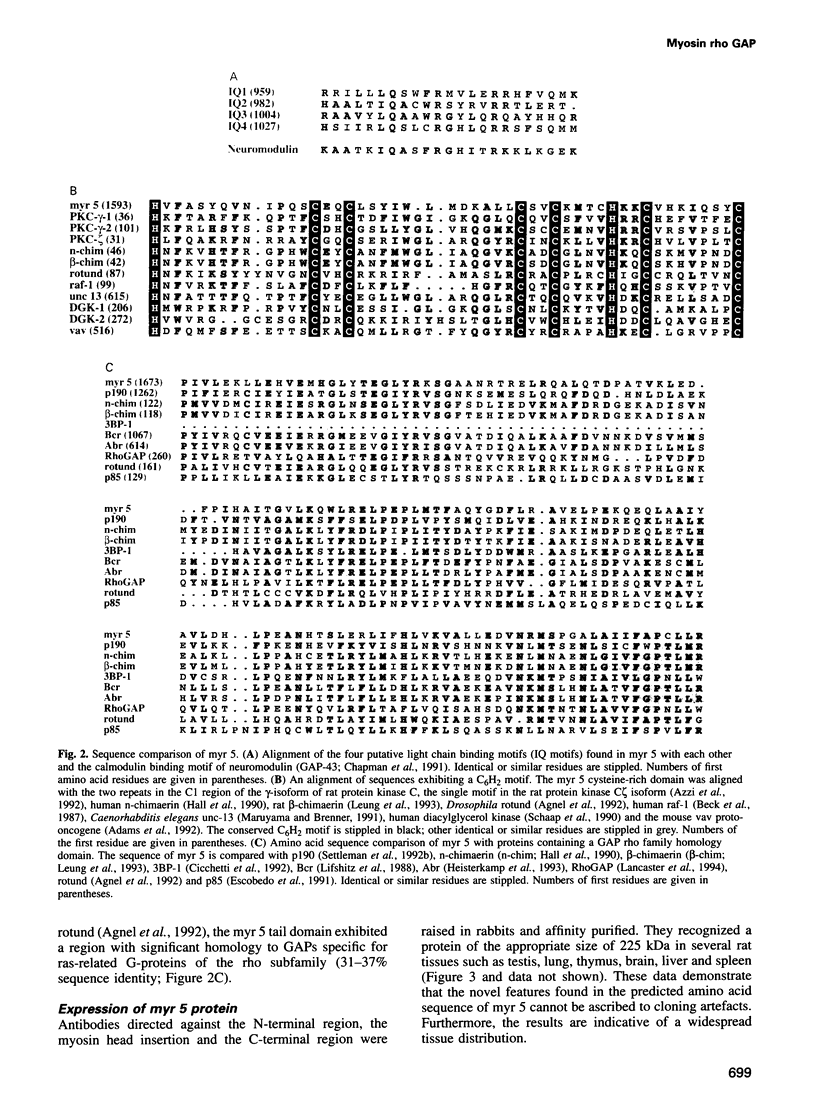
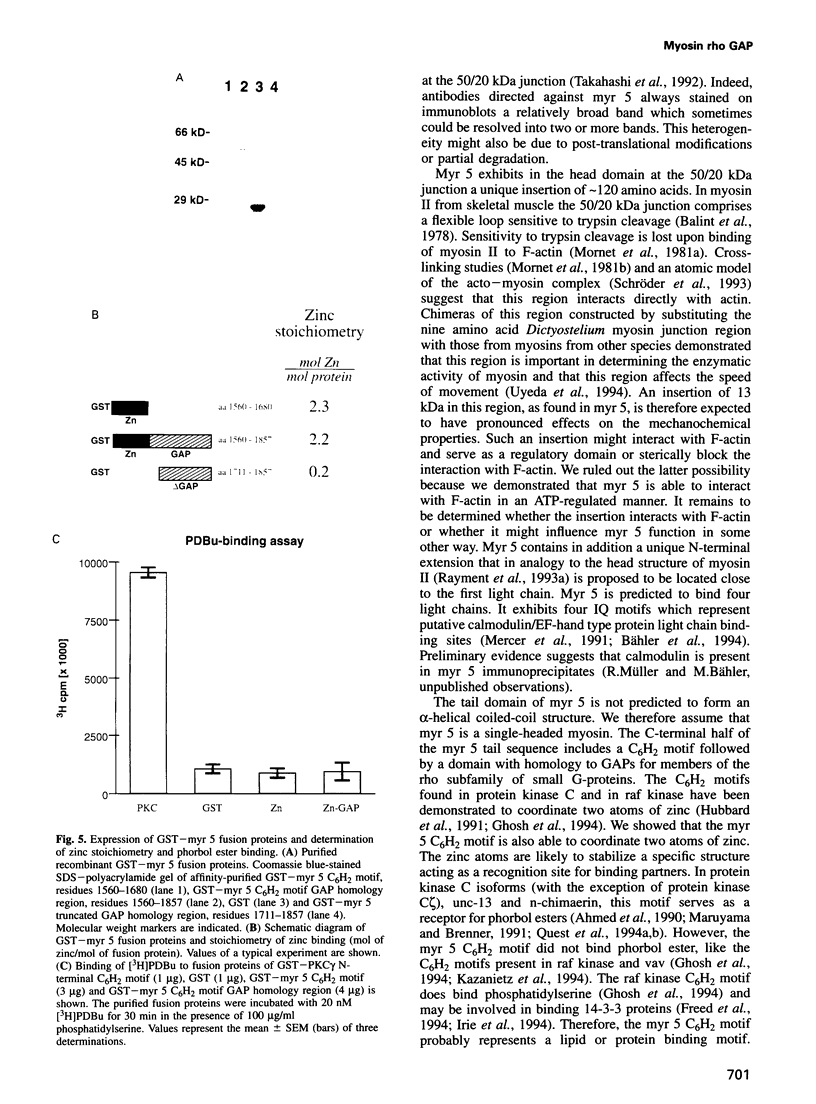
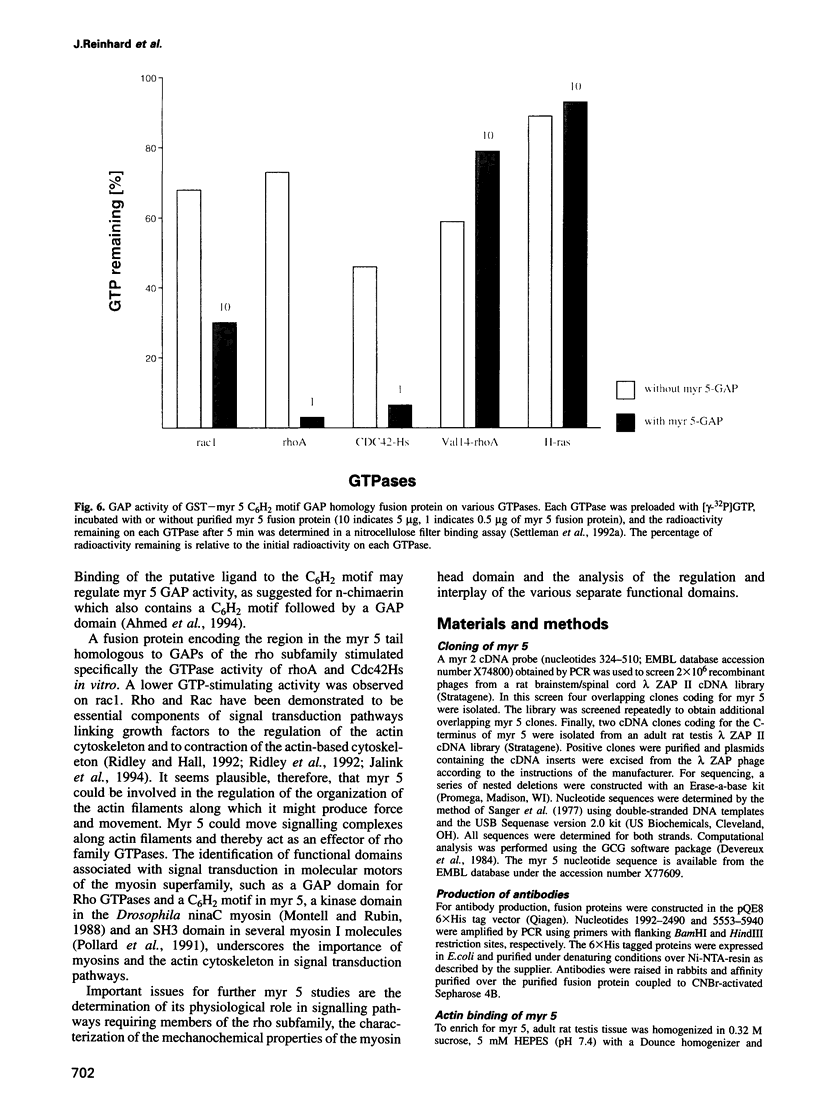
A novel widely expressed type of myosin (fifth unconventional myosin from rat: myr 5) from rat tissues, defining a ninth class of myosins, was identified. The predicted amino acid sequence of myr 5 exhibits several features not found previously in myosins. The myosin head domain contains a unique N-terminal extension and an insertion of 120 amino acids at a postulated myosin-actin contact site. Nevertheless, myr 5 is able to bind actin filaments in an ATP-regulated manner. The head domain is followed by four putative light chain binding sites. The tail domain of myr 5 contains a region which coordinates two atoms of zinc followed by a region that stimulates GTP hydrolysis of members of the ras-related rho subfamily of small G-proteins. Myr 5 therefore provides the first direct link between rho GTPases which have been implicated in the regulation of actin organization and the actin cytoskeleton. It is also the first unconventional myosin for which a tail binding partner(s), namely members of the rho family, has been identified.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Houston H., Allen J., Lints T., Harvey R. The hematopoietically expressed vav proto-oncogene shares homology with the dbl GDP-GTP exchange factor, the bcr gene and a yeast gene (CDC24) involved in cytoskeletal organization. Oncogene. 1992 Apr;7(4):611–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agnel M., Röder L., Vola C., Griffin-Shea R. A Drosophila rotund transcript expressed during spermatogenesis and imaginal disc morphogenesis encodes a protein which is similar to human Rac GTPase-activating (racGAP) proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5111–5122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed S., Kozma R., Monfries C., Hall C., Lim H. H., Smith P., Lim L. Human brain n-chimaerin cDNA encodes a novel phorbol ester receptor. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):767–773. doi: 10.1042/bj2720767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed S., Lee J., Wen L. P., Zhao Z., Ho J., Best A., Kozma R., Lim L. Breakpoint cluster region gene product-related domain of n-chimaerin. Discrimination between Rac-binding and GTPase-activating residues by mutational analysis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17642–17648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzi A., Boscoboinik D., Hensey C. The protein kinase C family. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Sep 15;208(3):547–557. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck T. W., Huleihel M., Gunnell M., Bonner T. I., Rapp U. R. The complete coding sequence of the human A-raf-1 oncogene and transforming activity of a human A-raf carrying retrovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):595–609. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bement W. M., Hasson T., Wirth J. A., Cheney R. E., Mooseker M. S. Identification and overlapping expression of multiple unconventional myosin genes in vertebrate cell types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6549–6553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):643–654. doi: 10.1038/366643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bálint M., Wolf I., Tarcsafalvi A., Gergely J., Sréter F. A. Location of SH-1 and SH-2 in the heavy chain segment of heavy meromyosin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Oct;190(2):793–799. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bähler M., Kroschewski R., Stöffler H. E., Behrmann T. Rat myr 4 defines a novel subclass of myosin I: identification, distribution, localization, and mapping of calmodulin-binding sites with differential calcium sensitivity. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(2):375–389. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman E. R., Au D., Alexander K. A., Nicolson T. A., Storm D. R. Characterization of the calmodulin binding domain of neuromodulin. Functional significance of serine 41 and phenylalanine 42. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):207–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney R. E., Mooseker M. S. Unconventional myosins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90055-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney R. E., Riley M. A., Mooseker M. S. Phylogenetic analysis of the myosin superfamily. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;24(4):215–223. doi: 10.1002/cm.970240402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicchetti P., Mayer B. J., Thiel G., Baltimore D. Identification of a protein that binds to the SH3 region of Abl and is similar to Bcr and GAP-rho. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):803–806. doi: 10.1126/science.1379745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Navankasattusas S., Kavanaugh W. M., Milfay D., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90409-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer J. T., Simmons R. M., Spudich J. A. Single myosin molecule mechanics: piconewton forces and nanometre steps. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):113–119. doi: 10.1038/368113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E., Symons M., Macdonald S. G., McCormick F., Ruggieri R. Binding of 14-3-3 proteins to the protein kinase Raf and effects on its activation. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1713–1716. doi: 10.1126/science.8085158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Xie W. Q., Quest A. F., Mabrouk G. M., Strum J. C., Bell R. M. The cysteine-rich region of raf-1 kinase contains zinc, translocates to liposomes, and is adjacent to a segment that binds GTP-ras. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):10000–10007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodson H. V., Spudich J. A. Molecular evolution of the myosin family: relationships derived from comparisons of amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C., Monfries C., Smith P., Lim H. H., Kozma R., Ahmed S., Vanniasingham V., Leung T., Lim L. Novel human brain cDNA encoding a 34,000 Mr protein n-chimaerin, related to both the regulatory domain of protein kinase C and BCR, the product of the breakpoint cluster region gene. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 5;211(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer J. A. Novel myosins. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;1(2-3):50–56. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90089-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisterkamp N., Kaartinen V., van Soest S., Bokoch G. M., Groffen J. Human ABR encodes a protein with GAPrac activity and homology to the DBL nucleotide exchange factor domain. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):16903–16906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. R., Bishop W. R., Kirschmeier P., George S. J., Cramer S. P., Hendrickson W. A. Identification and characterization of zinc binding sites in protein kinase C. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1776–1779. doi: 10.1126/science.1763327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie K., Gotoh Y., Yashar B. M., Errede B., Nishida E., Matsumoto K. Stimulatory effects of yeast and mammalian 14-3-3 proteins on the Raf protein kinase. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1716–1719. doi: 10.1126/science.8085159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishijima A., Harada Y., Kojima H., Funatsu T., Higuchi H., Yanagida T. Single-molecule analysis of the actomyosin motor using nano-manipulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Mar 15;199(2):1057–1063. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalink K., van Corven E. J., Hengeveld T., Morii N., Narumiya S., Moolenaar W. H. Inhibition of lysophosphatidate- and thrombin-induced neurite retraction and neuronal cell rounding by ADP ribosylation of the small GTP-binding protein Rho. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(3):801–810. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazanietz M. G., Bustelo X. R., Barbacid M., Kolch W., Mischak H., Wong G., Pettit G. R., Bruns J. D., Blumberg P. M. Zinc finger domains and phorbol ester pharmacophore. Analysis of binding to mutated form of protein kinase C zeta and the vav and c-raf proto-oncogene products. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11590–11594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi K., Sasaki T., Kuroda S., Itoh T., Takai Y. Regulation of cytoplasmic division of Xenopus embryo by rho p21 and its inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange protein (rho GDI). J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1187–1195. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung T., How B. E., Manser E., Lim L. Germ cell beta-chimaerin, a new GTPase-activating protein for p21rac, is specifically expressed during the acrosomal assembly stage in rat testis. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3813–3816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifshitz B., Fainstein E., Marcelle C., Shtivelman E., Amson R., Gale R. P., Canaani E. bcr genes and transcripts. Oncogene. 1988 Feb;2(2):113–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maita T., Yajima E., Nagata S., Miyanishi T., Nakayama S., Matsuda G. The primary structure of skeletal muscle myosin heavy chain: IV. Sequence of the rod, and the complete 1,938-residue sequence of the heavy chain. J Biochem. 1991 Jul;110(1):75–87. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama I. N., Brenner S. A phorbol ester/diacylglycerol-binding protein encoded by the unc-13 gene of Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5729–5733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. A., Seperack P. K., Strobel M. C., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Novel myosin heavy chain encoded by murine dilute coat colour locus. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):709–713. doi: 10.1038/349709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Rubin G. M. The Drosophila ninaC locus encodes two photoreceptor cell specific proteins with domains homologous to protein kinases and the myosin heavy chain head. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):757–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90413-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Bertrand R. U., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. Proteolytic approach to structure and function of actin recognition site in myosin heads. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2110–2120. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Bertrand R., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. Structure of the actin-myosin interface. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):301–306. doi: 10.1038/292301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. Determination of total protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:95–119. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Doberstein S. K., Zot H. G. Myosin-I. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:653–681. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quest A. F., Bardes E. S., Bell R. M. A phorbol ester binding domain of protein kinase C gamma. Deletion analysis of the Cys2 domain defines a minimal 43-amino acid peptide. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2961–2970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quest A. F., Bardes E. S., Bell R. M. A phorbol ester binding domain of protein kinase C gamma. High affinity binding to a glutathione-S-transferase/Cys2 fusion protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2953–2960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Holden H. M., Whittaker M., Yohn C. B., Lorenz M., Holmes K. C., Milligan R. A. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):58–65. doi: 10.1126/science.8316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Rypniewski W. R., Schmidt-Bäse K., Smith R., Tomchick D. R., Benning M. M., Winkelmann D. A., Wesenberg G., Holden H. M. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8316857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert C., Kroschewski R., Bähler M. Identification, characterization and cloning of myr 1, a mammalian myosin-I. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(6):1393–1403. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.6.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap D., de Widt J., van der Wal J., Vandekerckhove J., van Damme J., Gussow D., Ploegh H. L., van Blitterswijk W. J., van der Bend R. L. Purification, cDNA-cloning and expression of human diacylglycerol kinase. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81461-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder R. R., Manstein D. J., Jahn W., Holden H., Rayment I., Holmes K. C., Spudich J. A. Three-dimensional atomic model of F-actin decorated with Dictyostelium myosin S1. Nature. 1993 Jul 8;364(6433):171–174. doi: 10.1038/364171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., Albright C. F., Foster L. C., Weinberg R. A. Association between GTPase activators for Rho and Ras families. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):153–154. doi: 10.1038/359153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., Narasimhan V., Foster L. C., Weinberg R. A. Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding the GAP-associated protein p190: implications for a signaling pathway from ras to the nucleus. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):539–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90454-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Kawamoto S., Adelstein R. S. Evidence for inserted sequences in the head region of nonmuscle myosin specific to the nervous system. Cloning of the cDNA encoding the myosin heavy chain-B isoform of vertebrate nonmuscle myosin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17864–17871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda T. Q., Ruppel K. M., Spudich J. A. Enzymatic activities correlate with chimaeric substitutions at the actin-binding face of myosin. Nature. 1994 Apr 7;368(6471):567–569. doi: 10.1038/368567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Kahn C. R. The insulin signaling system. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie X., Harrison D. H., Schlichting I., Sweet R. M., Kalabokis V. N., Szent-Györgyi A. G., Cohen C. Structure of the regulatory domain of scallop myosin at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):306–312. doi: 10.1038/368306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]