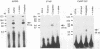Abstract
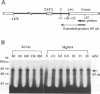
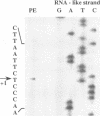
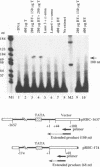
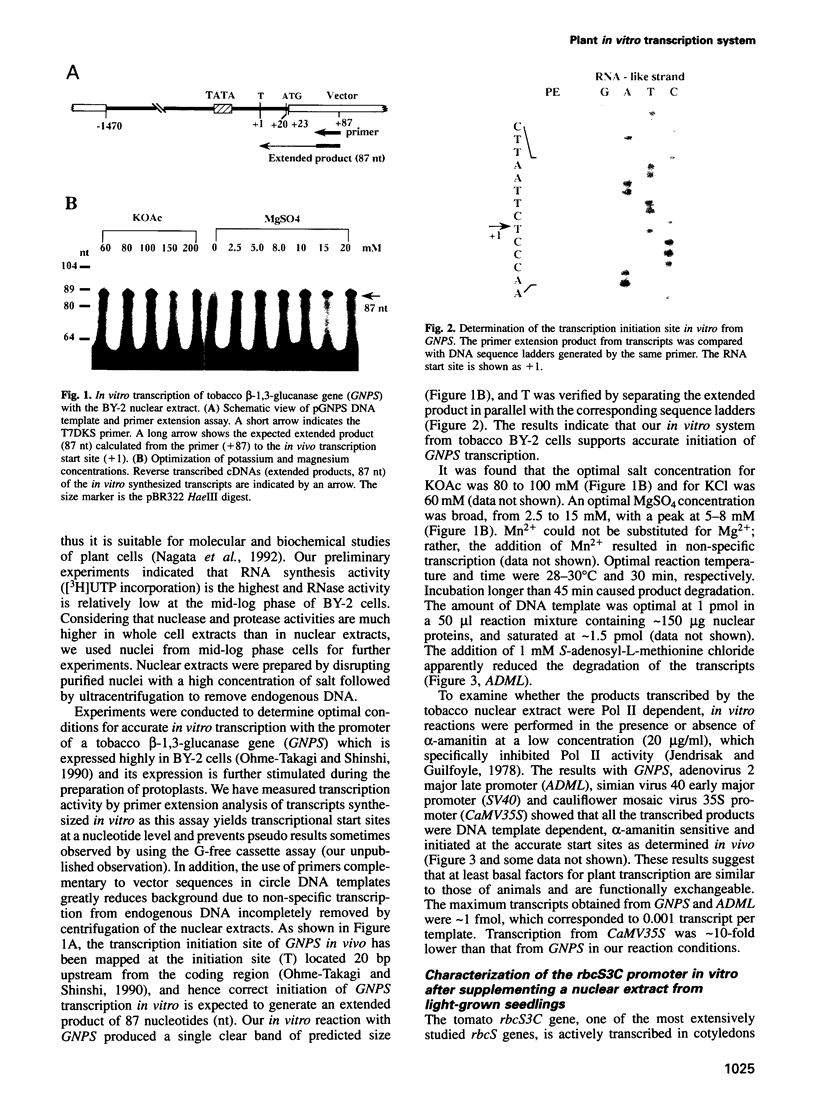
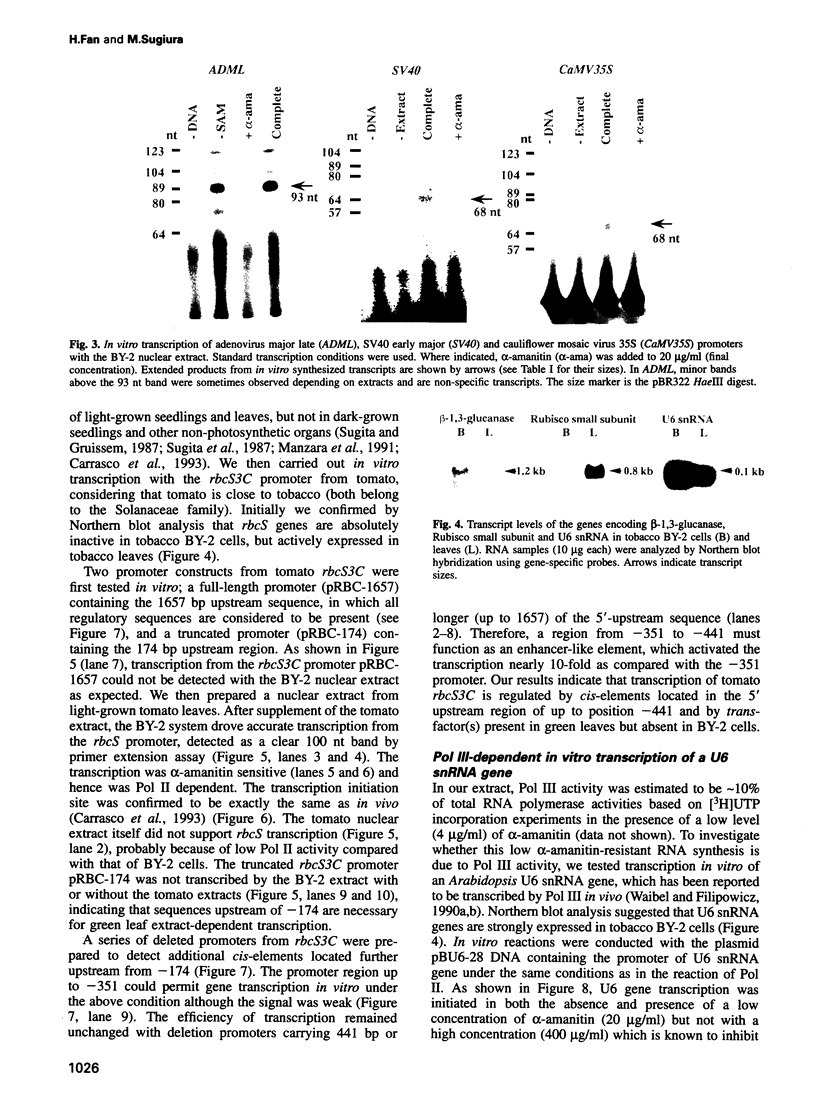
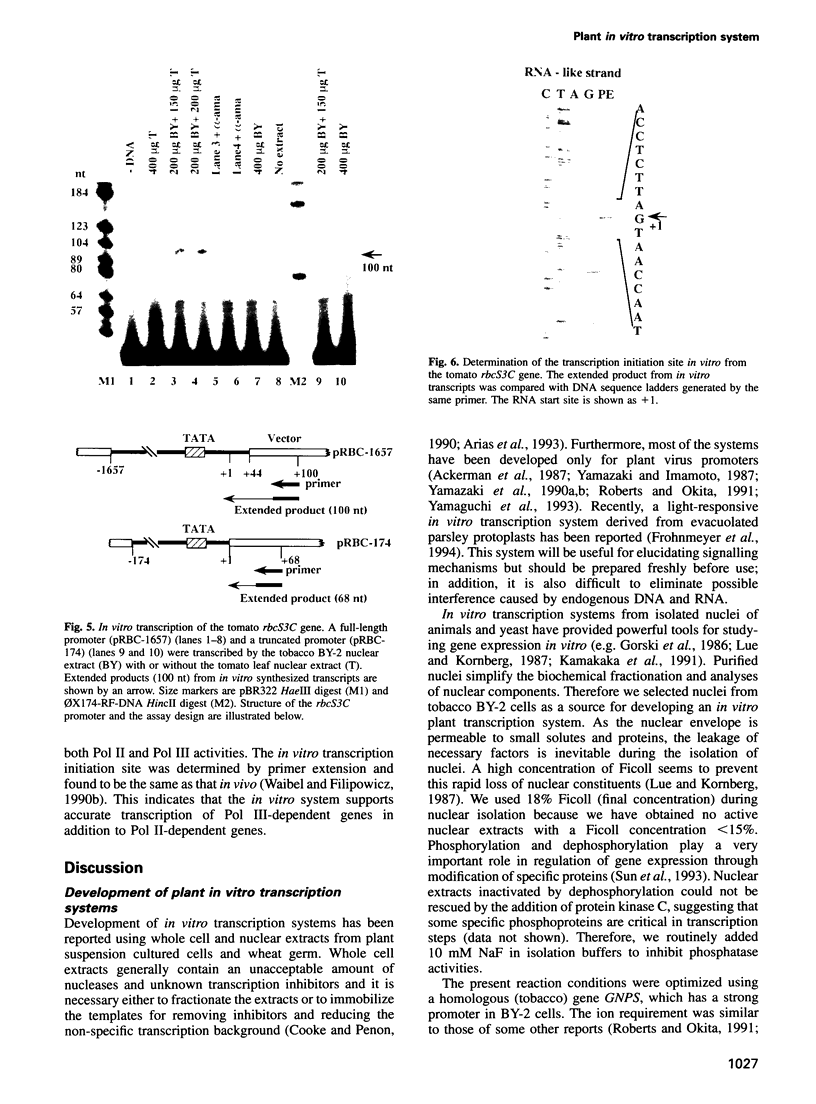
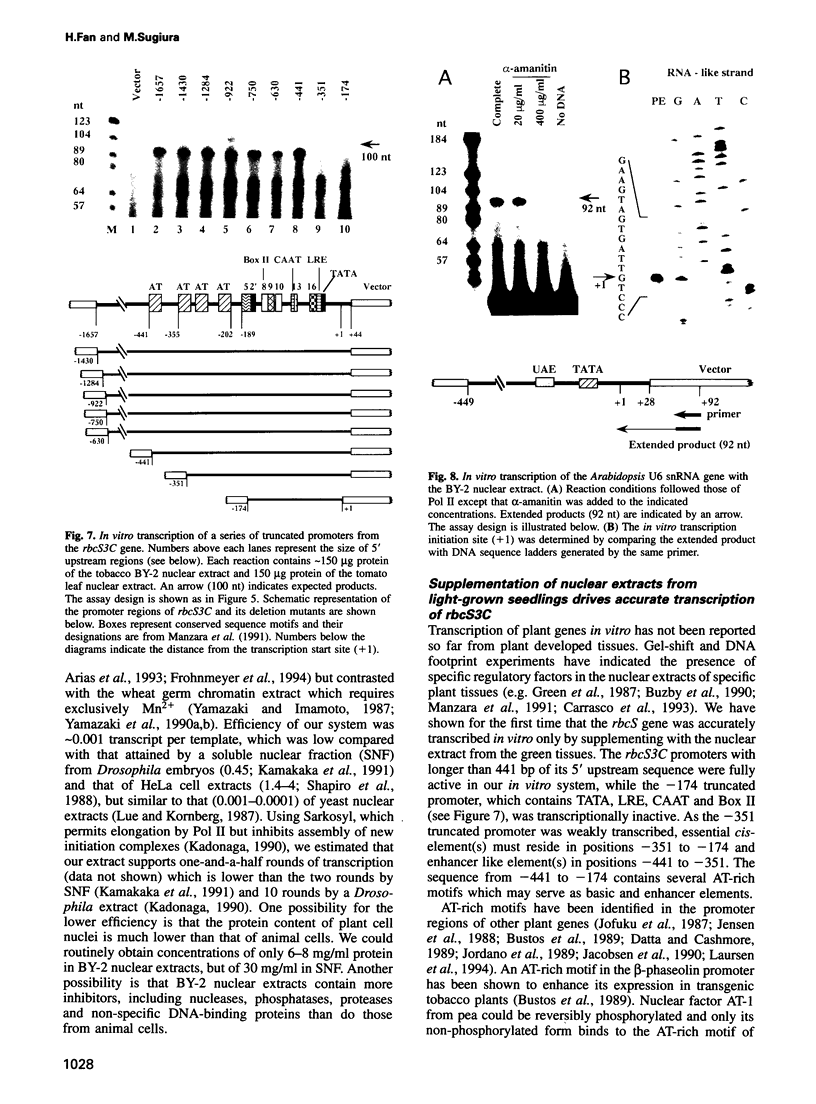
An in vitro transcription initiation system has been developed from nuclei of rapidly growing, non-green tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) cultured (BY-2) cells. Conditions for nuclear extraction and in vitro transcription reaction have been optimized with a tobacco beta-1,3-glucanase gene, a constitutively expressed gene in BY-2 cells. The in vitro system supports accurate transcription of RNA polymerase II-dependent promoters from not only plant genes (tobacco beta-1,3-glucanase gene, cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter) but also animal genes (adenovirus 2 major late promoter, simian virus 40 early major promoter). In addition, this system drives accurate transcription of an RNA polymerase III-dependent Arabidopsis thaliana U6 snRNA gene. As BY-2 cells do not differentiate in response to light or any other stimuli, they would provide a basal transcription system which lacks tissue-specific and light-responsive nuclear signals as well as chloroplast-derived signals. Consequently, the BY-2 cell-free system is unable to transcribe the tomato gene encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rbcS3C) whose expression is tissue-specific and light-inducible. However, the transcription of rbcS3C was obtained by supplementing the BY-2 system with a nuclear extract of light-grown tomato seedlings. The promoter regions necessary for rbcS transcription was mapped in vitro using a series of 5' deletion mutants. The 351 bp upstream sequence is essential and the further upstream region from -351 to -441 enhances its transcription. The in vitro basal system will be useful to identify specific signals from both the nucleus and chloroplast in green leaves and other organs/tissues.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arias J. A., Dixon R. A., Lamb C. J. Dissection of the functional architecture of a plant defense gene promoter using a homologous in vitro transcription initiation system. Plant Cell. 1993 Apr;5(4):485–496. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.4.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustos M. M., Guiltinan M. J., Jordano J., Begum D., Kalkan F. A., Hall T. C. Regulation of beta-glucuronidase expression in transgenic tobacco plants by an A/T-rich, cis-acting sequence found upstream of a French bean beta-phaseolin gene. Plant Cell. 1989 Sep;1(9):839–853. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.9.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzby J. S., Yamada T., Tobin E. M. A light-regulated DNA-binding activity interacts with a conserved region of a Lemna gibba rbcS promoter. Plant Cell. 1990 Aug;2(8):805–814. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.8.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco P., Manzara T., Gruissem W. Developmental and organ-specific changes in DNA-protein interactions in the tomato rbcS3B and rbcS3C promoter regions. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Jan;21(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00039613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly S., Filipowicz W. Activity of chimeric U small nuclear RNA (snRNA)/mRNA genes in transfected protoplasts of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia: U snRNA 3'-end formation and transcription initiation can occur independently in plants. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6403–6415. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Penon P. In vitro transcription from cauliflower mosaic virus promoters by a cell-free extract from tobacco cells. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Mar;14(3):391–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00028775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Cashmore A. R. Binding of a pea nuclear protein to promoters of certain photoregulated genes is modulated by phosphorylation. Plant Cell. 1989 Nov;1(11):1069–1077. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.11.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohnmeyer H., Hahlbrock K., Schäfer E. A light-responsive in vitro transcription system from evacuolated parsley protoplasts. Plant J. 1994 Mar;5(3):437–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.1994.00437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Kay S. A., Chua N. H. Sequence-specific interactions of a pea nuclear factor with light-responsive elements upstream of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2543–2549. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Estrella L., Van den Broeck G., Maenhaut R., Van Montagu M., Schell J., Timko M., Cashmore A. Light-inducible and chloroplast-associated expression of a chimaeric gene introduced into Nicotiana tabacum using a Ti plasmid vector. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):115–120. doi: 10.1038/310115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen K., Laursen N. B., Jensen E. O., Marcker A., Poulsen C., Marcker K. A. HMG I-like proteins from leaf and nodule nuclei interact with different AT motifs in soybean nodulin promoters. Plant Cell. 1990 Jan;2(1):85–94. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jendrisak J., Guilfoyle T. J. Eukaryotic RNA polymerase: comparative subunit structures, immunological properties, and alpha-amanitin sensitivities of the class II enzymes from higher plants. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1322–1327. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. Ø, Marcker K. A., Schell J., Bruijn F. J. Interaction of a nodule specific, trans-acting factor with distinct DNA elements in the soybean leghaemoglobin Ibc(3) 5' upstream region. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1265–1271. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02940.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jofuku K. D., Okamuro J. K., Goldberg R. B. Interaction of an embryo DNA binding protein with a soybean lectin gene upstream region. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):734–737. doi: 10.1038/328734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordano J., Almoguera C., Thomas T. L. A sunflower helianthinin gene upstream sequence ensemble contains an enhancer and sites of nuclear protein interaction. Plant Cell. 1989 Sep;1(9):855–866. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.9.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T. Assembly and disassembly of the Drosophila RNA polymerase II complex during transcription. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2624–2631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamakaka R. T., Tyree C. M., Kadonaga J. T. Accurate and efficient RNA polymerase II transcription with a soluble nuclear fraction derived from Drosophila embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1024–1028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen N. B., Larsen K., Knudsen J. Y., Hoffmann H. J., Poulsen C., Marcker K. A., Jensen E. O. A protein binding AT-rich sequence in the soybean leghemoglobin c3 promoter is a general cis element that requires proximal DNA elements to stimulate transcription. Plant Cell. 1994 May;6(5):659–668. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.5.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Nagayoshi S., Sugita M., Sugiura M. Structure and expression of the tobacco nuclear gene encoding the 33 kDa chloroplast ribonucleoprotein. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 May;239(1-2):304–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00281632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linard C. G., Mbikay M., Seidah N. G., Chretien M. Primary structure of mouse chromogranin B deduced from cDNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1298–1298. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Accurate initiation at RNA polymerase II promoters in extracts from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8839–8843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzara T., Carrasco P., Gruissem W. Developmental and organ-specific changes in promoter DNA-protein interactions in the tomato rbcS gene family. Plant Cell. 1991 Dec;3(12):1305–1316. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.12.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohme-Takagi M., Shinshi H. Structure and expression of a tobacco beta-1,3-glucanase gene. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Dec;15(6):941–946. doi: 10.1007/BF00039434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. W., Okita T. W. Accurate in vitro transcription of plant promoters with nuclear extracts prepared from cultured plant cells. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 May;16(5):771–786. doi: 10.1007/BF00015070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita M., Gruissem W. Developmental, organ-specific, and light-dependent expression of the tomato ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita M., Manzara T., Pichersky E., Cashmore A., Gruissem W. Genomic organization, sequence analysis and expression of all five genes encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from tomato. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):247–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00329650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M. The chloroplast genome. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 May;19(1):149–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00015612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L., Doxsee R. A., Harel E., Tobin E. M. CA-1, a novel phosphoprotein, interacts with the promoter of the cab140 gene in Arabidopsis and is undetectable in det1 mutant seedlings. Plant Cell. 1993 Jan;5(1):109–121. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susek R. E., Ausubel F. M., Chory J. Signal transduction mutants of Arabidopsis uncouple nuclear CAB and RBCS gene expression from chloroplast development. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):787–799. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90459-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waibel F., Filipowicz W. RNA-polymerase specificity of transcription of Arabidopsis U snRNA genes determined by promoter element spacing. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):199–202. doi: 10.1038/346199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waibel F., Filipowicz W. U6 snRNA genes of Arabidopsis are transcribed by RNA polymerase III but contain the same two upstream promoter elements as RNA polymerase II-transcribed U-snRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3451–3458. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki K., Katagiri F., Imaseki H., Chua N. H. TGA1a, a tobacco DNA-binding protein, increases the rate of preinitiation complex formation in a plant in vitro transcription system [corrected]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7035–7039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki K, Imamoto F. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the T-DNA promoter in a soluble chromatin extract from wheat germ. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):445–452. doi: 10.1007/BF00331148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]