Abstract
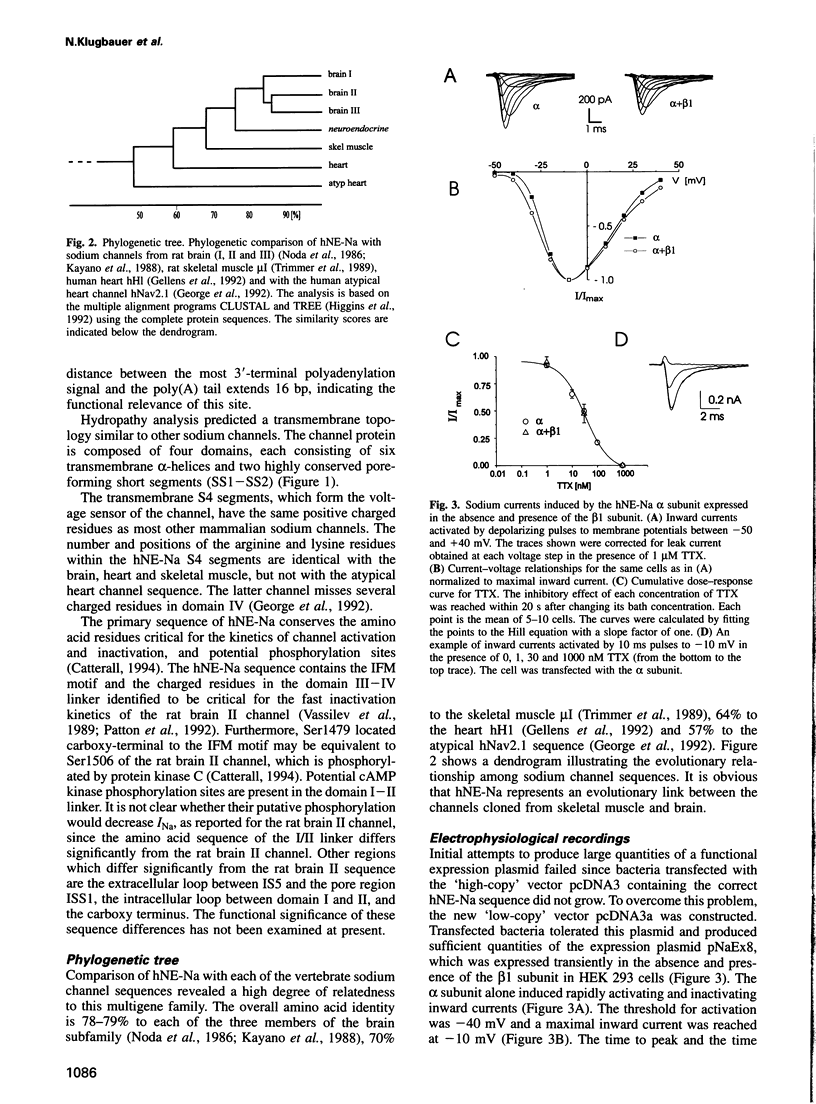
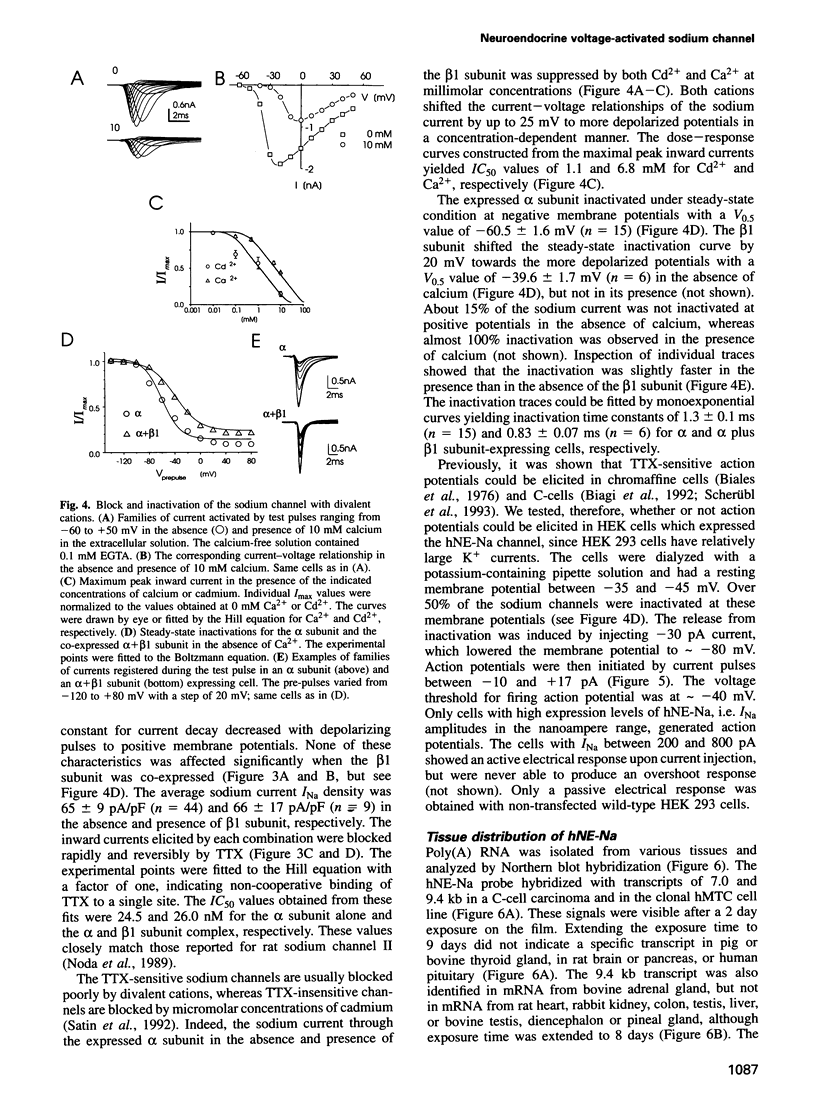
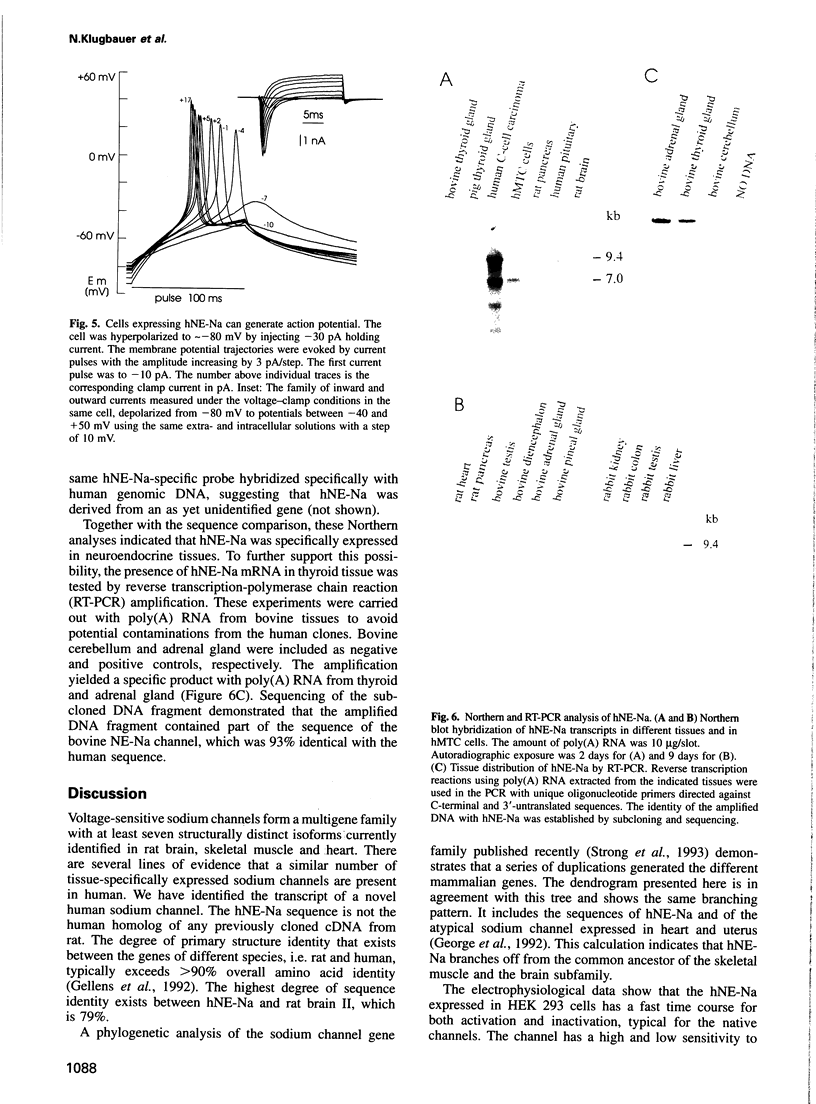
A member of a new subclass of the voltage-activated sodium channel genes has been cloned from the human medullary thyroid carcinoma (hMTC) cell line. The cDNA of hNE-Na (human neuroendocrine sodium channel) encodes a 1977 amino acid protein which phylogenetically represents a link between sodium channels isolated from skeletal muscle and brain. The hNE-Na alpha subunit was transiently expressed in human embryonic kidney cells either alone or in combination with the human sodium channel beta 1 subunit. The channel exhibited rapid activation and inactivation kinetics, and was blocked by tetrodotoxin and cadmium with IC50 values of 24.5 nM and 1.1 mM, respectively. Action potentials were generated in cells expressing high levels of hNE-Na. Northern blot and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analyses demonstrated its expression in hMTC cells, in a C-cell carcinoma, and in thyroid and adrenal gland. Transcripts were not identified in pituitary gland, brain, heart, liver or kidney, indicating that the hNE-Na is a sodium channel solely expressed in neuroendocrine cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckh S. Differential expression of sodium channel mRNAs in rat peripheral nervous system and innervated tissues. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80218-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckh S., Noda M., Lübbert H., Numa S. Differential regulation of three sodium channel messenger RNAs in the rat central nervous system during development. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3611–3616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biagi B. A., Mlinar B., Enyeart J. J. Membrane currents in a calcitonin-secreting human C cell line. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):C986–C994. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.5.C986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biales B., Dichter M., Tischler A. Electrical excitability of cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(3):743–753. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Molecular mechanisms of inactivation and modulation of sodium channels. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1994 May-Aug;17(3-4):121–125. doi: 10.1159/000173798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Arcangelo G., Paradiso K., Shepherd D., Brehm P., Halegoua S., Mandel G. Neuronal growth factor regulation of two different sodium channel types through distinct signal transduction pathways. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):915–921. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautron S., Dos Santos G., Pinto-Henrique D., Koulakoff A., Gros F., Berwald-Netter Y. The glial voltage-gated sodium channel: cell- and tissue-specific mRNA expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7272–7276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellens M. E., George A. L., Jr, Chen L. Q., Chahine M., Horn R., Barchi R. L., Kallen R. G. Primary structure and functional expression of the human cardiac tetrodotoxin-insensitive voltage-dependent sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):554–558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George A. L., Jr, Knittle T. J., Tamkun M. M. Molecular cloning of an atypical voltage-gated sodium channel expressed in human heart and uterus: evidence for a distinct gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4893–4897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Catterall W. A. Auxiliary subunits of voltage-gated ion channels. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1183–1194. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Patton D. E., Reber B. F., Offord J., Charbonneau H., Walsh K., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. Primary structure and functional expression of the beta 1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1375395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallen R. G., Cohen S. A., Barchi R. L. Structure, function and expression of voltage-dependent sodium channels. Mol Neurobiol. 1993 Fall-Winter;7(3-4):383–428. doi: 10.1007/BF02769184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayano T., Noda M., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Numa S. Primary structure of rat brain sodium channel III deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 8;228(1):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80614-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel G. Tissue-specific expression of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel. J Membr Biol. 1992 Feb;125(3):193–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00236433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClatchey A. I., Cannon S. C., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Gusella J. F. The cloning and expression of a sodium channel beta 1-subunit cDNA from human brain. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jun;2(6):745–749. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.6.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ikeda T., Kayano T., Suzuki H., Takeshima H., Kurasaki M., Takahashi H., Numa S. Existence of distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):188–192. doi: 10.1038/320188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Suzuki H., Numa S., Stühmer W. A single point mutation confers tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin insensitivity on the sodium channel II. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81531-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton D. E., West J. W., Catterall W. A., Goldin A. L. Amino acid residues required for fast Na(+)-channel inactivation: charge neutralizations and deletions in the III-IV linker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10905–10909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin J., Kyle J. W., Chen M., Bell P., Cribbs L. L., Fozzard H. A., Rogart R. B. A mutant of TTX-resistant cardiac sodium channels with TTX-sensitive properties. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1202–1205. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherübl H., Kleppisch T., Zink A., Raue F., Krautwurst D., Hescheler J. Major role of dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channels in Ca(2+)-induced calcitonin secretion. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 1):E354–E360. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1993.264.3.E354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong M., Chandy K. G., Gutman G. A. Molecular evolution of voltage-sensitive ion channel genes: on the origins of electrical excitability. Mol Biol Evol. 1993 Jan;10(1):221–242. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a039986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev P., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Inhibition of inactivation of single sodium channels by a site-directed antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8147–8151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West J. W., Scheuer T., Maechler L., Catterall W. A. Efficient expression of rat brain type IIA Na+ channel alpha subunits in a somatic cell line. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90108-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]