Abstract
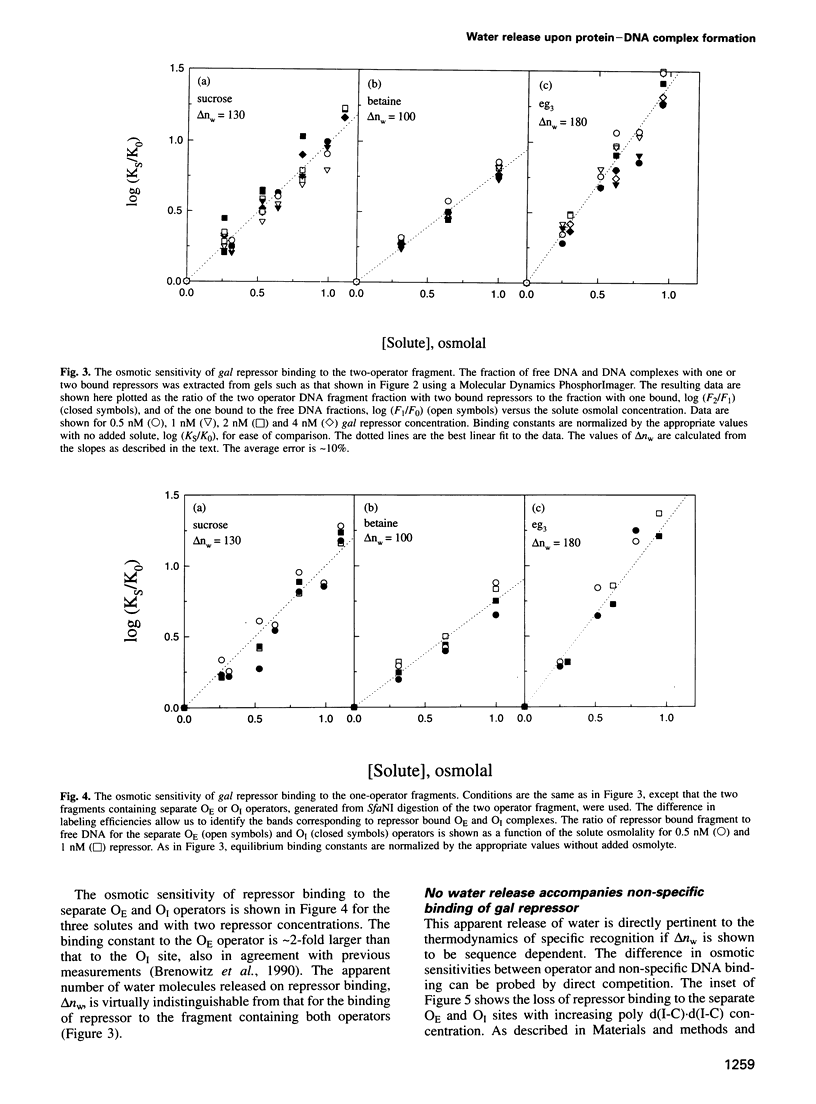
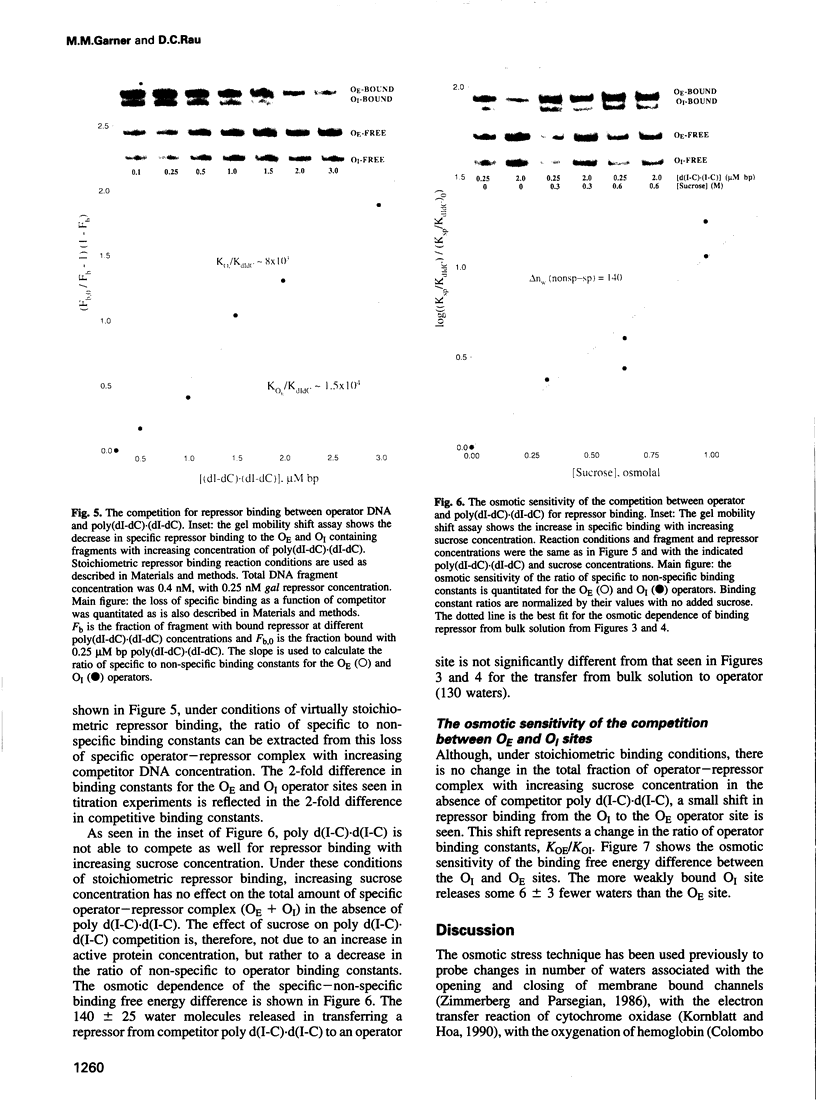
Water release coupled to the association of gal repressor with DNA is measured from the sensitivity of the binding constant to the solution osmotic pressure, using neutral solutes that are typically excluded from polar protein and DNA surfaces. Differences in water release for binding of repressor to different sequences are linked with differences in specificity and binding energies. With sucrose, the specific binding of repressor to operator sequences is accompanied by the release of 130 water molecules. No water release is seen for the weak, non-specific binding of repressor to poly(dI-dC).(dI-dC). A difference in the release of six water molecules is seen even for the binding of gal repressor to two different operator sequences that differ in affinity by only a factor of two.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S. Multipartite genetic control elements: communication by DNA loop. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:227–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa T., Timasheff S. N. Preferential interactions of proteins with solvent components in aqueous amino acid solutions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 1;224(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa T., Timasheff S. N. Stabilization of protein structure by sugars. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6536–6544. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenowitz M., Jamison E., Majumdar A., Adhya S. Interaction of the Escherichia coli Gal repressor protein with its DNA operators in vitro. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3374–3383. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayley S., Lewis B. A., Guttman H. J., Record M. T., Jr Characterization of the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli K-12 as a function of external osmolarity. Implications for protein-DNA interactions in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1991 Nov 20;222(2):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90212-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo M. F., Rau D. C., Parsegian V. A. Protein solvation in allosteric regulation: a water effect on hemoglobin. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):655–659. doi: 10.1126/science.1585178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M. G. Measurement of protein-DNA interaction parameters by electrophoresis mobility shift assay. Electrophoresis. 1989 May-Jun;10(5-6):366–376. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Perez A., Burg M. B. Renal medullary organic osmolytes. Physiol Rev. 1991 Oct;71(4):1081–1115. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.4.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Burg M. B. Macromolecular crowding and confinement in cells exposed to hypertonicity. Am J Physiol. 1994 Apr;266(4 Pt 1):C877–C892. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.4.C877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblatt J. A., Hoa G. H. A nontraditional role for water in the cytochrome c oxidase reaction. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 9;29(40):9370–9376. doi: 10.1021/bi00492a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladbury J. E., Wright J. G., Sturtevant J. M., Sigler P. B. A thermodynamic study of the trp repressor-operator interaction. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 20;238(5):669–681. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson C. L., Carey J. Tandem binding in crystals of a trp repressor/operator half-site complex. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):178–182. doi: 10.1038/366178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Timasheff S. N. The stabilization of proteins by sucrose. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7193–7201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leikin S., Parsegian V. A., Rau D. C., Rand R. P. Hydration forces. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 1993;44:369–395. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pc.44.100193.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesser D. R., Kurpiewski M. R., Jen-Jacobson L. The energetic basis of specificity in the Eco RI endonuclease--DNA interaction. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):776–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2237428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A., Adhya S. Demonstration of two operator elements in gal: in vitro repressor binding studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6100–6104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar A., Rudikoff S., Adhya S. Purification and properties of Gal repressor:pL-galR fusion in pKC31 plasmid vector. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2326–2331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossing M. C., Record M. T., Jr Thermodynamic origins of specificity in the lac repressor-operator interaction. Adaptability in the recognition of mutant operator sites. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90106-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otwinowski Z., Schevitz R. W., Zhang R. G., Lawson C. L., Joachimiak A., Marmorstein R. Q., Luisi B. F., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of trp repressor/operator complex at atomic resolution. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):321–329. doi: 10.1038/335321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Fuller N. L., Butko P., Francis G., Nicholls P. Measured change in protein solvation with substrate binding and turnover. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 15;32(23):5925–5929. doi: 10.1021/bi00074a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senear D. F., Brenowitz M. Determination of binding constants for cooperative site-specific protein-DNA interactions using the gel mobility-shift assay. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13661–13671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spolar R. S., Record M. T., Jr Coupling of local folding to site-specific binding of proteins to DNA. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):777–784. doi: 10.1126/science.8303294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interaction: the sources of sequence-specific binding. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Aug;23(3):205–280. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Ross P. D., Mudd C. P. Thermodynamics of Cro protein-DNA interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8180–8184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timasheff S. N. The control of protein stability and association by weak interactions with water: how do solvents affect these processes? Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:67–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerberg J., Parsegian V. A. Polymer inaccessible volume changes during opening and closing of a voltage-dependent ionic channel. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):36–39. doi: 10.1038/323036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B., Minton A. P. Macromolecular crowding: biochemical, biophysical, and physiological consequences. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:27–65. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H. Protein-DNA recognition: new perspectives and underlying themes. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):769–770. doi: 10.1126/science.8303292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]