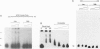Abstract
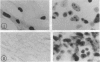
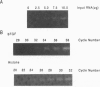
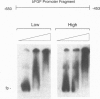
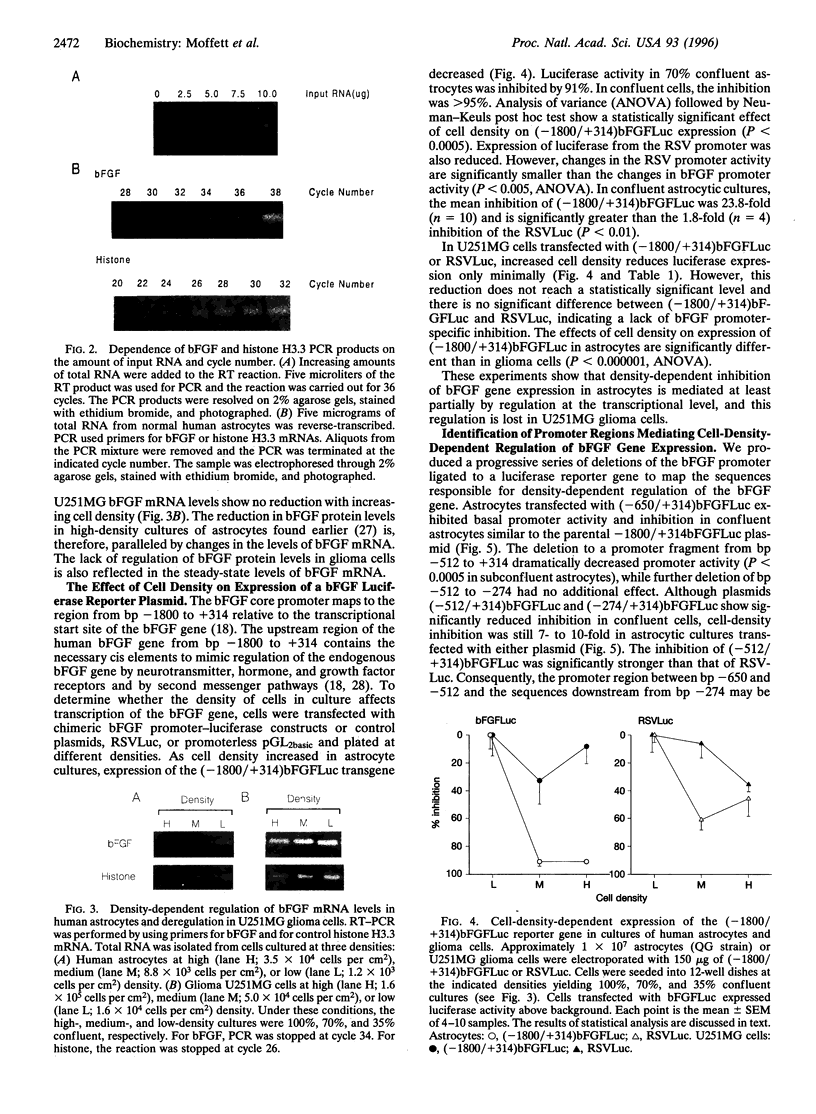
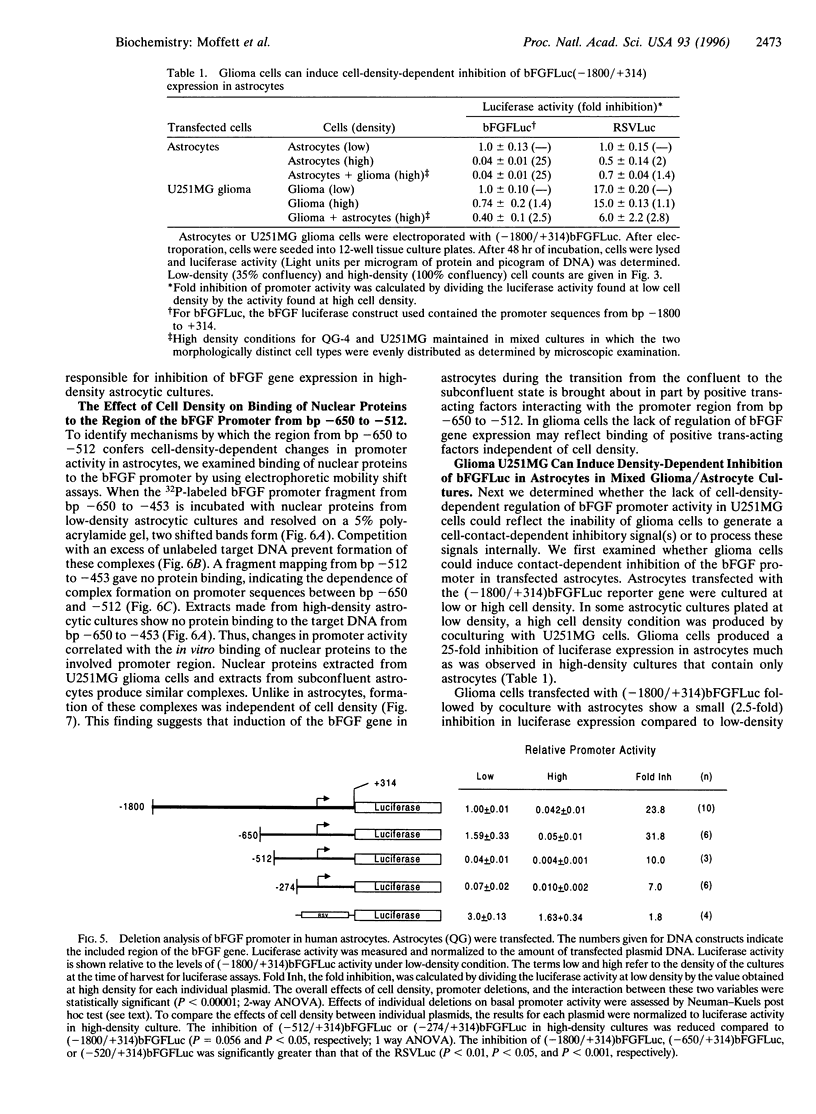
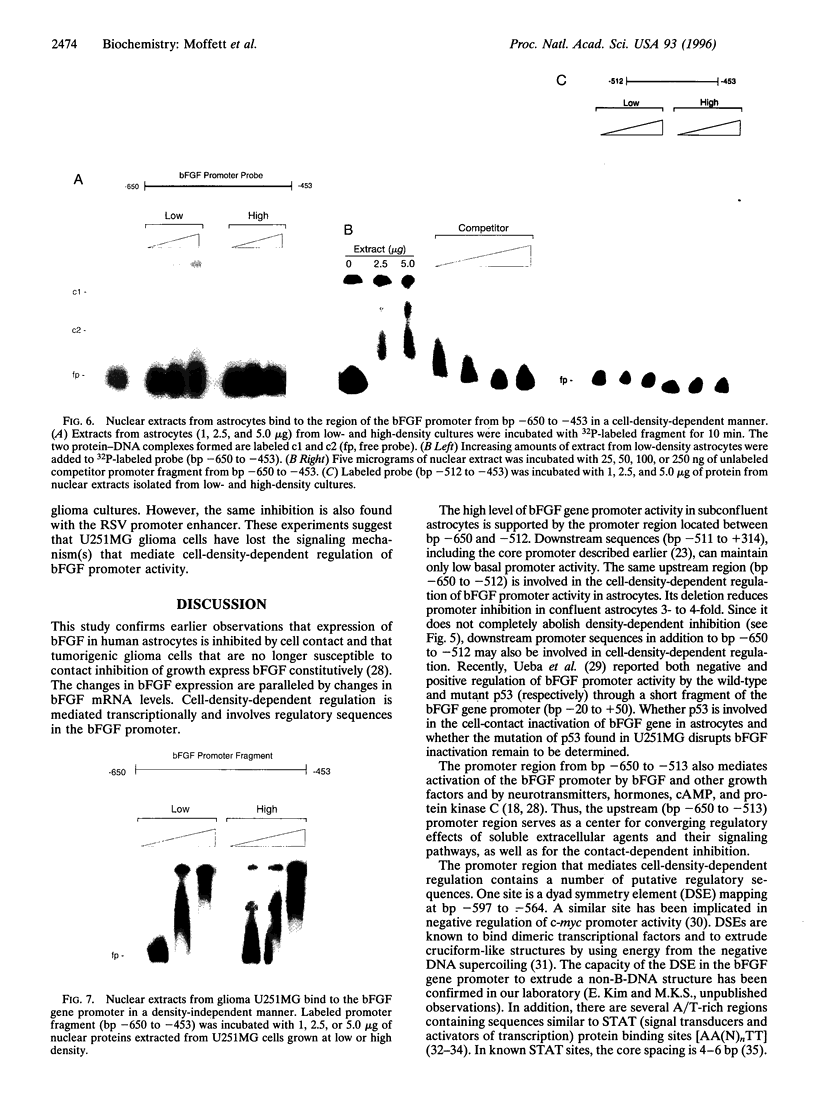
Expression of mitogenic basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in the central nervous system is inhibited by direct cell contact and is implicated in reactive and neoplastic transformation of astrocytes. The molecular mechanisms controlling expression of bFGF were examined in cultures of human astrocytes. Cell-density-dependent depletion of bFGF mRNA levels parallels changes in bFGF gene protein. Regulation of transcription of a bFGF luciferase reporter gene containing an upstream region (bp -1800 to +314) of the bFGF gene promoter mimicks the density-dependent regulation of the endogenous bFGF gene in transfected astrocytes. Deletion analysis has identified a fragment (bp -650 to -513) and sequences further downstream (bp -274 to +314) as the regions required for the regulation of bFGF gene activity by cell density. Unlike in astrocytes, changing the cell density of glioma cell cultures does not affect the levels of bFGF protein and mRNA. bFGF luciferase constructs were expressed at the same level in high- or low-density cultures of glioma cells, indicating altered regulation of the bFGF gene promoter. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays showed binding of nuclear proteins to a fragment of bFGF gene promoter from bp -650 to -453. This binding was abolished by a deletion of the upstream cell-density-responsive region (bp -650 to -512). Binding was observed with nuclear extracts from subconfluent astrocytes but was reduced in extracts from confluent astrocytes. Our results indicate that induction of bFGF in astrocytes upon reduction of cell density is mediated transcriptionally by positive trans-acting factors interacting with bFGF promoter. In contrast, nuclear proteins from glioma cells bind to the promoter region from bp -650 to -453 independent of cell density. Thus, the constitutive binding of trans-acting factor(s) to the region of the bFGF promoter from bp -650 to -453 may be responsible for the continuous expression of bFGF that leads to the uncontrolled growth of glioma cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asch A. S., Leung L. L., Shapiro J., Nachman R. L. Human brain glial cells synthesize thrombospondin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2904–2908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigner D. D., Bigner S. H., Pontén J., Westermark B., Mahaley M. S., Ruoslahti E., Herschman H., Eng L. F., Wikstrand C. J. Heterogeneity of Genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of fifteen permanent cell lines derived from human gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 May;40(3):201–229. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198105000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr, Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1415–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.8197455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng L. F., Yu A. C., Lee Y. L. Astrocytic response to injury. Prog Brain Res. 1992;94:353–365. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61764-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finklestein S. P., Apostolides P. J., Caday C. G., Prosser J., Philips M. F., Klagsbrun M. Increased basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) immunoreactivity at the site of focal brain wounds. Brain Res. 1988 Sep 20;460(2):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90370-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frautschy S. A., Walicke P. A., Baird A. Localization of basic fibroblast growth factor and its mRNA after CNS injury. Brain Res. 1991 Jul 12;553(2):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90837-l. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goc A., Stachowiak M. K. Bovine tyrosine hydroxylase gene-promoter regions involved in basal and angiotensin II-stimulated expression in nontransformed adrenal medullary cells. J Neurochem. 1994 Mar;62(3):834–843. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62030834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimovitz-Friedman A., Balaban N., McLoughlin M., Ehleiter D., Michaeli J., Vlodavsky I., Fuks Z. Protein kinase C mediates basic fibroblast growth factor protection of endothelial cells against radiation-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1994 May 15;54(10):2591–2597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Bishop J. M., Levens D. Regulatory elements that modulate expression of human c-myc. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):659–671. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Yamamoto K., Thierfelder W. E., Kreider B., Silvennoinen O. Signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily: JAKs and STATs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 May;19(5):222–227. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotanides H., Reich N. C. Requirement of tyrosine phosphorylation for rapid activation of a DNA binding factor by IL-4. Science. 1993 Nov 19;262(5137):1265–1267. doi: 10.1126/science.7694370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Bindereif A., Green M. R. A small-scale procedure for preparation of nuclear extracts that support efficient transcription and pre-mRNA splicing. Gene Anal Tech. 1988 Mar-Apr;5(2):22–31. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(88)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libermann T. A., Friesel R., Jaye M., Lyall R. M., Westermark B., Drohan W., Schmidt A., Maciag T., Schlessinger J. An angiogenic growth factor is expressed in human glioma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1627–1632. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H. M., Chen H. H. Correlation between fibroblast growth factor expression and cell proliferation in experimental brain infarct: studied with proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunohistochemistry. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1994 Mar;53(2):118–126. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199403000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell S. K. Development and decision-making in the mammalian cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1988 Jan-Mar;472(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(88)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillian M. K., Thai L., Hong J. S., O'Callaghan J. P., Pennypacker K. R. Brain injury in a dish: a model for reactive gliosis. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Apr;17(4):138–142. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. S., Gross J. L., Herblin W. F., Reilly T. M., LaSala P. A., Alterman R. L., Moskal J. R., Kornblith P. L., Dexter D. L. Basic fibroblast growth factor-like activity and receptors are expressed in a human glioma cell line. Cancer Res. 1990 Apr 15;50(8):2524–2529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. S. Suppression of basic fibroblast growth factor expression by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides inhibits the growth of transformed human astrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):728–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. R., Sato R., Sato Y., Friesen H. G. Fibroblast growth factor messenger ribonucleic acid expression in a human astrocytoma cell line: regulation by serum and cell density. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Jul;2(7):591–598. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-7-591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. R., Sato Y., Sato R., Friesen H. G. Regulation of multiple basic fibroblast growth factor messenger ribonucleic acid transcripts by protein kinase C activators. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1196–1201. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieper R. O., Futscher B. W., Dong Q., Ellis T. M., Erickson L. C. Comparison of O-6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) mRNA levels in Mer+ and Mer- human tumor cell lines containing the MGMT gene by the polymerase chain reaction technique. Cancer Commun. 1990;2(1):13–20. doi: 10.3727/095535490820874812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puchacz E., Stachowiak E. K., Florkiewicz R. Z., Lukas R. J., Stachowiak M. K. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) regulates tyrosine hydroxylase and proenkephalin mRNA levels in adrenal chromaffin cells. Brain Res. 1993 Apr 30;610(1):39–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91214-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Van Dyke M. W., Gregor P. D., Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of the human gene-specific transcription factor USF. I. Complete purification and identification of USF from HeLa cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11985–11993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel H. M., Milocco L. H., Lamb P., Darnell J. E., Jr, Stein R. B., Rosen J. Spacing of palindromic half sites as a determinant of selective STAT (signal transducers and activators of transcription) DNA binding and transcriptional activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):3041–3045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.3041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata F., Baird A., Florkiewicz R. Z. Functional characterization of the human basic fibroblast growth factor gene promoter. Growth Factors. 1991;4(4):277–287. doi: 10.3109/08977199109043913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachowiak M. K., Moffett J., Joy A., Puchacz E., Florkiewicz R., Stachowiak E. K. Regulation of bFGF gene expression and subcellular distribution of bFGF protein in adrenal medullary cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(1):203–223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi J. A., Mori H., Fukumoto M., Igarashi K., Jaye M., Oda Y., Kikuchi H., Hatanaka M. Gene expression of fibroblast growth factors in human gliomas and meningiomas: demonstration of cellular source of basic fibroblast growth factor mRNA and peptide in tumor tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5710–5714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueba T., Nosaka T., Takahashi J. A., Shibata F., Florkiewicz R. Z., Vogelstein B., Oda Y., Kikuchi H., Hatanaka M. Transcriptional regulation of basic fibroblast growth factor gene by p53 in human glioblastoma and hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):9009–9013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.9009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner B. J., Hayes T. E., Hoban C. J., Cochran B. H. The SIF binding element confers sis/PDGF inducibility onto the c-fos promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4477–4484. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagzag D., Miller D. C., Sato Y., Rifkin D. B., Burstein D. E. Immunohistochemical localization of basic fibroblast growth factor in astrocytomas. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 15;50(22):7393–7398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]