Abstract
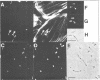
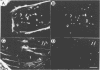
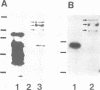
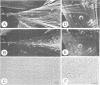
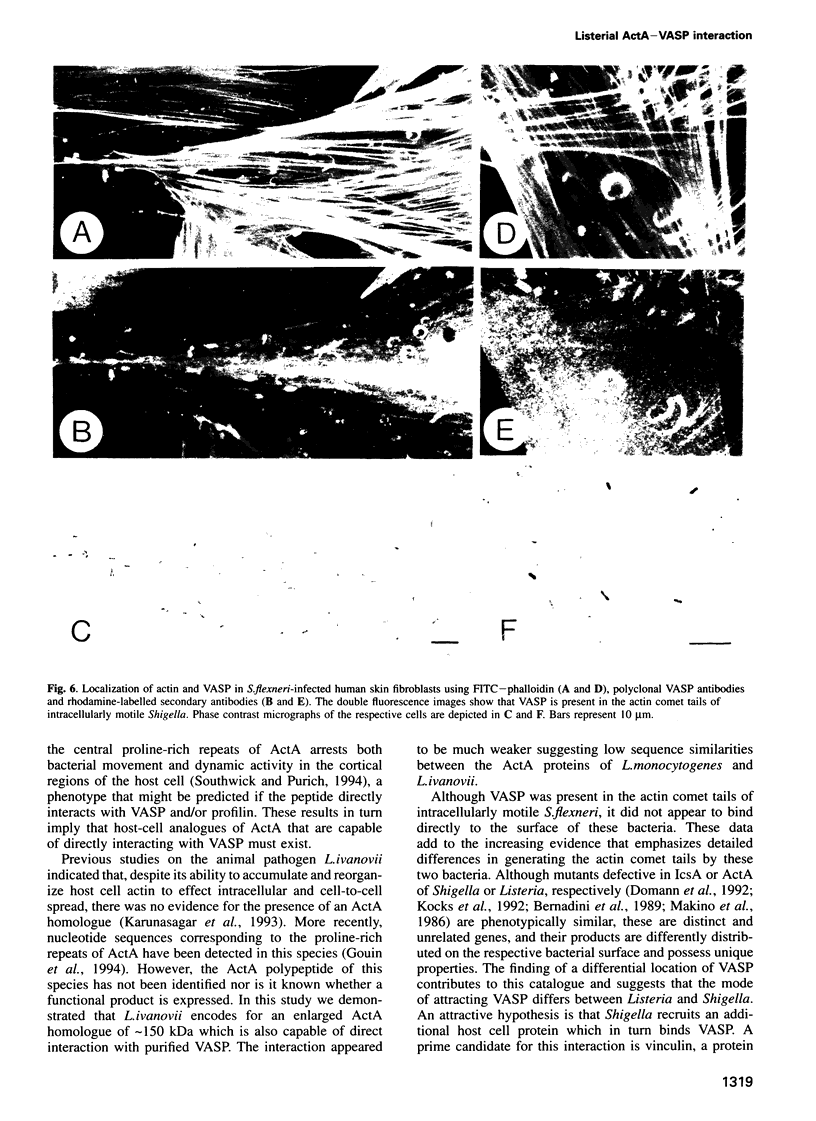
The surface-bound ActA polypeptide of the intracellular bacterial pathogen Listeria monocytogenes is the sole listerial factor needed for recruitment of host actin filaments by intracellularly motile bacteria. Here we report that following Listeria infection the host vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP), a microfilament- and focal adhesion-associated substrate of both the cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinases, accumulates on the surface of intracytoplasmic bacteria prior to the detection of F-actin 'clouds'. VASP remains associated with the surface of highly motile bacteria, where it is polarly located, juxtaposed between one extremity of the bacterial surface and the front of the actin comet tail. Since actin filament polymerization occurs only at the very front of the tail, VASP exhibits properties of a host protein required to promote actin polymerization. Purified VASP binds directly to the ActA polypeptide in vitro. A ligand-overlay blot using purified radiolabelled VASP enabled us to identify the ActA homologue of the related intracellular motile pathogen, Listeria ivanovii, as a protein with a molecular mass of approximately 150 kDa. VASP also associates with actin filaments recruited by another intracellularly motile bacterial pathogen, Shigella flexneri. Hence, by the simple expedient of expressing surface-bound attractor molecules, bacterial pathogens effectively harness cytoskeletal components to achieve intracellular movement.
Full text
PDF

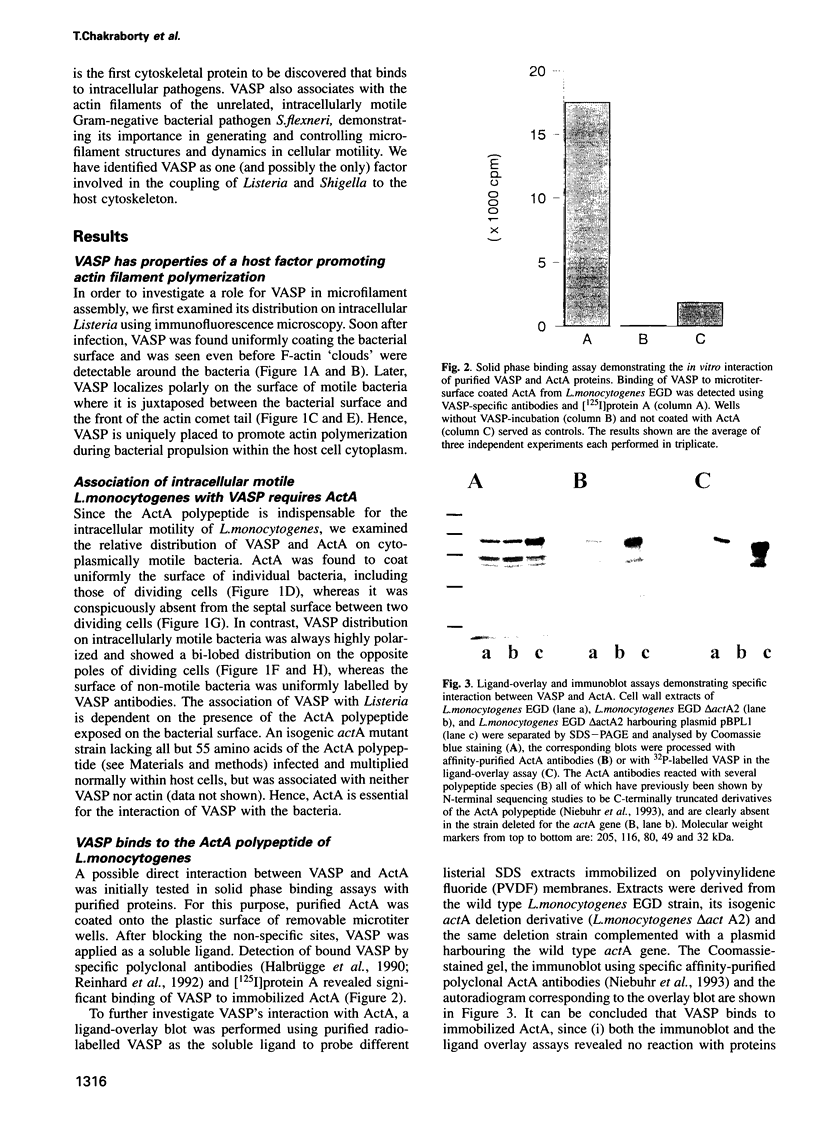




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernardini M. L., Mounier J., d'Hauteville H., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of icsA, a plasmid locus of Shigella flexneri that governs bacterial intra- and intercellular spread through interaction with F-actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3867–3871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundage R. A., Smith G. A., Camilli A., Theriot J. A., Portnoy D. A. Expression and phosphorylation of the Listeria monocytogenes ActA protein in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11890–11894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt E., Abel K., Krieger M., Palm D., Hoppe V., Hoppe J., Walter U. cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation sites of the focal adhesion vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) in vitro and in intact human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14509–14517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Leimeister-Wächter M., Domann E., Hartl M., Goebel W., Nichterlein T., Notermans S. Coordinate regulation of virulence genes in Listeria monocytogenes requires the product of the prfA gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):568–574. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.568-574.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Kocks C. The actin-based motility of the facultative intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Aug;13(3):395–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabiri G. A., Sanger J. M., Portnoy D. A., Southwick F. S. Listeria monocytogenes moves rapidly through the host-cell cytoplasm by inducing directional actin assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6068–6072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dold F. G., Sanger J. M., Sanger J. W. Intact alpha-actinin molecules are needed for both the assembly of actin into the tails and the locomotion of Listeria monocytogenes inside infected cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1994;28(2):97–107. doi: 10.1002/cm.970280202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domann E., Wehland J., Rohde M., Pistor S., Hartl M., Goebel W., Leimeister-Wächter M., Wuenscher M., Chakraborty T. A novel bacterial virulence gene in Listeria monocytogenes required for host cell microfilament interaction with homology to the proline-rich region of vinculin. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1981–1990. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05252.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigenthaler M., Nolte C., Halbrügge M., Walter U. Concentration and regulation of cyclic nucleotides, cyclic-nucleotide-dependent protein kinases and one of their major substrates in human platelets. Estimating the rate of cAMP-regulated and cGMP-regulated protein phosphorylation in intact cells. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Apr 15;205(2):471–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger B., Tokuyasu K. T., Dutton A. H., Singer S. J. Vinculin, an intracellular protein localized at specialized sites where microfilament bundles terminate at cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4127–4131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger J., Nolte C., Butt E., Sage S. O., Walter U. Role of cGMP and cGMP-dependent protein kinase in nitrovasodilator inhibition of agonist-evoked calcium elevation in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1031–1035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellin B. G., Broome C. V. Listeriosis. JAMA. 1989 Mar 3;261(9):1313–1320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. B., Bârzu O., Parsot C., Sansonetti P. J. Unipolar localization and ATPase activity of IcsA, a Shigella flexneri protein involved in intracellular movement. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(8):2189–2196. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.8.2189-2196.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouin E., Mengaud J., Cossart P. The virulence gene cluster of Listeria monocytogenes is also present in Listeria ivanovii, an animal pathogen, and Listeria seeligeri, a nonpathogenic species. Infect Immun. 1994 Aug;62(8):3550–3553. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.8.3550-3553.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. L., Killinger A. H. Listeria monocytogenes and listeric infections. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):309–382. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.309-382.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbrügge M., Friedrich C., Eigenthaler M., Schanzenbächer P., Walter U. Stoichiometric and reversible phosphorylation of a 46-kDa protein in human platelets in response to cGMP- and cAMP-elevating vasodilators. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3088–3093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbrügge M., Walter U. Purification of a vasodilator-regulated phosphoprotein from human platelets. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Oct 20;185(1):41–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L. Genetic basis of virulence in Shigella species. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):206–224. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.206-224.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzen R. A., Hayes S. F., Peacock M. G., Hackstadt T. Directional actin polymerization associated with spotted fever group Rickettsia infection of Vero cells. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):1926–1935. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.1926-1935.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzen R. A., Hayes S. F., Peacock M. G., Hackstadt T. Directional actin polymerization associated with spotted fever group Rickettsia infection of Vero cells. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):1926–1935. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.1926-1935.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadurugamuwa J. L., Rohde M., Wehland J., Timmis K. N. Intercellular spread of Shigella flexneri through a monolayer mediated by membranous protrusions and associated with reorganization of the cytoskeletal protein vinculin. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3463–3471. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3463-3471.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Cossart P. Directional actin assembly by Listeria monocytogenes at the site of polar surface expression of the actA gene product involving the actin-bundling protein plastin (fimbrin). Infect Agents Dis. 1993 Aug;2(4):207–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Gouin E., Tabouret M., Berche P., Ohayon H., Cossart P. L. monocytogenes-induced actin assembly requires the actA gene product, a surface protein. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):521–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90188-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocks C., Hellio R., Gounon P., Ohayon H., Cossart P. Polarized distribution of Listeria monocytogenes surface protein ActA at the site of directional actin assembly. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jul;105(Pt 3):699–710. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.3.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kärnell A., Sweiha H., Lindberg A. A. Auxotrophic live oral Shigella flexneri vaccine protects monkeys against challenge with S. flexneri of different serotypes. Vaccine. 1992;10(3):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lett M. C., Sasakawa C., Okada N., Sakai T., Makino S., Yamada M., Komatsu K., Yoshikawa M. virG, a plasmid-coded virulence gene of Shigella flexneri: identification of the virG protein and determination of the complete coding sequence. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):353–359. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.353-359.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Kurata T., Yoshikawa M. A genetic determinant required for continuous reinfection of adjacent cells on large plasmid in S. flexneri 2a. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90880-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niebuhr K., Chakraborty T., Rohde M., Gazlig T., Jansen B., Köllner P., Wehland J. Localization of the ActA polypeptide of Listeria monocytogenes in infected tissue culture cell lines: ActA is not associated with actin "comets". Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2793–2802. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2793-2802.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolte C., Eigenthaler M., Schanzenbächer P., Walter U. Endothelial cell-dependent phosphorylation of a platelet protein mediated by cAMP- and cGMP-elevating factors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14808–14812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa H., Nakamura A., Nakaya R. Cinemicrographic study of tissue cell cultures infected with Shigella flexneri. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1968 Aug;21(4):259–273. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.21.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S. F., Stewart G. S. High-efficiency transformation of Listeria monocytogenes by electroporation of penicillin-treated cells. Gene. 1990 Sep 28;94(1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90479-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pistor S., Chakraborty T., Niebuhr K., Domann E., Wehland J. The ActA protein of Listeria monocytogenes acts as a nucleator inducing reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):758–763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06318.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Chakraborty T., Goebel W., Cossart P. Molecular determinants of Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1263–1267. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1263-1267.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard M., Halbrügge M., Scheer U., Wiegand C., Jockusch B. M., Walter U. The 46/50 kDa phosphoprotein VASP purified from human platelets is a novel protein associated with actin filaments and focal contacts. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2063–2070. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. M., Sanger J. W., Southwick F. S. Host cell actin assembly is necessary and likely to provide the propulsive force for intracellular movement of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3609–3619. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3609-3619.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Mounier J., Prévost M. C., Mège R. M. Cadherin expression is required for the spread of Shigella flexneri between epithelial cells. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):829–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southwick F. S., Purich D. L. Arrest of Listeria movement in host cells by a bacterial ActA analogue: implications for actin-based motility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5168–5172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teysseire N., Chiche-Portiche C., Raoult D. Intracellular movements of Rickettsia conorii and R. typhi based on actin polymerization. Res Microbiol. 1992 Nov-Dec;143(9):821–829. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90069-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J. The nucleation-release model of actin filament dynamics in cell motility. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;2(8):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90298-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J. The three faces of profilin. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):835–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90527-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Mitchison T. J., Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. The rate of actin-based motility of intracellular Listeria monocytogenes equals the rate of actin polymerization. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):257–260. doi: 10.1038/357257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theriot J. A., Rosenblatt J., Portnoy D. A., Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Mitchison T. J. Involvement of profilin in the actin-based motility of L. monocytogenes in cells and in cell-free extracts. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):505–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Tilney M. S. The wily ways of a parasite: induction of actin assembly by Listeria. Trends Microbiol. 1993 Apr;1(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(93)90021-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trieu-Cuot P., Carlier C., Poyart-Salmeron C., Courvalin P. A pair of mobilizable shuttle vectors conferring resistance to spectinomycin for molecular cloning in Escherichia coli and in gram-positive bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4296–4296. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann R., Nieberding M., Walter U. Vasodilator-stimulated protein phosphorylation in platelets is mediated by cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinases. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 15;167(3):441–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]