Abstract
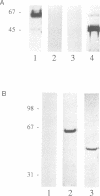
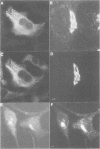
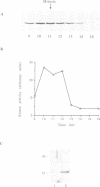
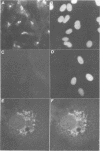
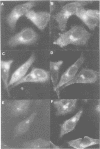
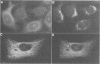
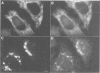
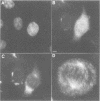
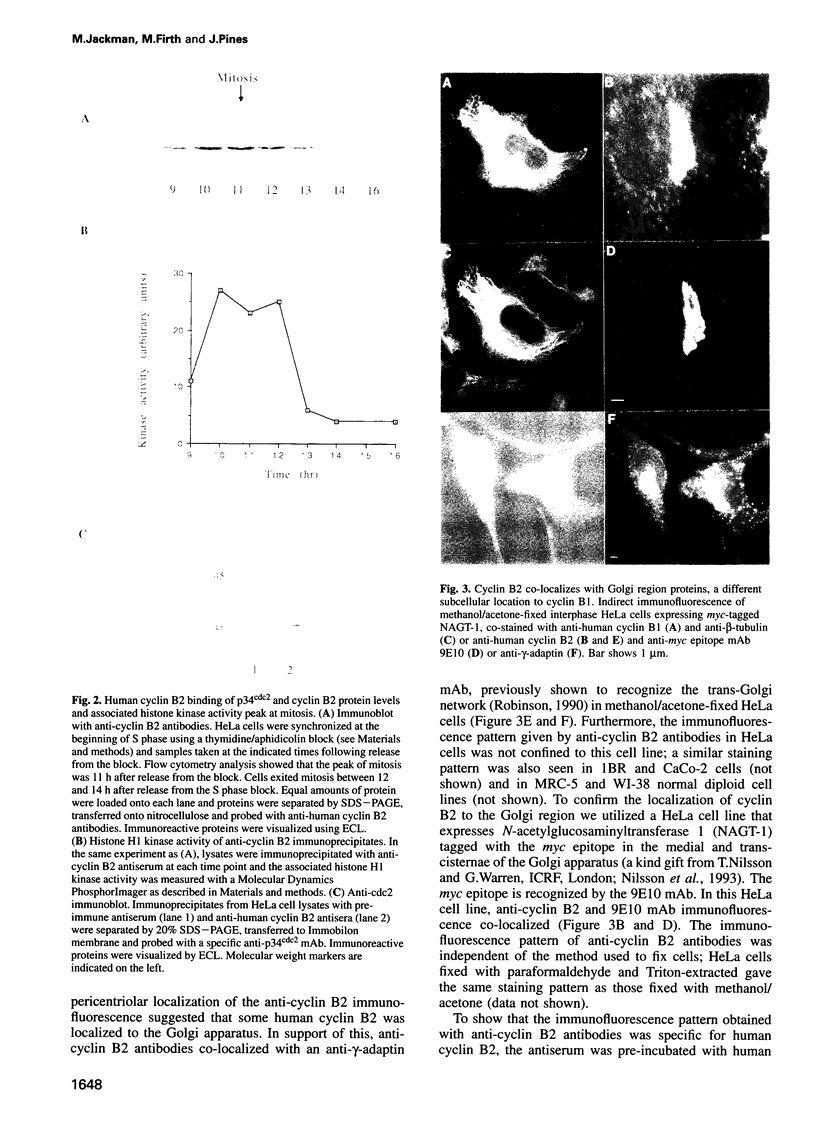
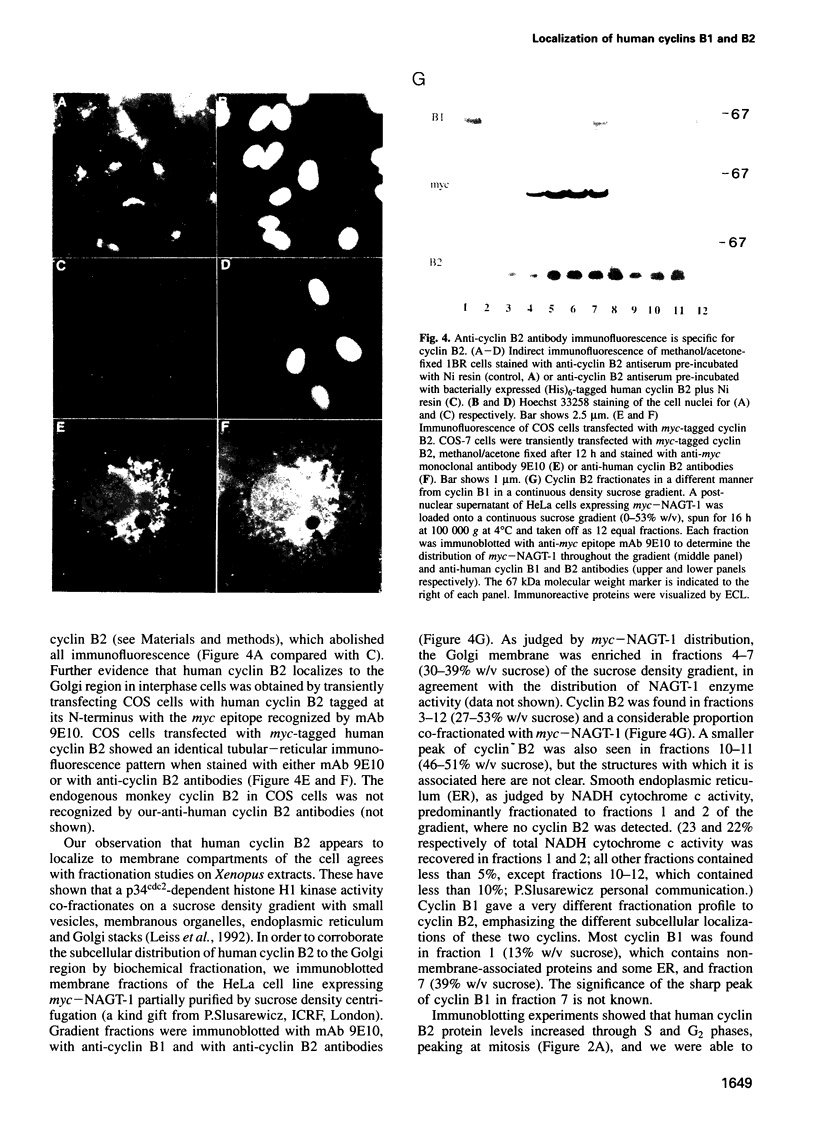
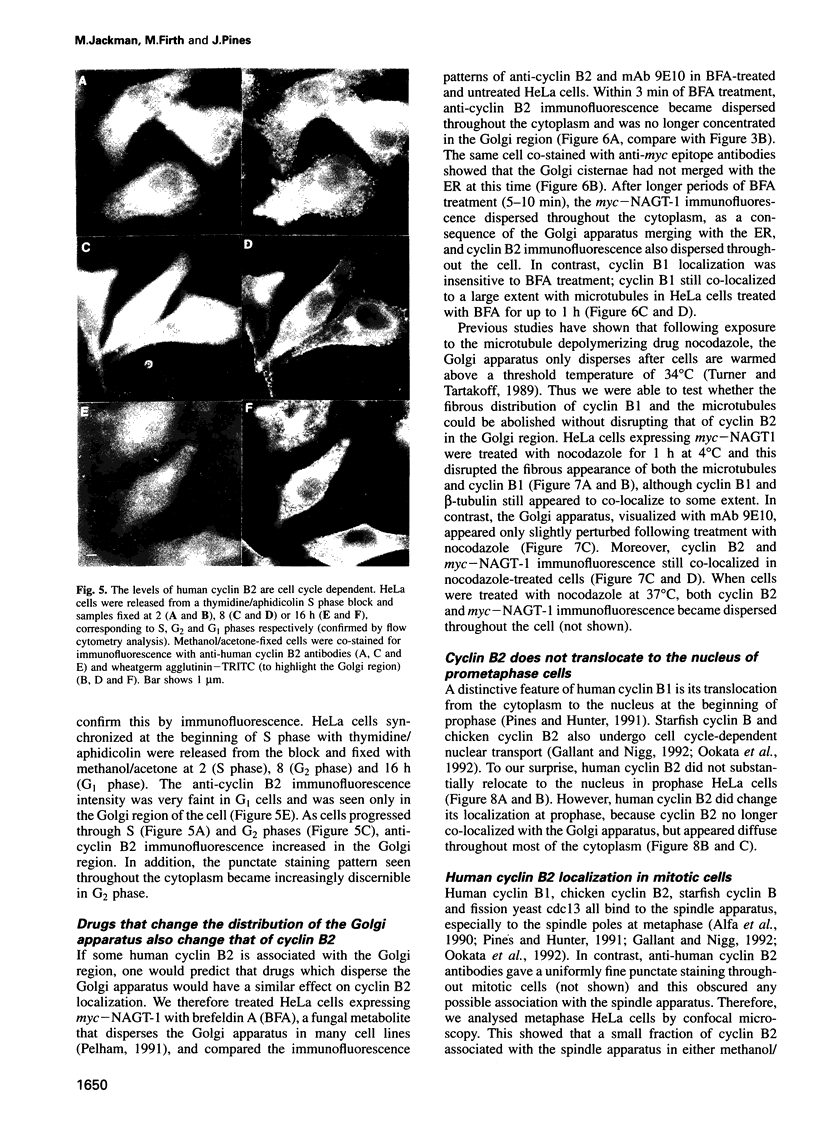
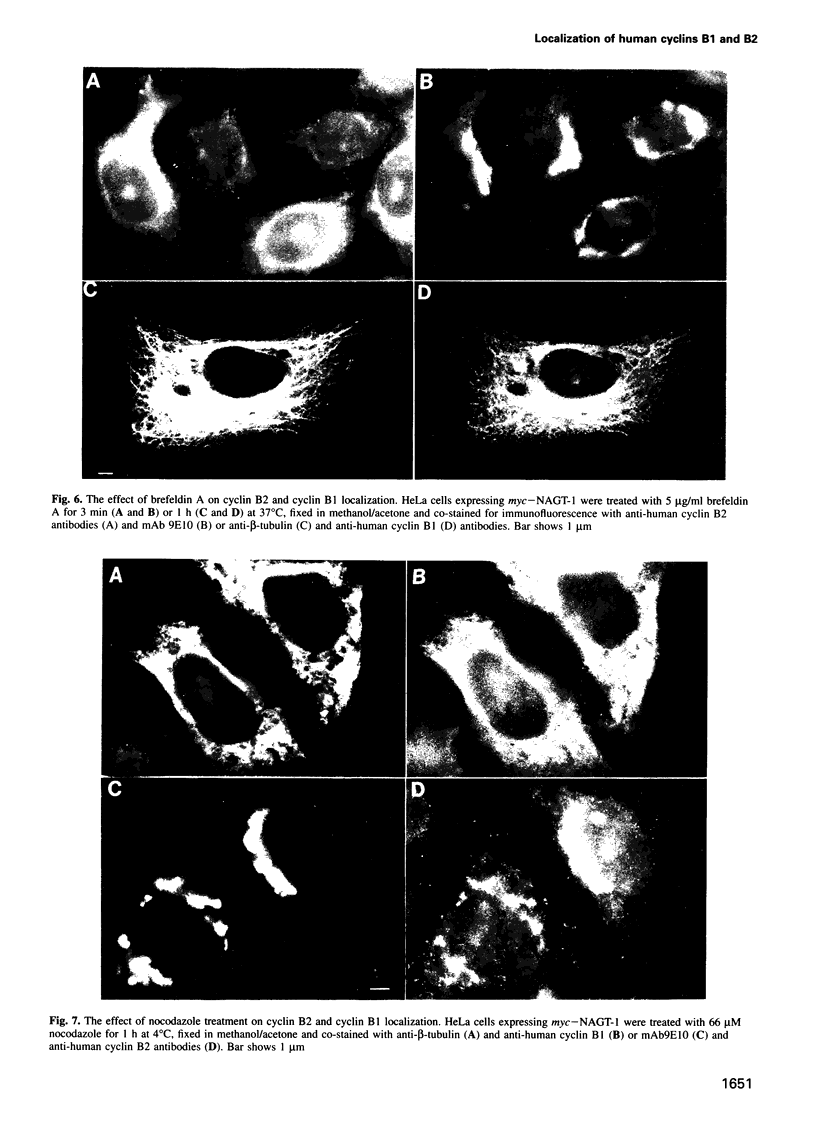
We have raised and characterized antibodies specific for human cyclin B2 and have compared the properties of cyclins B1 and B2 in human tissue culture cells. Cyclin B1 and B2 levels are very low in G1 phase, increase in S and G2 phases and peak at mitosis. Both B-type cyclins associate with p34cdc2; their associated kinase activities appear when cells enter mitosis and disappear as the cyclins are destroyed in anaphase. However, human cyclins B1 and B2 differ dramatically in their subcellular localization. Cyclin B1 co-localizes with microtubules, whereas cyclin B2 is primarily associated with the Golgi region. In contrast to cyclin B1, cyclin B2 does not relocate to the nucleus at prophase, but becomes uniformly distributed throughout the cell. The different subcellular locations of human cyclins B1 and B2 implicate them in the reorganization of different aspects of the cellular architecture at mitosis and indicate that different mitotic cyclin-cyclin-dependent kinase complexes may have distinct roles in the cell cycle.
Full text
PDF

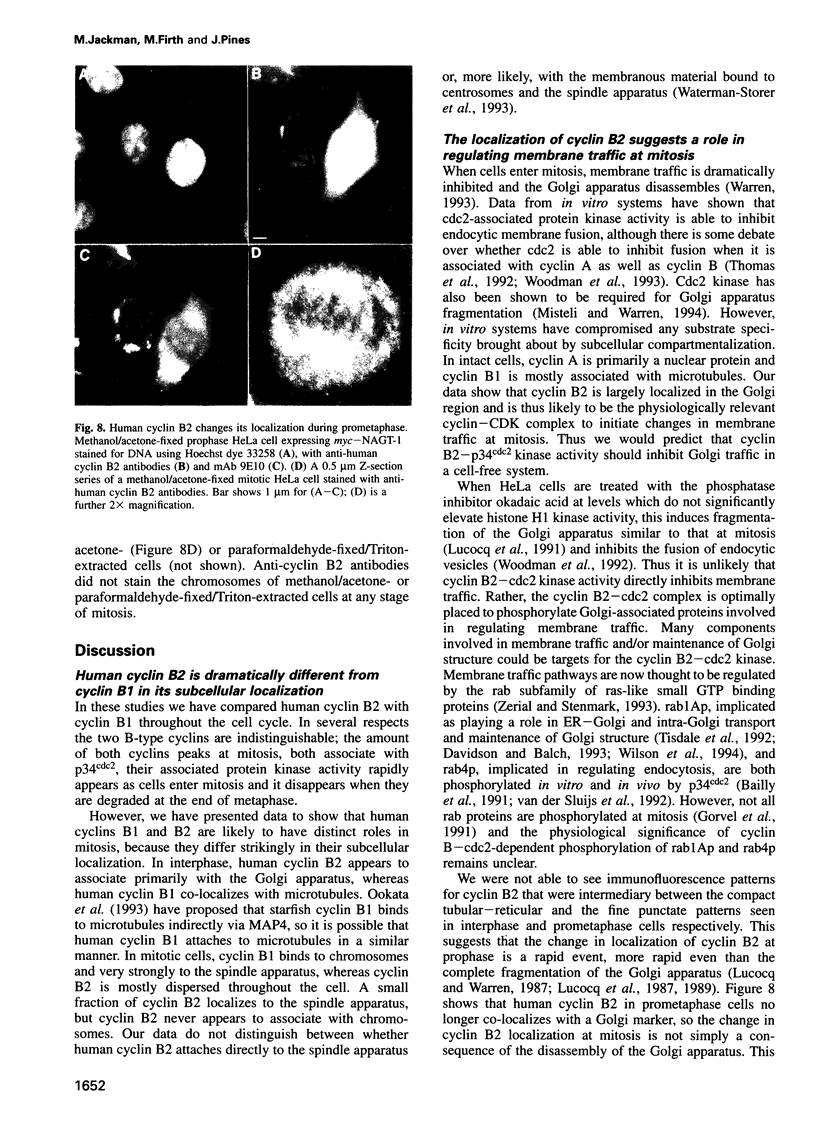


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfa C. E., Ducommun B., Beach D., Hyams J. S. Distinct nuclear and spindle pole body population of cyclin-cdc2 in fission yeast. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):680–682. doi: 10.1038/347680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly E., McCaffrey M., Touchot N., Zahraoui A., Goud B., Bornens M. Phosphorylation of two small GTP-binding proteins of the Rab family by p34cdc2. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):715–718. doi: 10.1038/350715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Dunphy W. G., Braell W. A., Rothman J. E. Reconstitution of the transport of protein between successive compartments of the Golgi measured by the coupled incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):405–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R. N., Alfa C. E., Hyams J. S., Beach D. H. The fission yeast cdc2/cdc13/suc1 protein kinase: regulation of catalytic activity and nuclear localization. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):485–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bueno A., Russell P. Two fission yeast B-type cyclins, cig2 and Cdc13, have different functions in mitosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2286–2297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou Y. H., Bischoff J. R., Beach D., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filament reorganization during mitosis is mediated by p34cdc2 phosphorylation of vimentin. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1063–1071. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90384-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T., Beach D. Interaction between the Cig1 and Cig2 B-type cyclins in the fission yeast cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):768–776. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., Balch W. E. Differential inhibition of multiple vesicular transport steps between the endoplasmic reticulum and trans Golgi network. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4216–4226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G. The decision to enter mitosis. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;4(6):202–207. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch I., Dahmann C., Surana U., Amon A., Nasmyth K., Goetsch L., Byers B., Futcher B. Characterization of four B-type cyclin genes of the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jul;3(7):805–818. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.7.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant P., Nigg E. A. Cyclin B2 undergoes cell cycle-dependent nuclear translocation and, when expressed as a non-destructible mutant, causes mitotic arrest in HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):213–224. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorvel J. P., Chavrier P., Zerial M., Gruenberg J. rab5 controls early endosome fusion in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90316-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandin N., Reed S. I. Differential function and expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae B-type cyclins in mitosis and meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2113–2125. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan I., Hayles J., Nurse P. Cloning and sequencing of the cyclin-related cdc13+ gene and a cytological study of its role in fission yeast mitosis. J Cell Sci. 1988 Dec;91(Pt 4):587–595. doi: 10.1242/jcs.91.4.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression: kinetics of accumulation and changes in the rate of synthesis and in the half-lives of individual histone mRNAs during the HeLa cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):539–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Cyclins and their partners: from a simple idea to complicated reality. Semin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;2(4):213–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Golsteyn R., Poon R., Stewart E., Gannon J., Minshull J., Smith R., Hunt T. Cyclins and their partners during Xenopus oocyte maturation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:437–447. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiss D., Félix M. A., Karsenti E. Association of cyclin-bound p34cdc2 with subcellular structures in xenopus eggs. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jun;102(Pt 2):285–297. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucocq J. M., Berger E. G., Warren G. Mitotic Golgi fragments in HeLa cells and their role in the reassembly pathway. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):463–474. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucocq J. M., Pryde J. G., Berger E. G., Warren G. A mitotic form of the Golgi apparatus in HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):865–874. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucocq J. M., Warren G. Fragmentation and partitioning of the Golgi apparatus during mitosis in HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3239–3246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02641.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucocq J., Warren G., Pryde J. Okadaic acid induces Golgi apparatus fragmentation and arrest of intracellular transport. J Cell Sci. 1991 Dec;100(Pt 4):753–759. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.4.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer L., Arion D., Golsteyn R., Pines J., Brizuela L., Hunt T., Beach D. Cyclin is a component of the sea urchin egg M-phase specific histone H1 kinase. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2275–2282. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Blow J. J., Hunt T. Translation of cyclin mRNA is necessary for extracts of activated xenopus eggs to enter mitosis. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):947–956. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90628-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Golsteyn R., Hill C. S., Hunt T. The A- and B-type cyclin associated cdc2 kinases in Xenopus turn on and off at different times in the cell cycle. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2865–2875. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misteli T., Warren G. COP-coated vesicles are involved in the mitotic fragmentation of Golgi stacks in a cell-free system. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):269–282. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A. Cellular substrates of p34(cdc2) and its companion cyclin-dependent kinases. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;3(9):296–301. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90011-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Pypaert M., Hoe M. H., Slusarewicz P., Berger E. G., Warren G. Overlapping distribution of two glycosyltransferases in the Golgi apparatus of HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):5–13. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ookata K., Hisanaga S., Okano T., Tachibana K., Kishimoto T. Relocation and distinct subcellular localization of p34cdc2-cyclin B complex at meiosis reinitiation in starfish oocytes. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1763–1772. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ookata K., Hisanaga S., Okumura E., Kishimoto T. Association of p34cdc2/cyclin B complex with microtubules in starfish oocytes. J Cell Sci. 1993 Aug;105(Pt 4):873–881. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.4.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Multiple targets for brefeldin A. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):449–451. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90517-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M., Heitlinger E., Häner M., Aebi U., Nigg E. A. Disassembly of in vitro formed lamin head-to-tail polymers by CDC2 kinase. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1535–1544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07673.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J. Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: take your partners. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jun;18(6):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90185-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclins A and B1 are differentially located in the cell and undergo cell cycle-dependent nuclear transport. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):1–17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. The differential localization of human cyclins A and B is due to a cytoplasmic retention signal in cyclin B. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3772–3781. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06688.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H., Lew D. J., Henze M., Sugimoto K., Reed S. I. Cyclin-B homologs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae function in S phase and in G2. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2021–2034. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. S. Cloning and expression of gamma-adaptin, a component of clathrin-coated vesicles associated with the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2319–2326. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwob E., Nasmyth K. CLB5 and CLB6, a new pair of B cyclins involved in DNA replication in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1160–1175. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L., Clarke P. R., Pagano M., Gruenberg J. Inhibition of membrane fusion in vitro via cyclin B but not cyclin A. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6183–6187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale E. J., Bourne J. R., Khosravi-Far R., Der C. J., Balch W. E. GTP-binding mutants of rab1 and rab2 are potent inhibitors of vesicular transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):749–761. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. R., Tartakoff A. M. The response of the Golgi complex to microtubule alterations: the roles of metabolic energy and membrane traffic in Golgi complex organization. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2081–2088. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verde F., Dogterom M., Stelzer E., Karsenti E., Leibler S. Control of microtubule dynamics and length by cyclin A- and cyclin B-dependent kinases in Xenopus egg extracts. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1097–1108. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. Membrane partitioning during cell division. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:323–348. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman-Storer C. M., Sanger J. W., Sanger J. M. Dynamics of organelles in the mitotic spindles of living cells: membrane and microtubule interactions. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;26(1):19–39. doi: 10.1002/cm.970260104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. S., Nuoffer C., Meinkoth J. L., McCaffery M., Feramisco J. R., Balch W. E., Farquhar M. G. A Rab1 mutant affecting guanine nucleotide exchange promotes disassembly of the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1994 May;125(3):557–571. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.3.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodman P. G., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., Warren G. In vitro fusion of endocytic vesicles is inhibited by cyclin A-cdc2 kinase. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 May;4(5):541–553. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.5.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodman P. G., Mundy D. I., Cohen P., Warren G. Cell-free fusion of endocytic vesicles is regulated by phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):331–338. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro S., Yamakita Y., Hosoya H., Matsumura F. Phosphorylation of non-muscle caldesmon by p34cdc2 kinase during mitosis. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):169–172. doi: 10.1038/349169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Stenmark H. Rab GTPases in vesicular transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;5(4):613–620. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90130-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Sluijs P., Hull M., Huber L. A., Mâle P., Goud B., Mellman I. Reversible phosphorylation--dephosphorylation determines the localization of rab4 during the cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4379–4389. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05538.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]