Abstract
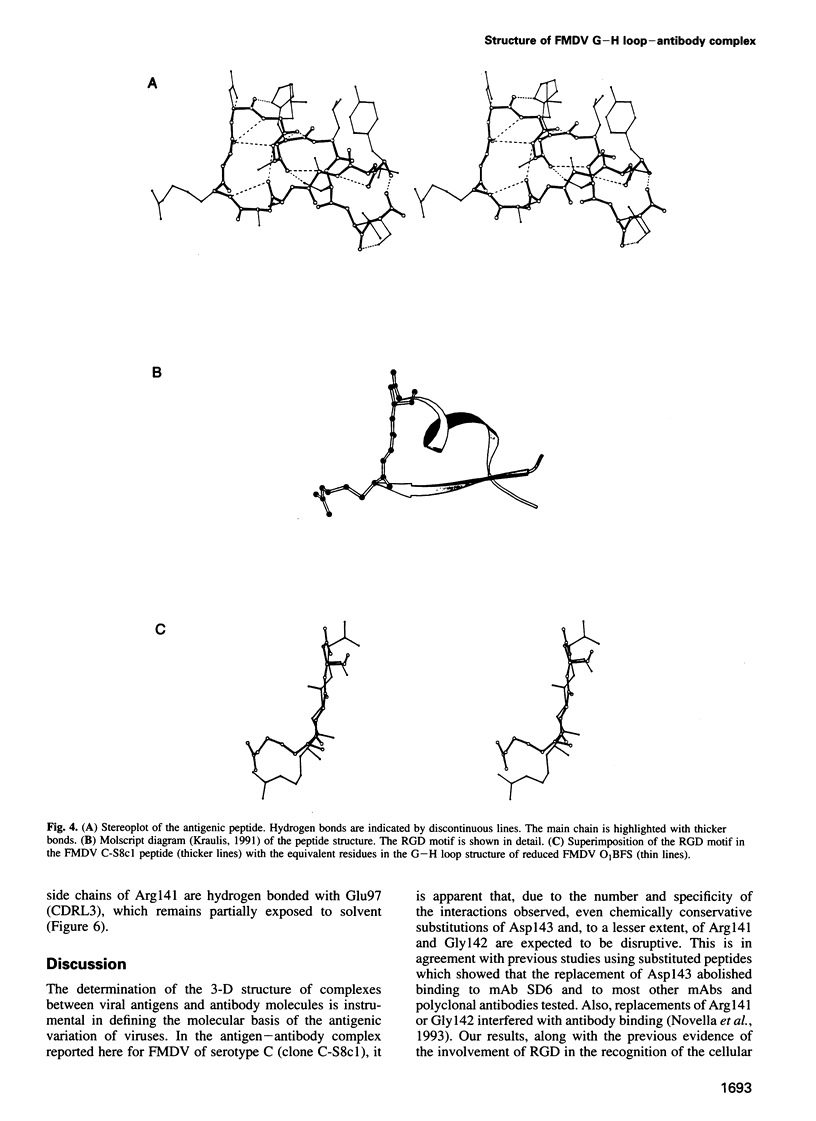
The crystal structure of a synthetic peptide representing the major antigenic loop of foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV), complexed with the Fab fragment of a neutralizing monoclonal antibody raised against the virus, has been determined at 2.8 A resolution. The peptide shows a high degree of internal structure with a nearly cyclic conformation. The conserved Arg-Gly-Asp motif, involved in the viral attachment of aphtoviruses to cells, participates directly in the interaction with several complementarity determining regions of the antibody molecule. The Arg-Gly-Asp triplet shows the same open turn conformation found in the reduced form of FMDV of another serotype and also in integrin binding proteins. The observed interactions provide a molecular interpretation of the amino acid replacements observed to occur in mutants resistant to neutralization by this antibody. The structure also suggests a number of restrictions to variation within the epitope which are imposed to keep the Arg-Gly-Asp motif in its functional conformation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acharya R., Fry E., Stuart D., Fox G., Rowlands D., Brown F. The three-dimensional structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus at 2.9 A resolution. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):709–716. doi: 10.1038/337709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach H. L. Foot-and-mouth disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:201–244. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt B., Becker Y. The effect of peptides containing the arginine-glycine-aspartic acid sequence on the adsorption of foot-and-mouth disease virus to tissue culture cells. Virus Genes. 1990 Jun;4(1):73–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00308567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt B., Morgan D. O., Robertson B. H., Timpone C. A. Epitopes on foot-and-mouth disease virus outer capsid protein VP1 involved in neutralization and cell attachment. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):298–305. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.298-305.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittle J. L., Houghten R. A., Alexander H., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Protection against foot-and-mouth disease by immunization with a chemically synthesized peptide predicted from the viral nucleotide sequence. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):30–33. doi: 10.1038/298030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrego B., Novella I. S., Giralt E., Andreu D., Domingo E. Distinct repertoire of antigenic variants of foot-and-mouth disease virus in the presence or absence of immune selection. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6071–6079. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6071-6079.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F. New approaches to vaccination against foot-and-mouth disease. Vaccine. 1992;10(14):1022–1026. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90111-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreño C., Roig X., Cairo J., Camarero J., Mateu M. G., Domingo E., Giralt E., Andreu D. Studies on antigenic variability of C strains of foot-and-mouth disease virus by means of synthetic peptides and monoclonal antibodies. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1992 Jan;39(1):41–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1992.tb01554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo C., Plana J., Mascarella R., Bergadá J., Sobrino F. Genetic and phenotypic variability during replication of foot-and-mouth disease virus in swine. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):890–892. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90162-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case D. A., Karplus M. Dynamics of ligand binding to heme proteins. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):343–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90265-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke B. E., Newton S. E., Carroll A. R., Francis M. J., Appleyard G., Syred A. D., Highfield P. E., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Improved immunogenicity of a peptide epitope after fusion to hepatitis B core protein. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):381–384. doi: 10.1038/330381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton S. R., Nelsen B., Kirkegaard K. Temperature-sensitive poliovirus mutant fails to cleave VP0 and accumulates provirions. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4067–4075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4067-4075.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R., Padlan E. A., Sheriff S. Antibody-antigen complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:439–473. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMarchi R., Brooke G., Gale C., Cracknell V., Doel T., Mowat N. Protection of cattle against foot-and-mouth disease by a synthetic peptide. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):639–641. doi: 10.1126/science.3008333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diez J., Mateu M. G., Domingo E. Selection of antigenic variants of foot-and-mouth disease virus in the absence of antibodies, as revealed by an in situ assay. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3281–3289. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo E., Díez J., Martínez M. A., Hernández J., Holguín A., Borrego B., Mateu M. G. New observations on antigenic diversification of RNA viruses. Antigenic variation is not dependent on immune selection. J Gen Virol. 1993 Oct;74(Pt 10):2039–2045. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-10-2039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo E., Escarmis C., Martinez M. A., Martinez-Salas E., Mateu M. G. Foot-and-mouth disease virus populations are quasispecies. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;176:33–47. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77011-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G., Parry N. R., Barnett P. V., McGinn B., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. The cell attachment site on foot-and-mouth disease virus includes the amino acid sequence RGD (arginine-glycine-aspartic acid). J Gen Virol. 1989 Mar;70(Pt 3):625–637. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-3-625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebauer F., de la Torre J. C., Gomes I., Mateu M. G., Barahona H., Tiraboschi B., Bergmann I., de Mello P. A., Domingo E. Rapid selection of genetic and antigenic variants of foot-and-mouth disease virus during persistence in cattle. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2041–2049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2041-2049.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiara J. B., Stura E. A., Stanfield R. L., Profy A. T., Wilson I. A. Crystal structure of the principal neutralization site of HIV-1. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):82–85. doi: 10.1126/science.7511253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández J., Martínez M. A., Rocha E., Domingo E., Mateu M. G. Generation of a subtype-specific neutralization epitope in foot-and-mouth disease virus of a different subtype. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jan;73(Pt 1):213–216. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-1-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., De La Torre J. C., Steinhauer D. A. RNA virus populations as quasispecies. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;176:1–20. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77011-1_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krezel A. M., Wagner G., Seymour-Ulmer J., Lazarus R. A. Structure of the RGD protein decorsin: conserved motif and distinct function in leech proteins that affect blood clotting. Science. 1994 Jun 24;264(5167):1944–1947. doi: 10.1126/science.8009227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus R. A., McDowell R. S. Structural and functional aspects of RGD-containing protein antagonists of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1993 Aug;4(4):438–445. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(93)90009-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea S., Hernández J., Blakemore W., Brocchi E., Curry S., Domingo E., Fry E., Abu-Ghazaleh R., King A., Newman J. The structure and antigenicity of a type C foot-and-mouth disease virus. Structure. 1994 Feb 15;2(2):123–139. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy D. J., Hendrickson W. A., Aukhil I., Erickson H. P. Structure of a fibronectin type III domain from tenascin phased by MAD analysis of the selenomethionyl protein. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):987–991. doi: 10.1126/science.1279805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan D., Abu-Ghazaleh R., Blakemore W., Curry S., Jackson T., King A., Lea S., Lewis R., Newman J., Parry N. Structure of a major immunogenic site on foot-and-mouth disease virus. Nature. 1993 Apr 8;362(6420):566–568. doi: 10.1038/362566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez M. A., Carrillo C., González-Candelas F., Moya A., Domingo E., Sobrino F. Fitness alteration of foot-and-mouth disease virus mutants: measurement of adaptability of viral quasispecies. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3954–3957. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3954-3957.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez M. A., Hernández J., Piccone M. E., Palma E. L., Domingo E., Knowles N., Mateu M. G. Two mechanisms of antigenic diversification of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90439-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. W., Rieder E., Baxt B. RGD sequence of foot-and-mouth disease virus is essential for infecting cells via the natural receptor but can be bypassed by an antibody-dependent enhancement pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mateu M. G., Andreu D., Carreño C., Roig X., Cairó J. J., Camarero J. A., Giralt E., Domingo E. Non-additive effects of multiple amino acid substitutions on antigen-antibody recognition. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jun;22(6):1385–1389. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mateu M. G., Hernández J., Martínez M. A., Feigelstock D., Lea S., Pérez J. J., Giralt E., Stuart D., Palma E. L., Domingo E. Antigenic heterogeneity of a foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype in the field is mediated by very limited sequence variation at several antigenic sites. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1407–1417. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1407-1417.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mateu M. G., Martínez M. A., Capucci L., Andreu D., Giralt E., Sobrino F., Brocchi E., Domingo E. A single amino acid substitution affects multiple overlapping epitopes in the major antigenic site of foot-and-mouth disease virus of serotype C. J Gen Virol. 1990 Mar;71(Pt 3):629–637. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-3-629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mateu M. G., Martínez M. A., Rocha E., Andreu D., Parejo J., Giralt E., Sobrino F., Domingo E. Implications of a quasispecies genome structure: effect of frequent, naturally occurring amino acid substitutions on the antigenicity of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5883–5887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mateu M. G., Rocha E., Vicente O., Vayreda F., Navalpotro C., Andreu D., Pedroso E., Giralt E., Enjuanes L., Domingo E. Reactivity with monoclonal antibodies of viruses from an episode of foot-and-mouth disease. Virus Res. 1987 Sep;8(3):261–274. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novella I. S., Borrego B., Mateu M. G., Domingo E., Giralt E., Andreu D. Use of substituted and tandem-repeated peptides to probe the relevance of the highly conserved RGD tripeptide in the immune response against foot-and-mouth disease virus. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 20;330(3):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80883-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson N. H., Kolatkar P. R., Oliveira M. A., Cheng R. H., Greve J. M., McClelland A., Baker T. S., Rossmann M. G. Structure of a human rhinovirus complexed with its receptor molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):507–511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry N., Fox G., Rowlands D., Brown F., Fry E., Acharya R., Logan D., Stuart D. Structural and serological evidence for a novel mechanism of antigenic variation in foot-and-mouth disease virus. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):569–572. doi: 10.1038/347569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff E., Mussgay M., Böhm H. O., Schulz G. E., Schaller H. Antibodies against a preselected peptide recognize and neutralize foot and mouth disease virus. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):869–874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01262.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C., Page G., Zhou H., Chow M. Identification of residues in VP2 that contribute to poliovirus neutralization antigenic site 3B. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90856-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rini J. M., Schulze-Gahmen U., Wilson I. A. Structural evidence for induced fit as a mechanism for antibody-antigen recognition. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):959–965. doi: 10.1126/science.1546293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G. The canyon hypothesis. Hiding the host cell receptor attachment site on a viral surface from immune surveillance. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14587–14590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. J., Clarke B. E., Carroll A. R., Brown F., Nicholson B. H., Bittle J. L., Houghten R. A., Lerner R. A. Chemical basis of antigenic variation in foot-and-mouth disease virus. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):694–697. doi: 10.1038/306694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Fibronectin and its receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:375–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Olson N. H., Cheng R. H., Liu H., Chase E. S., Lee W. M., Leippe D. M., Mosser A. G., Rueckert R. R., Baker T. S. Structure of human rhinovirus complexed with Fab fragments from a neutralizing antibody. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1148–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1148-1158.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhauer D. A., Holland J. J. Rapid evolution of RNA viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:409–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohmaier K., Franze R., Adam K. H. Location and characterization of the antigenic portion of the FMDV immunizing protein. J Gen Virol. 1982 Apr;59(Pt 2):295–306. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormo J., Blaas D., Parry N. R., Rowlands D., Stuart D., Fita I. Crystal structure of a human rhinovirus neutralizing antibody complexed with a peptide derived from viral capsid protein VP2. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2247–2256. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06506.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulip W. R., Varghese J. N., Webster R. G., Laver W. G., Colman P. M. Crystal structures of two mutant neuraminidase-antibody complexes with amino acid substitutions in the interface. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 5;227(1):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90688-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdaguer N., Mateu M. G., Bravo J., Tormo J., Giralt E., Andreu D., Domingo E., Fita I. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of a monoclonal antibody Fab fragment against foot-and-mouth disease virus and of its complex with the main antigenic site peptide. Proteins. 1994 Feb;18(2):201–203. doi: 10.1002/prot.340180212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistow G., Turnell B., Summers L., Slingsby C., Moss D., Miller L., Lindley P., Blundell T. X-ray analysis of the eye lens protein gamma-II crystallin at 1.9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 15;170(1):175–202. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]