Abstract
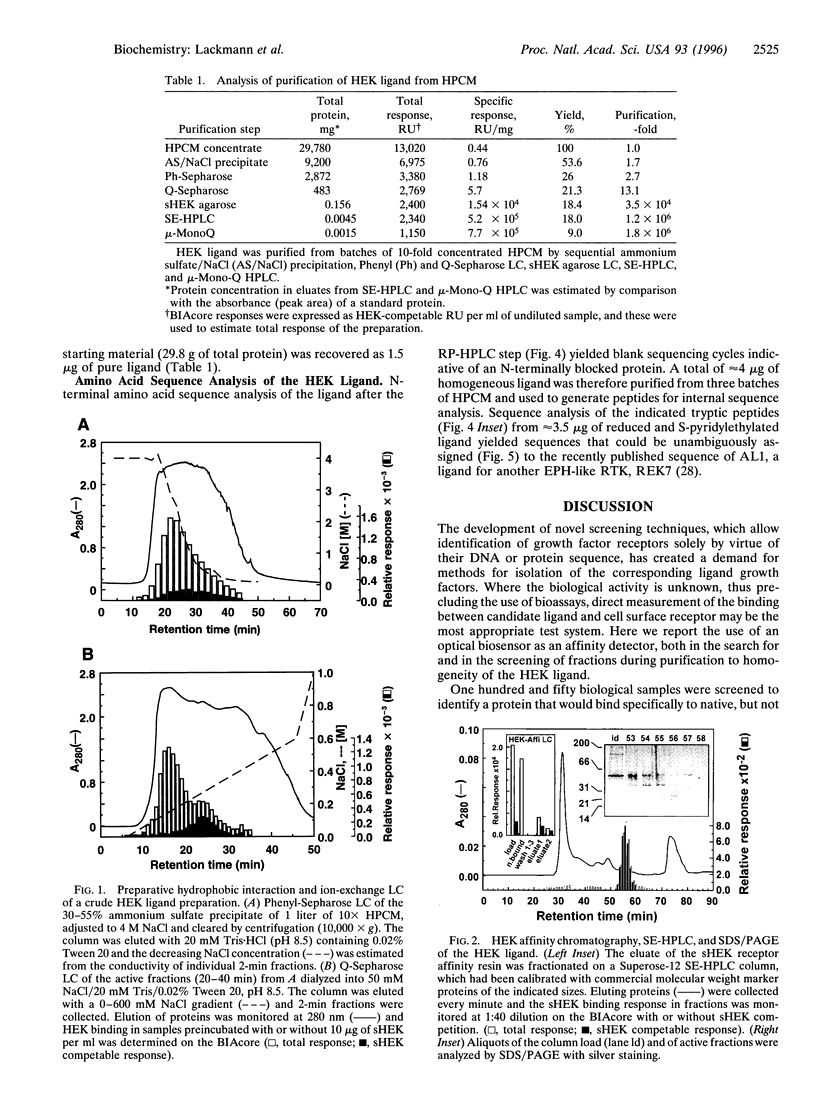
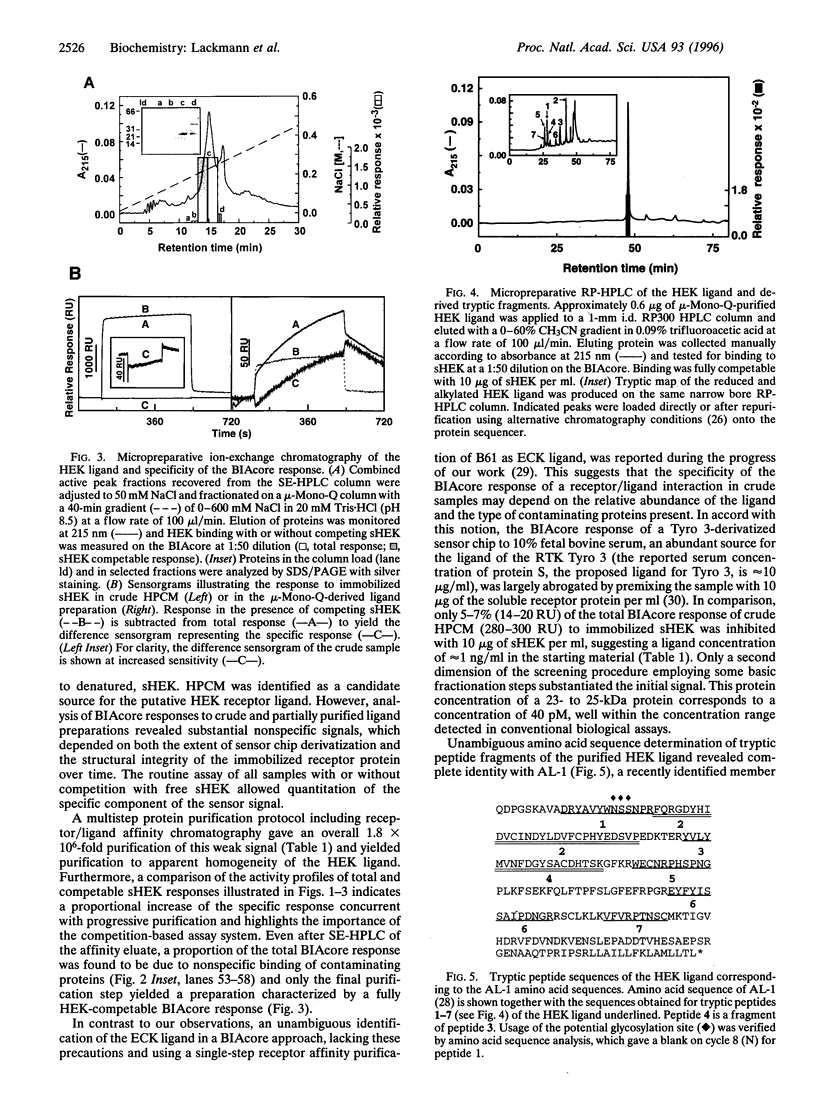
Advances in screening technologies allowing the identification of growth factor receptors solely by virtue of DNA or protein sequence comparison call for novel methods to isolate corresponding ligand growth factors. The EPH-like receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) HEK (human EPH-like kinase) was identified previously as a membrane antigen on the LK63 human pre-B-cell line and overexpression in leukemic specimens and cell lines suggested a role in oncogenesis. We developed a biosensor-based approach using the immobilized HEK receptor exodomain to detect and monitor purification of the HEK ligand. A protein purification protocol, which included HEK affinity chromatography, achieved a 1.8 X 10(6)-fold purification of an approximately 23-kDa protein from human placental conditioned medium. Analysis of specific sHEK (soluble extracellular domain of HEK) ligand interactions in the first and final purification steps suggested a ligand concentration of 40 pM in the source material and a Kd of 2-3 nM. Since the purified ligand was N-terminally blocked, we generated tryptic peptides and N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis of 7 tryptic fragments of the S-pyridylethylated protein unequivocally matched the sequence for AL-1, a recently reported ligand for the related EPH-like RTK REK7 (Winslow, J.W., Moran, P., Valverde, J., Shih, A., Yuan, J.Q., Wong, S.C., Tsai, S.P., Goddard, A., Henzel, W.J., Hefti, F., Beck, K.D., & Caras, I.W. (1995) Neuron 14, 973-981). Our findings demonstrate the application of biosensor technology in ligand purification and show that AL-1, as has been found for other ligands of the EPH-like RTK family, binds more than one receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres A. C., Reid H. H., Zürcher G., Blaschke R. J., Albrecht D., Ziemiecki A. Expression of two novel eph-related receptor protein tyrosine kinases in mammary gland development and carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 1994 May;9(5):1461–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartley T. D., Hunt R. W., Welcher A. A., Boyle W. J., Parker V. P., Lindberg R. A., Lu H. S., Colombero A. M., Elliott R. L., Guthrie B. A. B61 is a ligand for the ECK receptor protein-tyrosine kinase. Nature. 1994 Apr 7;368(6471):558–560. doi: 10.1038/368558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett B. D., Wang Z., Kuang W. J., Wang A., Groopman J. E., Goeddel D. V., Scadden D. T. Cloning and characterization of HTK, a novel transmembrane tyrosine kinase of the EPH subfamily. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14211–14218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. W., Ward L. D., Wicks I. P., Simpson R. J., Salvaris E., Wilks A., Welch K., Loudovaris M., Rockman S., Busmanis I. Isolation and characterization of a novel receptor-type protein tyrosine kinase (hek) from a human pre-B cell line. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3262–3267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhme B., Holtrich U., Wolf G., Luzius H., Grzeschik K. H., Strebhardt K., Rübsamen-Waigmann H. PCR mediated detection of a new human receptor-tyrosine-kinase, HEK 2. Oncogene. 1993 Oct;8(10):2857–2862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J., Watt V. M. eek and erk, new members of the eph subclass of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases. Oncogene. 1991 Jun;6(6):1057–1061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. J., Flanagan J. G. Identification and cloning of ELF-1, a developmentally expressed ligand for the Mek4 and Sek receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):157–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90408-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Gale N. W., Aldrich T. H., Maisonpierre P. C., Lhotak V., Pawson T., Goldfarb M., Yancopoulos G. D. Ligands for EPH-related receptor tyrosine kinases that require membrane attachment or clustering for activity. Science. 1994 Nov 4;266(5186):816–819. doi: 10.1126/science.7973638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easty D. J., Guthrie B. A., Maung K., Farr C. J., Lindberg R. A., Toso R. J., Herlyn M., Bennett D. C. Protein B61 as a new growth factor: expression of B61 and up-regulation of its receptor epithelial cell kinase during melanoma progression. Cancer Res. 1995 Jun 15;55(12):2528–2532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganju P., Shigemoto K., Brennan J., Entwistle A., Reith A. D. The Eck receptor tyrosine kinase is implicated in pattern formation during gastrulation, hindbrain segmentation and limb development. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1613–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi-Hebenstreit P., Nieto M. A., Frain M., Mattéi M. G., Chestier A., Wilkinson D. G., Charnay P. An Eph-related receptor protein tyrosine kinase gene segmentally expressed in the developing mouse hindbrain. Oncogene. 1992 Dec;7(12):2499–2506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkemeyer M., Marengere L. E., McGlade J., Olivier J. P., Conlon R. A., Holmyard D. P., Letwin K., Pawson T. Immunolocalization of the Nuk receptor tyrosine kinase suggests roles in segmental patterning of the brain and axonogenesis. Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1001–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Maru Y., Hagiwara K., Nishida J., Takaku F. A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the eph gene. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1717–1720. doi: 10.1126/science.2825356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. L., Karavanova I., Maéno M., Ong R. C., Kung H. F., Daar I. O. Expression of an amphibian homolog of the Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinases is developmentally regulated. Oncogene. 1995 Mar 16;10(6):1111–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa E., Takai S., Tanaka M., Iwase T., Suzuki M., Xiang Y. Y., Naito Y., Yamada K., Sugimura H., Kino I. Overexpression of ERK, an EPH family receptor protein tyrosine kinase, in various human tumors. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 15;54(14):3645–3650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlosky C. J., Maraskovsky E., McGrew J. T., VandenBos T., Teepe M., Lyman S. D., Srinivasan S., Fletcher F. A., Gayle R. B., 3rd, Cerretti D. P. Ligands for the receptor tyrosine kinases hek and elk: isolation of cDNAs encoding a family of proteins. Oncogene. 1995 Jan 19;10(2):299–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letwin K., Yee S. P., Pawson T. Novel protein-tyrosine kinase cDNAs related to fps/fes and eph cloned using anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. Oncogene. 1988 Dec;3(6):621–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. A., Hunter T. cDNA cloning and characterization of eck, an epithelial cell receptor protein-tyrosine kinase in the eph/elk family of protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6316–6324. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonpierre P. C., Barrezueta N. X., Yancopoulos G. D. Ehk-1 and Ehk-2: two novel members of the Eph receptor-like tyrosine kinase family with distinctive structures and neuronal expression. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3277–3288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nagata S. pEF-BOS, a powerful mammalian expression vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5322–5322. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nice E., Lackmann M., Smyth F., Fabri L., Burgess A. W. Synergies between micropreparative high-performance liquid chromatography and an instrumental optical biosensor. J Chromatogr A. 1994 Feb 4;660(1-2):169–185. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(94)85110-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey A., Shao H., Marks R. M., Polverini P. J., Dixit V. M. Role of B61, the ligand for the Eck receptor tyrosine kinase, in TNF-alpha-induced angiogenesis. Science. 1995 Apr 28;268(5210):567–569. doi: 10.1126/science.7536959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquale E. B. Identification of chicken embryo kinase 5, a developmentally regulated receptor-type tyrosine kinase of the Eph family. Cell Regul. 1991 Jul;2(7):523–534. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.7.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G. E., Ji H., Eddes J. S., Moritz R. L., Simpson R. J. Nonreducing two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis of human colonic proteins. Electrophoresis. 1995 Jul;16(7):1120–1130. doi: 10.1002/elps.11501601189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajjadi F. G., Pasquale E. B. Five novel avian Eph-related tyrosine kinases are differentially expressed. Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):1807–1813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajjadi F. G., Pasquale E. B., Subramani S. Identification of a new eph-related receptor tyrosine kinase gene from mouse and chicken that is developmentally regulated and encodes at least two forms of the receptor. New Biol. 1991 Aug;3(8):769–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. J., Moritz R. L., Rubira M. R., Van Snick J. Murine hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor. Complete amino-acid sequence and relation to human interleukin-6. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 1;176(1):187–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt T. N., Conn G., Gore M., Lai C., Bruno J., Radziejewski C., Mattsson K., Fisher J., Gies D. R., Jones P. F. The anticoagulation factor protein S and its relative, Gas6, are ligands for the Tyro 3/Axl family of receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1995 Feb 24;80(4):661–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90520-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward L. D., Shi P. T., Simpson R. J. Binding of anti-human-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibodies to synthetic peptides of human interleukin-6 studied using surface plasmon resonance. Biochem Int. 1992 Mar;26(3):559–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicks I. P., Wilkinson D., Salvaris E., Boyd A. W. Molecular cloning of HEK, the gene encoding a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed by human lymphoid tumor cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1611–1615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winning R. S., Sargent T. D. Pagliaccio, a member of the Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinase genes, has localized expression in a subset of neural crest and neural tissues in Xenopus laevis embryos. Mech Dev. 1994 Jun;46(3):219–229. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(94)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow J. W., Moran P., Valverde J., Shih A., Yuan J. Q., Wong S. C., Tsai S. P., Goddard A., Henzel W. J., Hefti F. Cloning of AL-1, a ligand for an Eph-related tyrosine kinase receptor involved in axon bundle formation. Neuron. 1995 May;14(5):973–981. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90335-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Q., Holder N., Patient R., Wilson S. W. Spatially regulated expression of three receptor tyrosine kinase genes during gastrulation in the zebrafish. Development. 1994 Feb;120(2):287–299. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou R., Copeland T. D., Kromer L. F., Schulz N. T. Isolation and characterization of Bsk, a growth factor receptor-like tyrosine kinase associated with the limbic system. J Neurosci Res. 1994 Jan;37(1):129–143. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490370117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




