Abstract
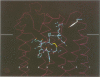
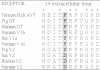
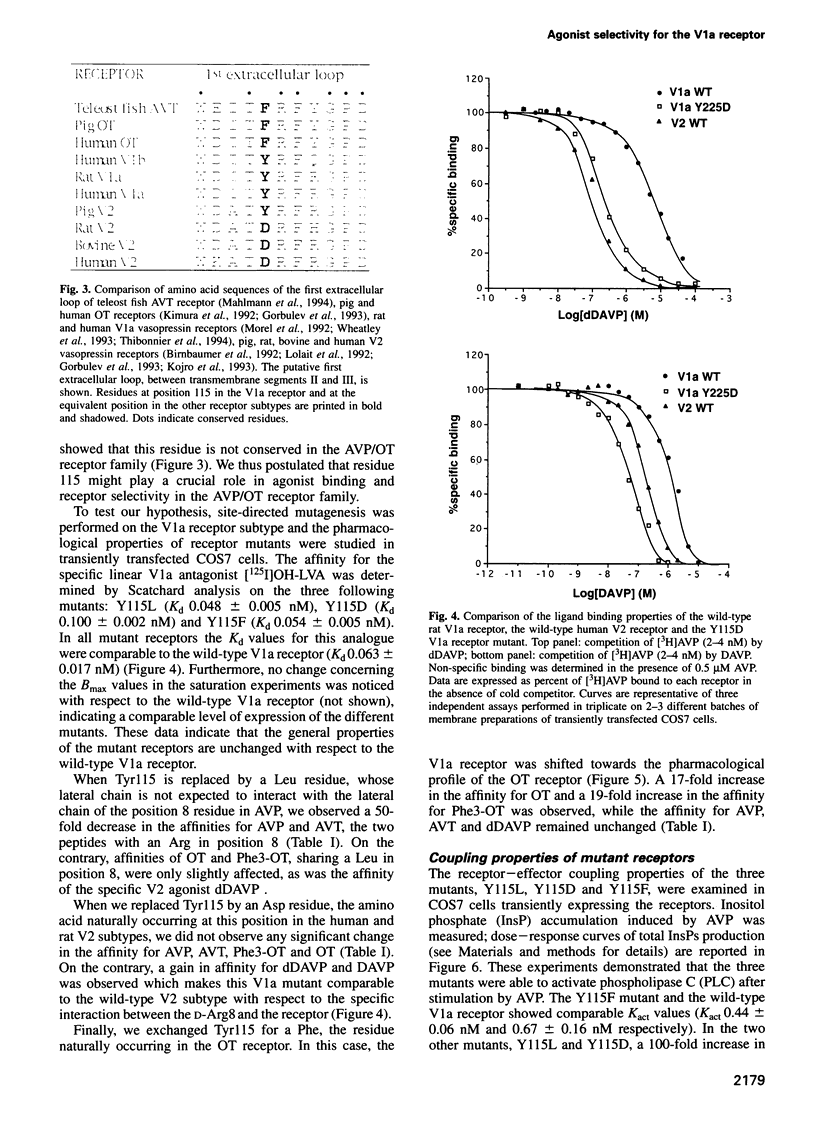
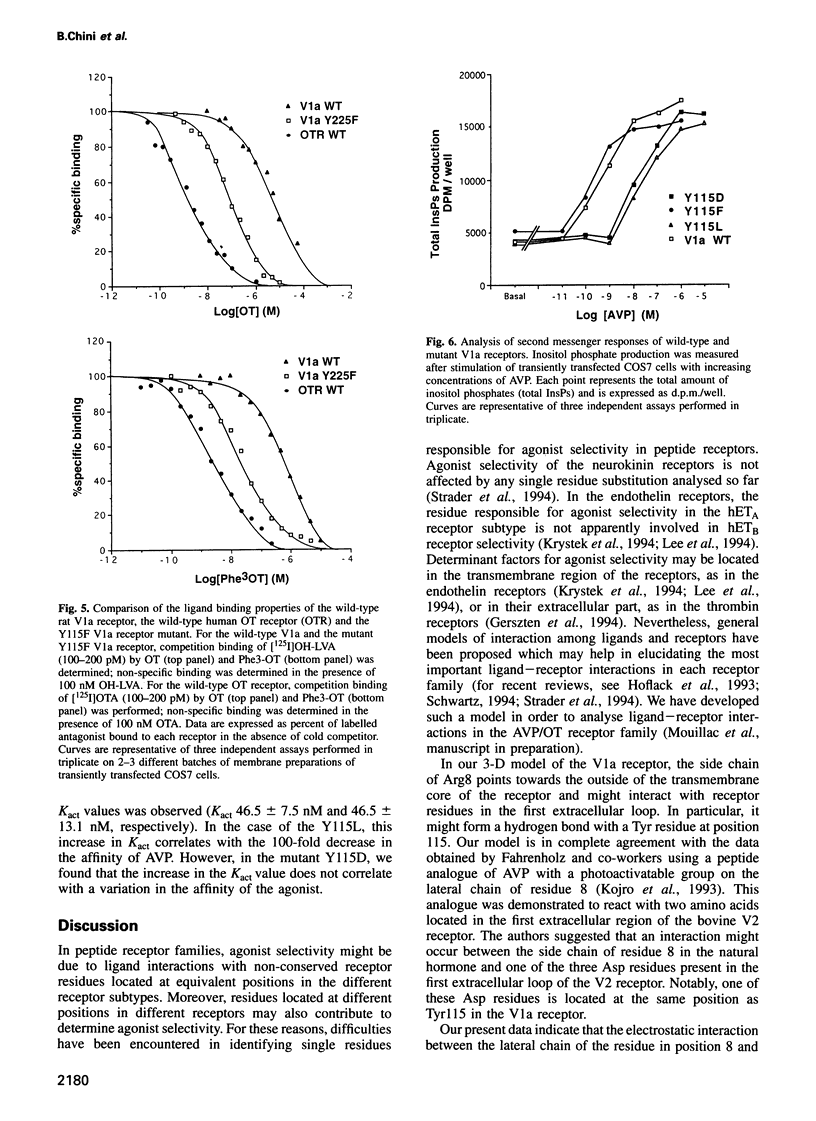
Using a three-dimensional model of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR), we have previously succeeded in docking the neurohypophysial hormone arginine-vasopressin (AVP) into the V1a receptor. According to this model, the hormone is completely embedded in the transmembrane part of the receptor. Only the side chain of the Arg residue at position 8 projects outside the transmembrane core of the receptor and possibly interacts with a Tyr residue located in the first extracellular loop at position 115. Residue 8 varies in the two natural neurohypophysial hormones, AVP and oxytocin (OT); similarly, different residues are present at position 115 in the different members of the AVP/OT receptor family. Here we show that Arg8 is crucial for high affinity binding of AVP to the rat V1a receptor. Moreover, when Tyr115 is replaced by an Asp and a Phe, the amino acids naturally occurring in the V2 and in the OT receptor subtypes, the agonist selectivity of the V1a receptor switches accordingly. Our results indicate that the interaction between peptide residue 8 and the receptor residue at position 115 is not only crucial for agonist high affinity binding but also for receptor selectivity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acher R. Neurohypophysial peptide systems: processing machinery, hydroosmotic regulation, adaptation and evolution. Regul Pept. 1993 Apr 29;45(1-2):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90174-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichet D. G., Razi M., Lonergan M., Arthus M. F., Papukna V., Kortas C., Barjon J. N. Hemodynamic and coagulation responses to 1-desamino[8-D-arginine] vasopressin in patients with congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. N Engl J Med. 1988 Apr 7;318(14):881–887. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198804073181403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer M., Seibold A., Gilbert S., Ishido M., Barberis C., Antaramian A., Brabet P., Rosenthal W. Molecular cloning of the receptor for human antidiuretic hormone. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):333–335. doi: 10.1038/357333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burley S. K., Petsko G. A. Amino-aromatic interactions in proteins. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 28;203(2):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80730-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantau B., Keppens S., De Wulf H., Jard S. (3H)-vasopressin binding to isolated rat hepatocytes and liver membranes: regulation by GTP and relation to glycogen phosphorylase activation. J Recept Res. 1980;1(2):137–168. doi: 10.3109/10799898009044096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elands J., Barberis C., Jard S., Tribollet E., Dreifuss J. J., Bankowski K., Manning M., Sawyer W. H. 125I-labelled d(CH2)5[Tyr(Me)2,Thr4,Tyr-NH2(9)]OVT: a selective oxytocin receptor ligand. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 1;147(2):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90778-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerszten R. E., Chen J., Ishii M., Ishii K., Wang L., Nanevicz T., Turck C. W., Vu T. K., Coughlin S. R. Specificity of the thrombin receptor for agonist peptide is defined by its extracellular surface. Nature. 1994 Apr 14;368(6472):648–651. doi: 10.1038/368648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbulev V., Büchner H., Akhundova A., Fahrenholz F. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of V2 [8-lysine] vasopressin and oxytocin receptors from a pig kidney cell line. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jul 1;215(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibert M. F., Trumpp-Kallmeyer S., Bruinvels A., Hoflack J. Three-dimensional models of neurotransmitter G-binding protein-coupled receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Jul;40(1):8–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby V. J., Chow M. S., Smith D. D. Conformational and structural considerations in oxytocin-receptor binding and biological activity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:501–534. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Tanizawa O., Mori K., Brownstein M. J., Okayama H. Structure and expression of a human oxytocin receptor. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):526–529. doi: 10.1038/356526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Guillon G., Balestre M. N., Jard S. Stimulation, by vasopressin and other agonists, of inositol-lipid breakdown and inositol phosphate accumulation in WRK 1 cells. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):197–204. doi: 10.1042/bj2400197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojro E., Eich P., Gimpl G., Fahrenholz F. Direct identification of an extracellular agonist binding site in the renal V2 vasopressin receptor. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 14;32(49):13537–13544. doi: 10.1021/bi00212a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystek S. R., Jr, Patel P. S., Rose P. M., Fisher S. M., Kienzle B. K., Lach D. A., Liu E. C., Lynch J. S., Novotny J., Webb M. L. Mutation of peptide binding site in transmembrane region of a G protein-coupled receptor accounts for endothelin receptor subtype selectivity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12383–12386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. A., Elliott J. D., Sutiphong J. A., Friesen W. J., Ohlstein E. H., Stadel J. M., Gleason J. G., Peishoff C. E. Tyr-129 is important to the peptide ligand affinity and selectivity of human endothelin type A receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7164–7168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lolait S. J., O'Carroll A. M., McBride O. W., Konig M., Morel A., Brownstein M. J. Cloning and characterization of a vasopressin V2 receptor and possible link to nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):336–339. doi: 10.1038/357336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahlmann S., Meyerhof W., Hausmann H., Heierhorst J., Schönrock C., Zwiers H., Lederis K., Richter D. Structure, function, and phylogeny of [Arg8]vasotocin receptors from teleost fish and toad. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1342–1345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning M., Bankowski K., Barberis C., Jard S., Elands J., Chan W. Y. Novel approach to the design of synthetic radioiodinated linear V1A receptor antagonists of vasopressin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1992 Sep-Oct;40(3-4):261–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1992.tb00300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning M., Sawyer W. H. Design, synthesis and some uses of receptor-specific agonists and antagonists of vasopressin and oxytocin. J Recept Res. 1993;13(1-4):195–214. doi: 10.3109/10799899309073655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Ruggeri Z. M., Pareti F. I., Capitanio A. 1-Deamino-8-d-arginine vasopressin: a new pharmacological approach to the management of haemophilia and von Willebrands' diseases. Lancet. 1977 Apr 23;1(8017):869–872. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel A., O'Carroll A. M., Brownstein M. J., Lolait S. J. Molecular cloning and expression of a rat V1a arginine vasopressin receptor. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):523–526. doi: 10.1038/356523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski J., Kjelsberg M. A., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Mutagenesis of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor: how structure elucidates function. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1992;32:167–183. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.32.040192.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C., Barth T., Jard S. Vasopressin-sensitive kidney adenylate cyclase. Structural requirements for attachment to the receptor and enzyme activation: studies with vasopressin analogues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):3149–3156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savarese T. M., Fraser C. M. In vitro mutagenesis and the search for structure-function relationships among G protein-coupled receptors. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 1;283(Pt 1):1–19. doi: 10.1042/bj2830001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schertler G. F., Villa C., Henderson R. Projection structure of rhodopsin. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):770–772. doi: 10.1038/362770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz T. W. Locating ligand-binding sites in 7TM receptors by protein engineering. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1994 Aug;5(4):434–444. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(94)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Fong T. M., Tota M. R., Underwood D., Dixon R. A. Structure and function of G protein-coupled receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:101–132. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strosberg A. D. Structure/function relationship of proteins belonging to the family of receptors coupled to GTP-binding proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Feb 26;196(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto T., Saito M., Mochizuki S., Watanabe Y., Hashimoto S., Kawashima H. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a cDNA encoding the human V1b vasopressin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):27088–27092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibonnier M., Auzan C., Madhun Z., Wilkins P., Berti-Mattera L., Clauser E. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and functional expression of a cDNA encoding the human V1a vasopressin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3304–3310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumpp-Kallmeyer S., Hoflack J., Bruinvels A., Hibert M. Modeling of G-protein-coupled receptors: application to dopamine, adrenaline, serotonin, acetylcholine, and mammalian opsin receptors. J Med Chem. 1992 Sep 18;35(19):3448–3462. doi: 10.1021/jm00097a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatley M., Howl J., Morel A., Davies A. R. Homology between neurohypophyseal hormone receptors. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 1;296(Pt 2):519–519. doi: 10.1042/bj2960519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]