Abstract
Translation initiation factor 2 (eIF-2) in eukaryotic organisms is composed of three non-identical subunits, alpha, beta and gamma. In a previous report, we identified GCD11 as an essential gene encoding the gamma subunit of eIF-2 in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The predicted amino acid sequence of yeast eIF-2 gamma displays remarkable similarity to bacterial elongation factor Tu, including the presence of sequence elements conserved in all known guanine nucleotide binding proteins. We have identified the molecular defects present in seven unique alleles of GCD11 characterized by a partial loss of function. Three of these mutations result in amino acid substitutions within the putative GTP binding domain of eIF-2 gamma. We show that the gcd11 mutations specifically alter regulation of GCN4 expression at the translational level, without altering the scanning mechanism for protein synthesis initiation. Six of the mutant alleles presumably alter the function of eIF-2 gamma, rather than its abundance. A single allele, gcd11-R510H, suppresses a mutant his4 allele that lacks a functional AUG start codon. The latter result indicates that the gamma subunit of eIF-2 participates in recognition of the start site for protein synthesis, a role previously demonstrated in yeast for eIF-2 alpha and eIF-2 beta.
Full text
PDF


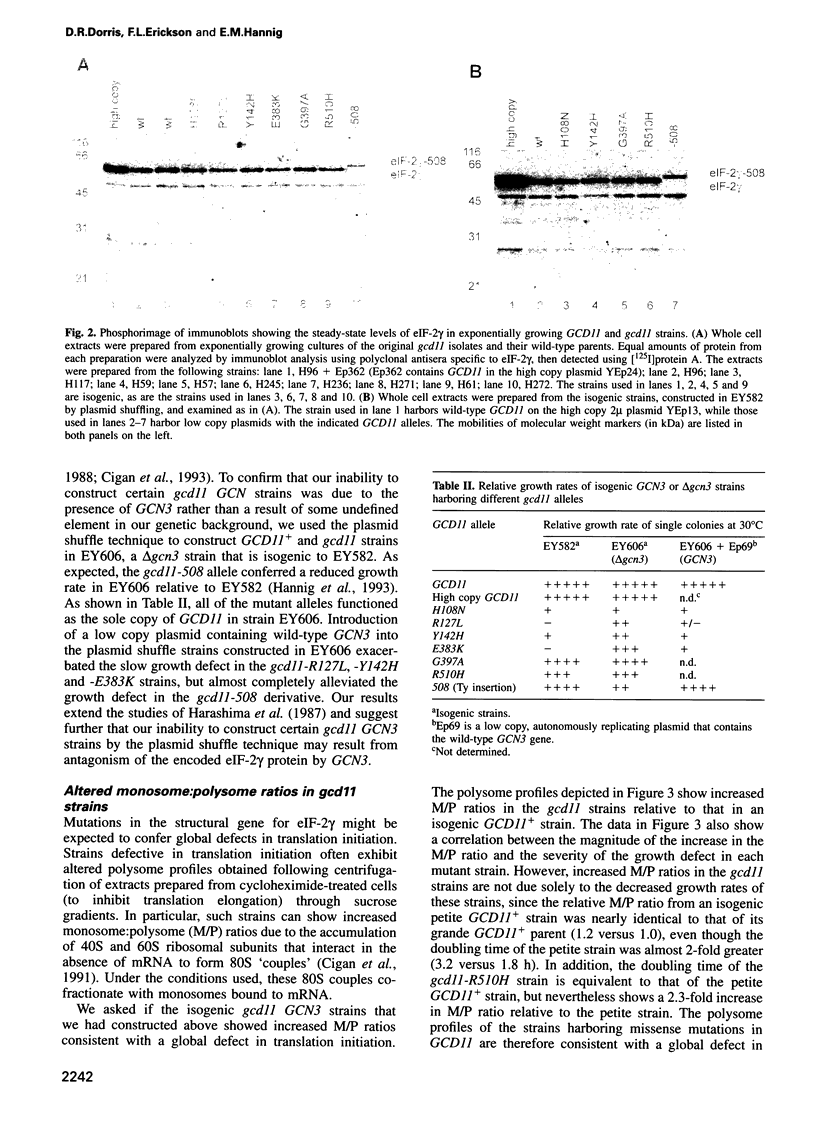

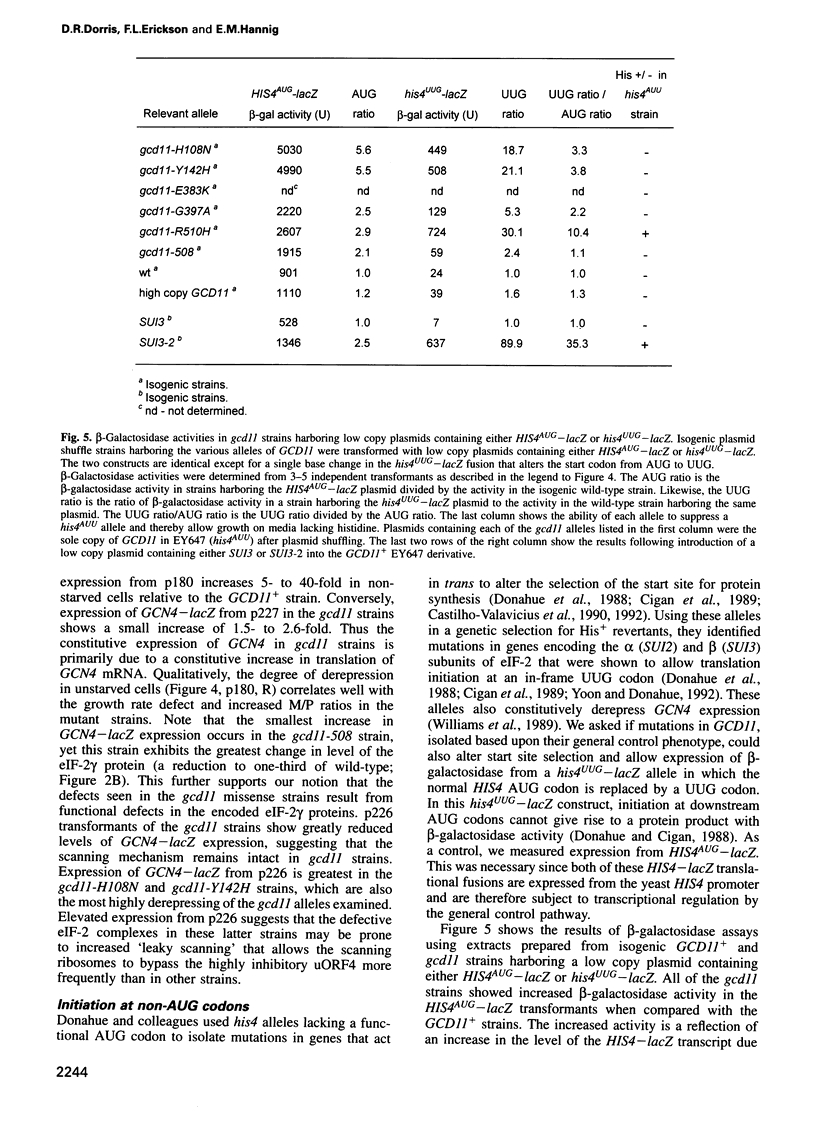

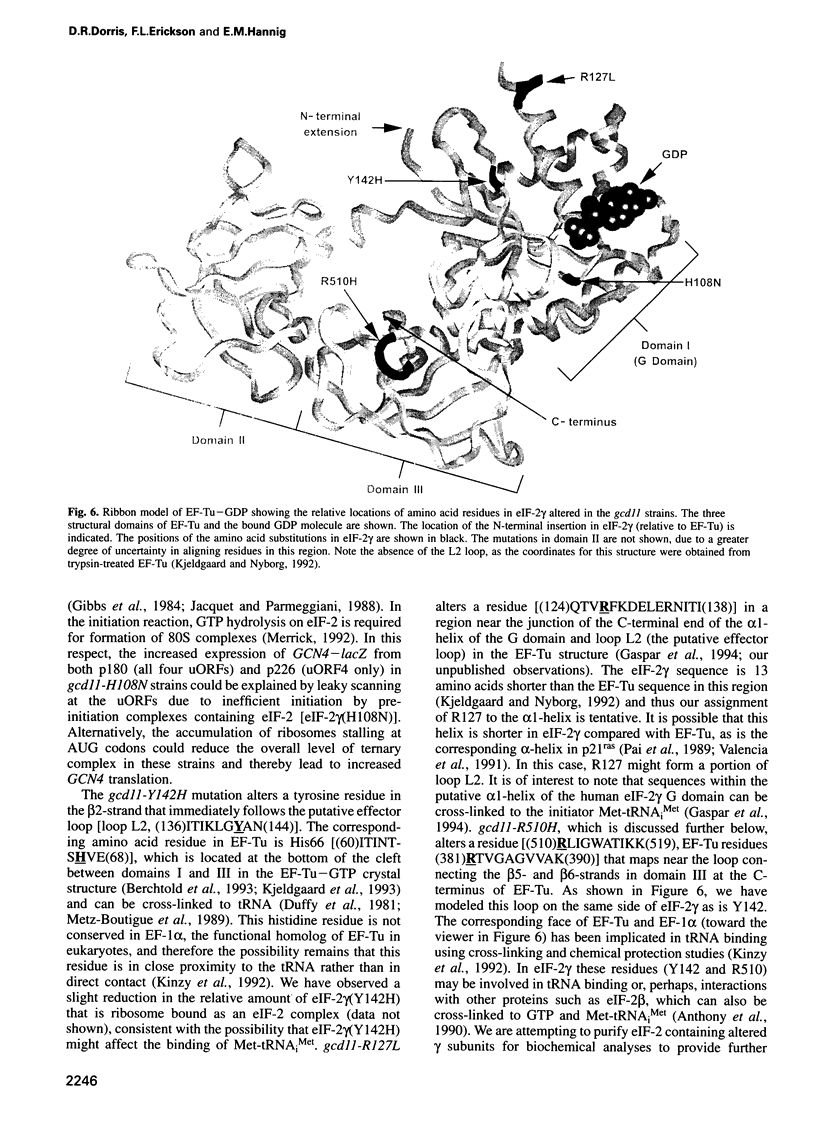



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alani E., Cao L., Kleckner N. A method for gene disruption that allows repeated use of URA3 selection in the construction of multiply disrupted yeast strains. Genetics. 1987 Aug;116(4):541–545. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.541.test. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony D. D., Jr, Kinzy T. G., Merrick W. C. Affinity labeling of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 and elongation factor 1 alpha beta gamma with GTP analogs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Aug 15;281(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90426-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber G. N., Wambach M., Wong M. L., Dever T. E., Hinnebusch A. G., Katze M. G. Translational regulation by the interferon-induced double-stranded-RNA-activated 68-kDa protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4621–4625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berchtold H., Reshetnikova L., Reiser C. O., Schirmer N. K., Sprinzl M., Hilgenfeld R. Crystal structure of active elongation factor Tu reveals major domain rearrangements. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):126–132. doi: 10.1038/365126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Trueheart J., Natsoulis G., Fink G. R. 5-Fluoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:164–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman J. L., Asuru A. I., Matts R. L., Hinnebusch A. G. Evidence that GCD6 and GCD7, translational regulators of GCN4, are subunits of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for eIF-2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1920–1932. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilho-Valavicius B., Thompson G. M., Donahue T. F. Mutation analysis of the Cys-X2-Cys-X19-Cys-X2-Cys motif in the beta subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2. Gene Expr. 1992;2(3):297–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilho-Valavicius B., Yoon H., Donahue T. F. Genetic characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae translational initiation suppressors sui1, sui2 and SUI3 and their effects on HIS4 expression. Genetics. 1990 Mar;124(3):483–495. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigan A. M., Bushman J. L., Boal T. R., Hinnebusch A. G. A protein complex of translational regulators of GCN4 mRNA is the guanine nucleotide-exchange factor for translation initiation factor 2 in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigan A. M., Feng L., Donahue T. F. tRNAi(met) functions in directing the scanning ribosome to the start site of translation. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):93–97. doi: 10.1126/science.3051379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigan A. M., Foiani M., Hannig E. M., Hinnebusch A. G. Complex formation by positive and negative translational regulators of GCN4. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3217–3228. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigan A. M., Pabich E. K., Feng L., Donahue T. F. Yeast translation initiation suppressor sui2 encodes the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 and shares sequence identity with the human alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2784–2788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J., Farabaugh P. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast Ty element: evidence for an unusual mechanism of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Feng L., Wek R. C., Cigan A. M., Donahue T. F., Hinnebusch A. G. Phosphorylation of initiation factor 2 alpha by protein kinase GCN2 mediates gene-specific translational control of GCN4 in yeast. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90193-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Cigan A. M. Genetic selection for mutations that reduce or abolish ribosomal recognition of the HIS4 translational initiator region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2955–2963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Cigan A. M., Pabich E. K., Valavicius B. C. Mutations at a Zn(II) finger motif in the yeast eIF-2 beta gene alter ribosomal start-site selection during the scanning process. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):621–632. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy L. K., Gerber L., Johnson A. E., Miller D. L. Identification of a histidine residue near the aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid binding site of elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4663–4666. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaspar N. J., Kinzy T. G., Scherer B. J., Hümbelin M., Hershey J. W., Merrick W. C. Translation initiation factor eIF-2. Cloning and expression of the human cDNA encoding the gamma-subunit. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3415–3422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Morris D. R. Initiation codons within 5'-leaders of mRNAs as regulators of translation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Apr;19(4):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Sigal I. S., Poe M., Scolnick E. M. Intrinsic GTPase activity distinguishes normal and oncogenic ras p21 molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5704–5708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. M., Hinnebusch A. G. Effect of sequence context at stop codons on efficiency of reinitiation in GCN4 translational control. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):606–618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. M., Miller P. F., Hinnebusch A. G. Requirements for intercistronic distance and level of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 activity in reinitiation on GCN4 mRNA vary with the downstream cistron. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2616–2628. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannig E. M., Cigan A. M., Freeman B. A., Kinzy T. G. GCD11, a negative regulator of GCN4 expression, encodes the gamma subunit of eIF-2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):506–520. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannig E. M., Hinnebusch A. G. Molecular analysis of GCN3, a translational activator of GCN4: evidence for posttranslational control of GCN3 regulatory function. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4808–4820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannig E. M., Williams N. P., Wek R. C., Hinnebusch A. G. The translational activator GCN3 functions downstream from GCN1 and GCN2 in the regulatory pathway that couples GCN4 expression to amino acid availability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1990 Nov;126(3):549–562. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harashima S., Hannig E. M., Hinnebusch A. G. Interactions between positive and negative regulators of GCN4 controlling gene expression and entry into the yeast cell cycle. Genetics. 1987 Nov;117(3):409–419. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.3.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harashima S., Hinnebusch A. G. Multiple GCD genes required for repression of GCN4, a transcriptional activator of amino acid biosynthetic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3990–3998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. E., Struhl K. Molecular characterization of GCD1, a yeast gene required for general control of amino acid biosynthesis and cell-cycle initiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9253–9265. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Gene-specific translational control of the yeast GCN4 gene by phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Oct;10(2):215–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet E., Parmeggiani A. Structure-function relationships in the GTP binding domain of EF-Tu: mutation of Val20, the residue homologous to position 12 in p21. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2861–2867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzy T. G., Freeman J. P., Johnson A. E., Merrick W. C. A model for the aminoacyl-tRNA binding site of eukaryotic elongation factor 1 alpha. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1623–1632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldgaard M., Nissen P., Thirup S., Nyborg J. The crystal structure of elongation factor EF-Tu from Thermus aquaticus in the GTP conformation. Structure. 1993 Sep 15;1(1):35–50. doi: 10.1016/0969-2126(93)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldgaard M., Nyborg J. Refined structure of elongation factor EF-Tu from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 5;223(3):721–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90986-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klopotowski T., Wiater A. Synergism of aminotriazole and phosphate on the inhibition of yeast imidazole glycerol phosphate dehydratase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Dec;112(3):562–566. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koromilas A. E., Roy S., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Sonenberg N. Malignant transformation by a mutant of the IFN-inducible dsRNA-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1685–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.1382315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupitza G., Thireos G. Translational activation of GCN4 mRNA in a cell-free system is triggered by uncharged tRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4375–4378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini G., Hinnebusch A. G., Chen C., Fink G. R. Positive regulatory interactions of the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1326–1333. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C. Mechanism and regulation of eukaryotic protein synthesis. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Jun;56(2):291–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.2.291-315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz-Boutigue M. H., Reinbolt J., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B. Crosslinking of elongation factor Tu to tRNA(Phe) by trans-diamminedichloroplatinum (II). Characterization of two crosslinking sites on EF-Tu. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):194–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. F., Hinnebusch A. G. Sequences that surround the stop codons of upstream open reading frames in GCN4 mRNA determine their distinct functions in translational control. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1217–1225. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. P., Harashima S., Hinnebusch A. G. A segment of GCN4 mRNA containing the upstream AUG codons confers translational control upon a heterologous yeast transcript. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2863–2867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. P., Hinnebusch A. G. Multiple upstream AUG codons mediate translational control of GCN4. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddon C. J., Hannig E. M., Hinnebusch A. G. Amino acid sequence similarity between GCN3 and GCD2, positive and negative translational regulators of GCN4: evidence for antagonism by competition. Genetics. 1989 Jul;122(3):551–559. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.3.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Kabsch W., Krengel U., Holmes K. C., John J., Wittinghofer A. Structure of the guanine-nucleotide-binding domain of the Ha-ras oncogene product p21 in the triphosphate conformation. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):209–214. doi: 10.1038/341209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price N. T., Francia G., Hall L., Proud C. G. Guanine nucleotide exchange factor for eukaryotic initiation factor-2. Cloning of cDNA for the delta-subunit of rabbit translation initiation factor-2B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Mar 1;1217(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Broach J. R. Cloning genes by complementation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:195–230. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Targeting, disruption, replacement, and allele rescue: integrative DNA transformation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:281–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J., Manne V., Ochoa S. Mechanism of translational control by partial phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):352–356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Stinchcomb D. T., Scherer S., Davis R. W. High-frequency transformation of yeast: autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong L., Milburn M. V., de Vos A. M., Kim S. H. Structure of ras proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):244–244. doi: 10.1126/science.2665078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valencia A., Kjeldgaard M., Pai E. F., Sander C. GTPase domains of ras p21 oncogene protein and elongation factor Tu: analysis of three-dimensional structures, sequence families, and functional sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5443–5447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez de Aldana C. R., Dever T. E., Hinnebusch A. G. Mutations in the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF-2 alpha) that overcome the inhibitory effect of eIF-2 alpha phosphorylation on translation initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7215–7219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. P., Hinnebusch A. G., Donahue T. F. Mutations in the structural genes for eukaryotic initiation factors 2 alpha and 2 beta of Saccharomyces cerevisiae disrupt translational control of GCN4 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7515–7519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfner M., Yep D., Messenguy F., Fink G. R. Integration of amino acid biosynthesis into the cell cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 5;96(2):273–290. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon H. J., Donahue T. F. The suil suppressor locus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a translation factor that functions during tRNA(iMet) recognition of the start codon. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):248–260. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Tong L., Milburn M. V., Matias P. M., Jancarik J., Noguchi S., Nishimura S., Miura K., Ohtsuka E., Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structure of an oncogene protein: catalytic domain of human c-H-ras p21. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):888–893. doi: 10.1126/science.2448879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]