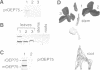Abstract
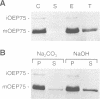
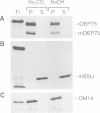
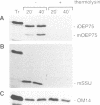
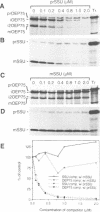
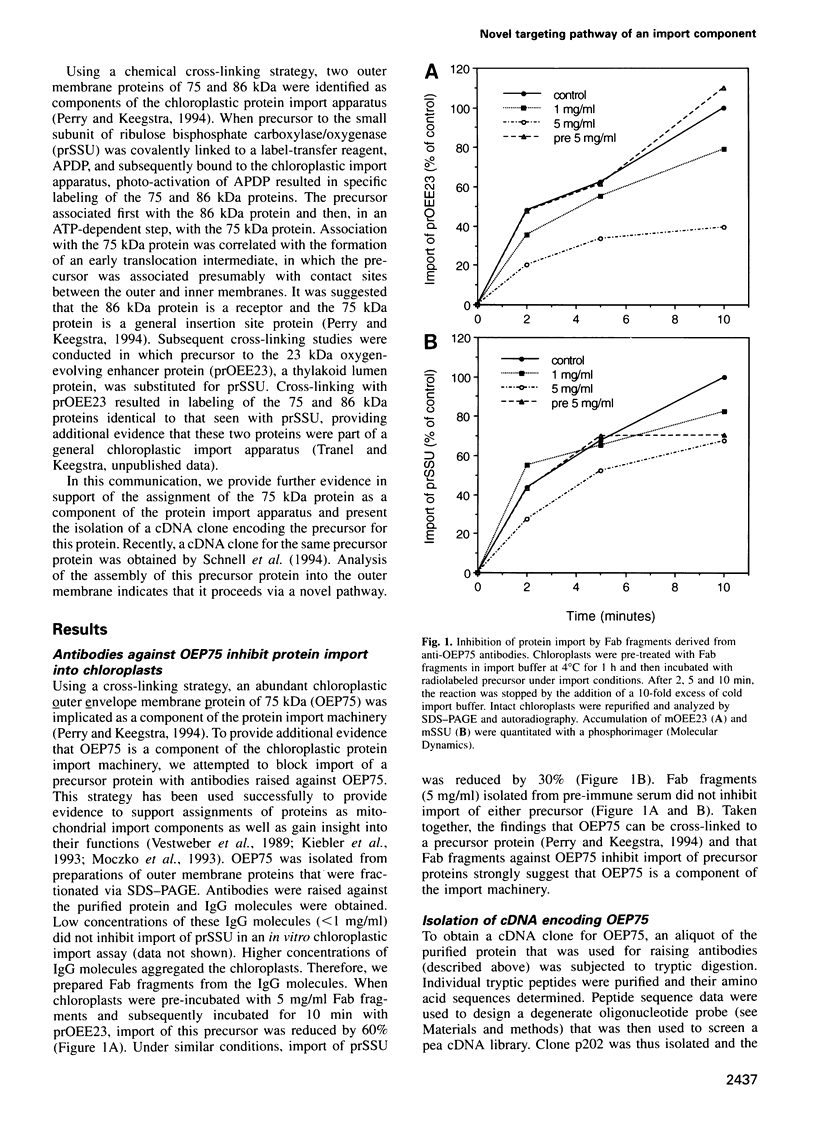
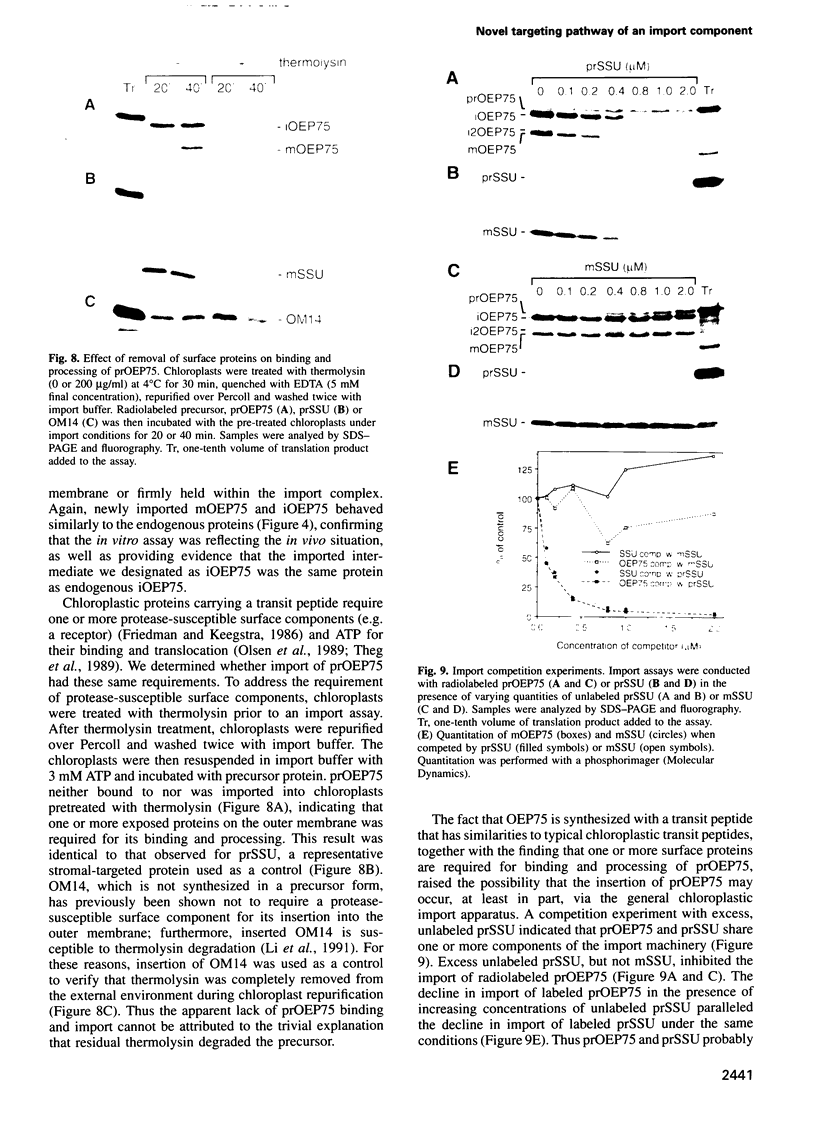
A chloroplastic outer envelope membrane protein of 75 kDa (OEP75) was identified previously as a component of the protein import machinery. Here we provide additional evidence that OEP75 is a component of protein import, present the isolation of a cDNA clone encoding this protein, briefly describe its developmental expression and tissue specificity, and characterize its insertion into the outer envelope membrane. OEP75 was synthesized as a higher molecular weight precursor (prOEP75) which bound to isolated chloroplasts in an in vitro import assay and subsequently was processed to the mature form (mOEP75). During this import assay, two proteins intermediate in size between prOEP75 and mOEP75 were detected. One of these intermediates was also detected in chloroplast envelopes isolated from young pea leaves. Binding and processing of prOEP75 required ATP and one or more surface-exposed proteinaceous components, and was competed by prSSU, a stromal-targeted protein. We propose that the N-terminus of the prOEP75 transit peptide acts as a stromal-targeting domain and a central, hydrophobic region of this transit peptide acts as a stop-transfer domain. A complex route of insertion and processing of prOEP75 may exist to ensure high fidelity targeting of this import component.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker K. P., Schatz G. Mitochondrial proteins essential for viability mediate protein import into yeast mitochondria. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):205–208. doi: 10.1038/349205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R. Permeation of hydrophilic solutes through mitochondrial outer membranes: review on mitochondrial porins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jun 29;1197(2):167–196. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(94)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Andrews J., Mersey B., Newcomb E. H., Keegstra K. Separation and characterization of inner and outer envelope membranes of pea chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3595–3599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Werner-Washburne M., Andrews J., Keegstra K. Thermolysin is a suitable protease for probing the surface of intact pea chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):675–678. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin C., Cline K. Developmental Regulation of the Plastid Protein Import Apparatus. Plant Cell. 1991 Oct;3(10):1131–1140. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.10.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douwe de Boer A., Weisbeek P. J. Chloroplast protein topogenesis: import, sorting and assembly. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 13;1071(3):221–253. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90015-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer K., Weber A., Arbinger B., Brink S., Eckerskorn C., Flügge U. I. The 24 kDa outer envelope membrane protein from spinach chloroplasts: molecular cloning, in vivo expression and import pathway of a protein with unusual properties. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 May;25(2):167–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00023235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. L., Keegstra K. Chloroplast protein import : quantitative analysis of precursor binding. Plant Physiol. 1989 Mar;89(3):993–999. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.3.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He Z. H., Li J., Sundqvist C., Timko M. P. Leaf Developmental Age Controls Expression of Genes Encoding Enzymes of Chlorophyll and Heme Biosynthesis in Pea (Pisum sativum L.). Plant Physiol. 1994 Oct;106(2):537–546. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.2.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch S., Muckel E., Heemeyer F., von Heijne G., Soll J. A receptor component of the chloroplast protein translocation machinery. Science. 1994 Dec 23;266(5193):1989–1992. doi: 10.1126/science.7801125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil P., Pfanner N. Insertion of MOM22 into the mitochondrial outer membrane strictly depends on surface receptors. FEBS Lett. 1993 Apr 26;321(2-3):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil P., Weinzierl A., Kiebler M., Dietmeier K., Söllner T., Pfanner N. Biogenesis of the mitochondrial receptor complex. Two receptors are required for binding of MOM38 to the outer membrane surface. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19177–19180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler F., Blobel G., Patel H. A., Schnell D. J. Identification of two GTP-binding proteins in the chloroplast protein import machinery. Science. 1994 Nov 11;266(5187):1035–1039. doi: 10.1126/science.7973656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiebler M., Keil P., Schneider H., van der Klei I. J., Pfanner N., Neupert W. The mitochondrial receptor complex: a central role of MOM22 in mediating preprotein transfer from receptors to the general insertion pore. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):483–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80050-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko K., Bornemisza O., Kourtz L., Ko Z. W., Plaxton W. C., Cashmore A. R. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding a cognate 70-kDa heat shock protein of the chloroplast envelope. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):2986–2993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. M., Moore T., Keegstra K. Targeting of proteins to the outer envelope membrane uses a different pathway than transport into chloroplasts. Plant Cell. 1991 Jul;3(7):709–717. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.7.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczko M., Gärtner F., Pfanner N. The protein import receptor MOM19 of yeast mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jul 12;326(1-3):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81801-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T., Keegstra K. Characterization of a cDNA clone encoding a chloroplast-targeted Clp homologue. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Feb;21(3):525–537. doi: 10.1007/BF00028809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen L. J., Keegstra K. The binding of precursor proteins to chloroplasts requires nucleoside triphosphates in the intermembrane space. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):433–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen L. J., Theg S. M., Selman B. R., Keegstra K. ATP is required for the binding of precursor proteins to chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6724–6729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. E., Keegstra K. Envelope membrane proteins that interact with chloroplastic precursor proteins. Plant Cell. 1994 Jan;6(1):93–105. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon M., Fischer K., Flügge U. I., Soll J. Sequence analysis and protein import studies of an outer chloroplast envelope polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5778–5782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz G. The protein import machinery of mitochondria. Protein Sci. 1993 Feb;2(2):141–146. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Söllner T., Dietmeier K., Eckerskorn C., Lottspeich F., Trülzsch B., Neupert W., Pfanner N. Targeting of the master receptor MOM19 to mitochondria. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1659–1662. doi: 10.1126/science.1661031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell D. J., Kessler F., Blobel G. Isolation of components of the chloroplast protein import machinery. Science. 1994 Nov 11;266(5187):1007–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.7973649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf M., Waegemann K., Soll J. A constituent of the chloroplast import complex represents a new type of GTP-binding protein. Plant J. 1995 Mar;7(3):401–411. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1995.7030401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Pfaller R., Griffiths G., Pfanner N., Neupert W. A mitochondrial import receptor for the ADP/ATP carrier. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theg S. M., Bauerle C., Olsen L. J., Selman B. R., Keegstra K. Internal ATP is the only energy requirement for the translocation of precursor proteins across chloroplastic membranes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6730–6736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theg S. M., Scott S. V. Protein import into chloroplasts. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;3(6):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90212-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestweber D., Brunner J., Baker A., Schatz G. A 42K outer-membrane protein is a component of the yeast mitochondrial protein import site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):205–209. doi: 10.1038/341205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner-Washburne M., Cline K., Keegstra K. Analysis of pea chloroplast inner and outer envelope membrane proteins by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and their comparison with stromal proteins. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):569–575. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Steppuhn J., Herrmann R. G. Domain structure of mitochondrial and chloroplast targeting peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 1;180(3):535–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]