Abstract
Macrophage infectivity potentiators are membrane proteins described as virulence factors in bacterial intracellular parasites, such as Legionella and Chlamydia. These factors share amino acid homology to eukaryotic peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases that are inhibited by FK506, an inhibitor of signal transduction in mammalian cells with potent immunosuppressor activity. We report here the characterization of a protein released into the culture medium by the infective stage of the protozoan intracellular parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. The protein possesses a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity that is inhibited by FK506 and its non-immunosuppressing derivative L-685,818. The corresponding gene presents sequence homology with bacterial macrophage infectivity potentiators. The addition of the protein, produced heterologously in Escherichia coli, to cultures of trypomastigotes and simian epithelial or HeLa cells enhances invasion of the mammalian cells by the parasites. Antibodies raised in mice against the T.cruzi isomerase greatly reduce infectivity. A similar reduction of infectivity is obtained by addition to the cultures of FK506 and L-685,818. We concluded that the T.cruzi isomerase is involved in cell invasion.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agabian N. Trans splicing of nuclear pre-mRNAs. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1157–1160. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90674-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. W., Colli W. Adhesion and interiorization of Trypanosoma cruzi in mammalian cells. J Protozool. 1982 May;29(2):264–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1982.tb04024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. W., Hong K. S., Robbins E. S., Nussenzweig V. Stage-specific surface antigens expressed during the morphogenesis of vertebrate forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Dec;64(3):474–484. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. W., Whitlow M. B. Secretion by Trypanosoma cruzi of a hemolysin active at low pH. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Mar 15;33(3):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliska J. B., Galán J. E., Falkow S. Signal transduction in the mammalian cell during bacterial attachment and entry. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):903–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90270-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brener Z. Biology of Trypanosoma cruzi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:347–382. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brillantes A. B., Ondrias K., Scott A., Kobrinsky E., Ondriasová E., Moschella M. C., Jayaraman T., Landers M., Ehrlich B. E., Marks A. R. Stabilization of calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) function by FK506-binding protein. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):513–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellani O., Ribeiro L. V., Fernandes J. F. Differentiation of Trypanosoma cruzi in culture. J Protozool. 1967 Aug;14(3):447–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1967.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N. P., Eisenstein B. I., Mody C. H., Toews G. B., Engleberg N. C. A Legionella pneumophila gene encoding a species-specific surface protein potentiates initiation of intracellular infection. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1255–1262. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1255-1262.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N. P., Fields B. S. Legionella pneumophila mip gene potentiates intracellular infection of protozoa and human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5188–5191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lange T., Berkvens T. M., Veerman H. J., Frasch A. C., Barry J. D., Borst P. Comparison of the genes coding for the common 5' terminal sequence of messenger RNAs in three trypanosome species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4431–4443. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
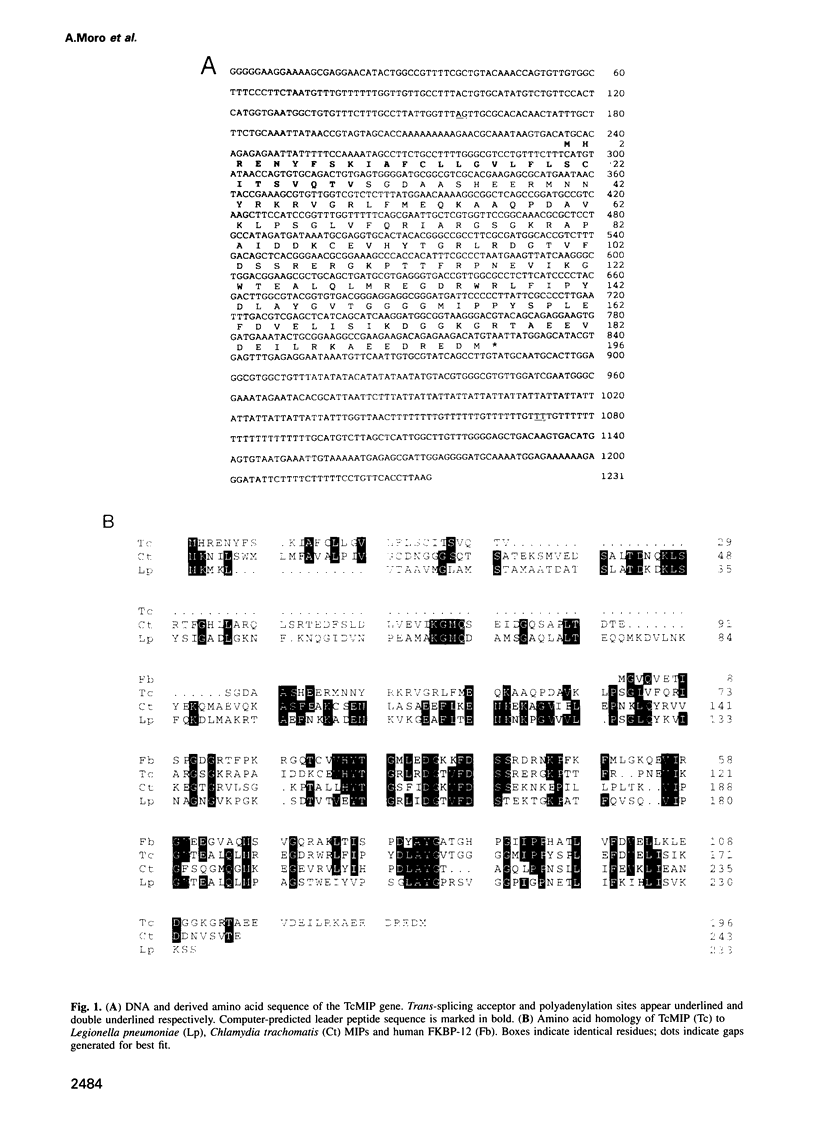
- Dragon E. A., Sias S. R., Kato E. A., Gabe J. D. The genome of Trypanosoma cruzi contains a constitutively expressed, tandemly arranged multicopy gene homologous to a major heat shock protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1271–1275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
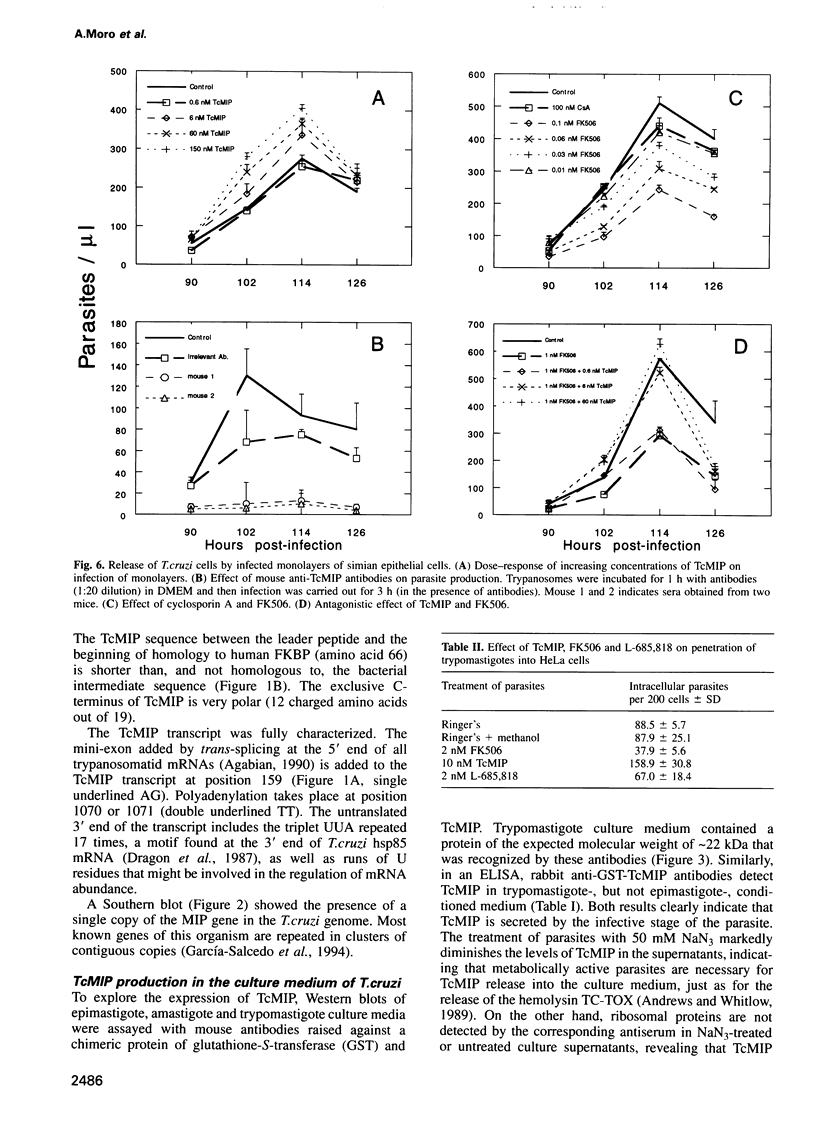
- Dumont F. J., Staruch M. J., Koprak S. L., Siekierka J. J., Lin C. S., Harrison R., Sewell T., Kindt V. M., Beattie T. R., Wyvratt M. The immunosuppressive and toxic effects of FK-506 are mechanistically related: pharmacology of a novel antagonist of FK-506 and rapamycin. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):751–760. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
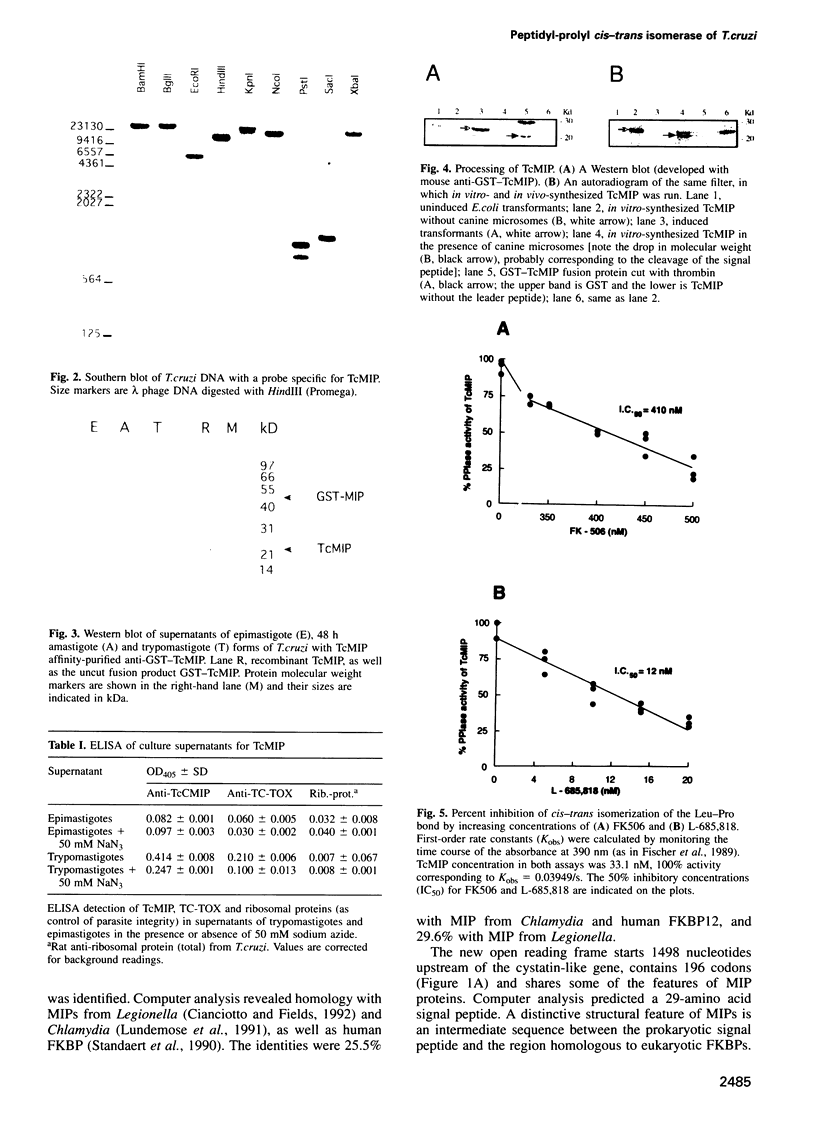
- Fischer G., Bang H., Ludwig B., Mann K., Hacker J. Mip protein of Legionella pneumophila exhibits peptidyl-prolyl-cis/trans isomerase (PPlase) activity. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(10):1375–1383. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Wittmann-Liebold B., Lang K., Kiefhaber T., Schmid F. X. Cyclophilin and peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase are probably identical proteins. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):476–478. doi: 10.1038/337476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruman D. A., Burakoff S. J., Bierer B. E. Immunophilins in protein folding and immunosuppression. FASEB J. 1994 Apr 1;8(6):391–400. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.6.7513288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
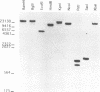
- García-Salcedo J. A., Oliver J. L., Stock R. P., González A. Molecular characterization and transcription of the histone H2B gene from the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Sep;13(6):1033–1043. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. C., von Hippel P. H. Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 1;182(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90602-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M. G. The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase, FK506-binding protein, is most likely the 12 kd endogenous inhibitor 2 of protein kinase C. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1051–1052. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90258-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez A., Lerner T. J., Huecas M., Sosa-Pineda B., Nogueira N., Lizardi P. M. Apparent generation of a segmented mRNA from two separate tandem gene families in Trypanosoma cruzi. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 26;13(16):5789–5804. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.16.5789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González A., Rosales J. L., Ley V., Díaz C. Cloning and characterization of a gene coding for a protein (KAP) associated with the kinetoplast of epimastigotes and amastigotes of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 May;40(2):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90045-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker J., Fischer G. Immunophilins: structure-function relationship and possible role in microbial pathogenicity. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Nov;10(3):445–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman T., Brillantes A. M., Timerman A. P., Fleischer S., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Marks A. R. FK506 binding protein associated with the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9474–9477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L., Tipper C., Amherdt M., Orci L., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A's effects on endosomes, lysosomes, and the TGN suggest a general mechanism for regulating organelle structure and membrane traffic. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):601–616. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90534-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Farmer J. D., Jr, Lane W. S., Friedman J., Weissman I., Schreiber S. L. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundemose A. G., Birkelund S., Fey S. J., Larsen P. M., Christiansen G. Chlamydia trachomatis contains a protein similar to the Legionella pneumophila mip gene product. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):109–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michels P. A., Opperdoes F. R. The evolutionary origin of glycosomes. Parasitol Today. 1991 May;7(5):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(91)90167-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S. N., Silva J., Vercesi A. E., Docampo R. Cytosolic-free calcium elevation in Trypanosoma cruzi is required for cell invasion. J Exp Med. 1994 Oct 1;180(4):1535–1540. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.4.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation and preservation of competent bacterial cells by freezing. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:326–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhich M. L., Boothroyd J. C. Polycistronic transcripts in trypanosomes and their accumulation during heat shock: evidence for a precursor role in mRNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3837–3846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. J., Watkins K. P., Agabian N. Identification of a novel Y branch structure as an intermediate in trypanosome mRNA processing: evidence for trans splicing. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90616-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rondinelli E. Conservation of heat-shock proteins in Trypanosoma cruzi. Parasitol Today. 1994 May;10(5):172–176. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(94)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotonda J., Burbaum J. J., Chan H. K., Marcy A. I., Becker J. W. Improved calcineurin inhibition by yeast FKBP12-drug complexes. Crystallographic and functional analysis. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7607–7609. doi: 10.2210/pdb1yat/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman S., Robbins E. S., Nussenzweig V. Attachment of Trypanosoma cruzi to mammalian cells requires parasite energy, and invasion can be independent of the target cell cytoskeleton. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):645–654. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.645-654.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid F. X. Prolyl isomerase: enzymatic catalysis of slow protein-folding reactions. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:123–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L. Chemistry and biology of the immunophilins and their immunosuppressive ligands. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):283–287. doi: 10.1126/science.1702904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J. J., Wiederrecht G., Greulich H., Boulton D., Hung S. H., Cryan J., Hodges P. J., Sigal N. H. The cytosolic-binding protein for the immunosuppressant FK-506 is both a ubiquitous and highly conserved peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21011–21015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L., Shaw J. RNA editing and the mitochondrial cryptogenes of kinetoplastid protozoa. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):355–366. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90911-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standaert R. F., Galat A., Verdine G. L., Schreiber S. L. Molecular cloning and overexpression of the human FK506-binding protein FKBP. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):671–674. doi: 10.1038/346671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieux I., Nathanson M. H., Andrews N. W. Role in host cell invasion of Trypanosoma cruzi-induced cytosolic-free Ca2+ transients. J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):1017–1022. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieux I., Webster P., Ravesloot J., Boron W., Lunn J. A., Heuser J. E., Andrews N. W. Lysosome recruitment and fusion are early events required for trypanosome invasion of mammalian cells. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1117–1130. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timerman A. P., Ogunbumni E., Freund E., Wiederrecht G., Marks A. R., Fleischer S. The calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum is modulated by FK-506-binding protein. Dissociation and reconstitution of FKBP-12 to the calcium release channel of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):22992–22999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tropschug M., Wachter E., Mayer S., Schönbrunner E. R., Schmid F. X. Isolation and sequence of an FK506-binding protein from N. crassa which catalyses protein folding. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):674–677. doi: 10.1038/346674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yem A. W., Reardon I. M., Leone J. W., Heinrikson R. L., Deibel M. R., Jr An active FK506-binding domain of 17,000 daltons is isolated following limited proteolysis of chicken thymus hsp56. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 30;32(47):12571–12576. doi: 10.1021/bi00210a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Souza W. Cell biology of Trypanosoma cruzi. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;86:197–283. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]