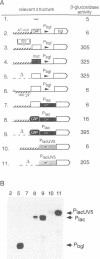
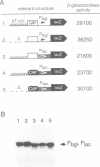
Abstract
Silencing of a transcriptional unit by flanking sequence elements has so far only been described for eukaryotic systems. Here, a similar system is described in bacteria. The Escherichia coli bgl operon (beta-glucoside utilization) is normally cryptic due to very low promoter activity. However, low activity is not attributable to the quality of the promoter itself but is caused by its chromosomal context. The bgl promoter is perfectly active when tested outside of its normal context of a stretch of a few hundred base pairs. In addition, other promoters become inactivated when placed into the bgl region. Both the deletion of an upstream sequence element and the replacement of sequences located downstream result in promoter de-repression, demonstrating that silencing of promoters within this stretch of DNA in vivo is an active process brought about by the combined action of upstream and downstream chromosomal elements.
Full text
PDF
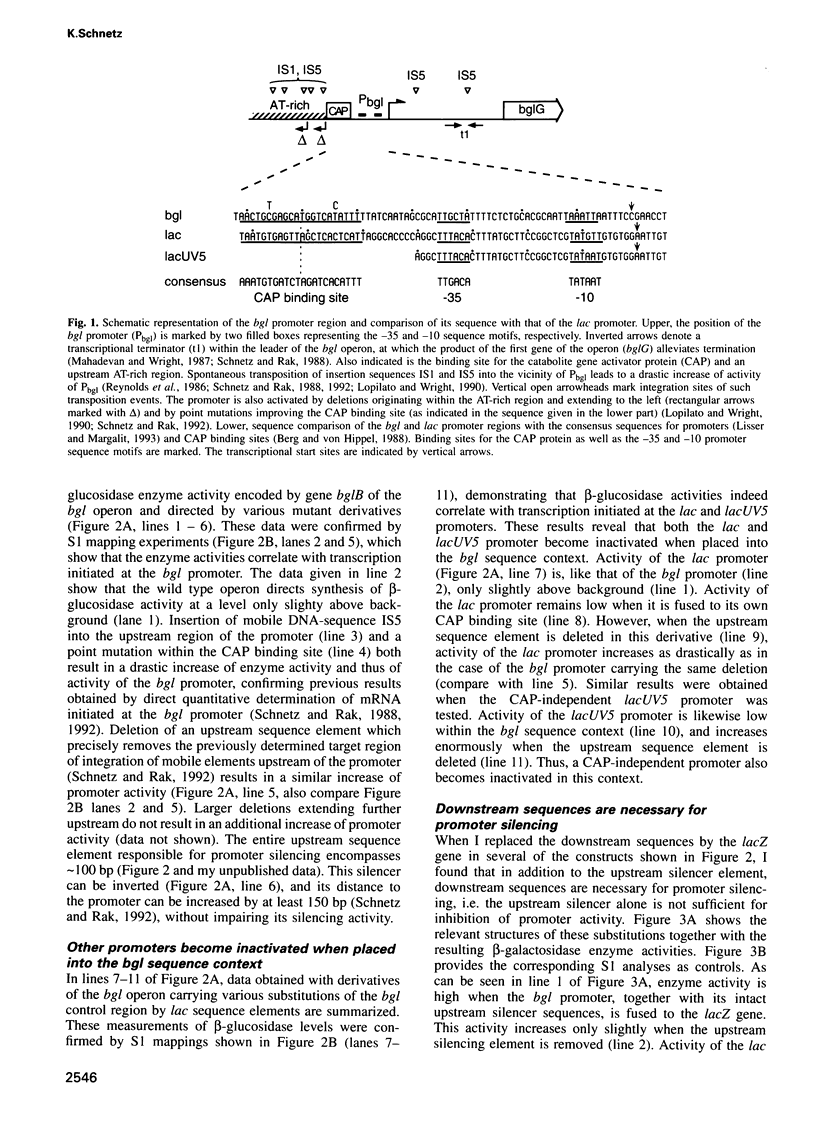
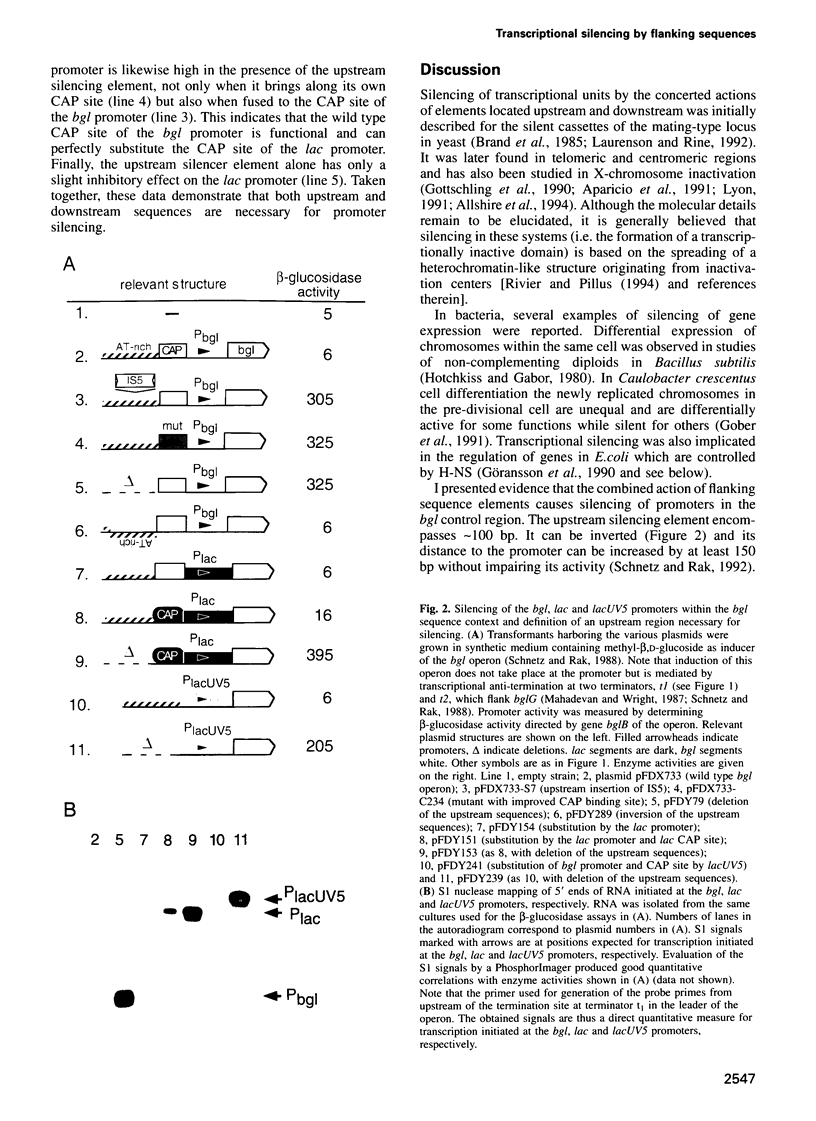



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allshire R. C., Javerzat J. P., Redhead N. J., Cranston G. Position effect variegation at fission yeast centromeres. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):157–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio O. M., Billington B. L., Gottschling D. E. Modifiers of position effect are shared between telomeric and silent mating-type loci in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1279–1287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins. II. The binding specificity of cyclic AMP receptor protein to recognition sites. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):709–723. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90482-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracco L., Kotlarz D., Kolb A., Diekmann S., Buc H. Synthetic curved DNA sequences can act as transcriptional activators in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4289–4296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defez R., De Felice M. Cryptic operon for beta-glucoside metabolism in Escherichia coli K12: genetic evidence for a regulatory protein. Genetics. 1981 Jan;97(1):11–25. doi: 10.1093/genetics/97.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K. A., Sternglanz R., Reynolds A. E., Wright A. Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I mutants have compensatory mutations in DNA gyrase genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90403-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Rouviere-Yaniv J. Histonelike proteins of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):301–319. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.301-319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falconi M., McGovern V., Gualerzi C., Hillyard D., Higgins N. P. Mutations altering chromosomal protein H-NS induce mini-Mu transposition. New Biol. 1991 Jun;3(6):615–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsman K., Sondén B., Göransson M., Uhlin B. E. Antirepression function in Escherichia coli for the cAMP-cAMP receptor protein transcriptional activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9880–9884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gober J. W., Champer R., Reuter S., Shapiro L. Expression of positional information during cell differentiation of Caulobacter. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90646-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschling D. E., Aparicio O. M., Billington B. L., Zakian V. A. Position effect at S. cerevisiae telomeres: reversible repression of Pol II transcription. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):751–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90141-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göransson M., Sondén B., Nilsson P., Dagberg B., Forsman K., Emanuelsson K., Uhlin B. E. Transcriptional silencing and thermoregulation of gene expression in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):682–685. doi: 10.1038/344682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. G., Xu L. Nucleotide sequence, function, activation, and evolution of the cryptic asc operon of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Biol Evol. 1992 Jul;9(4):688–706. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Dorman C. J., Stirling D. A., Waddell L., Booth I. R., May G., Bremer E. A physiological role for DNA supercoiling in the osmotic regulation of gene expression in S. typhimurium and E. coli. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):569–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hinton J. C., Hulton C. S., Owen-Hughes T., Pavitt G. D., Seirafi A. Protein H1: a role for chromatin structure in the regulation of bacterial gene expression and virulence? Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2007–2012. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkiss R. D., Gabor M. H. Biparental products of bacterial protoplast fusion showing unequal parental chromosome expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3553–3557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulton C. S., Seirafi A., Hinton J. C., Sidebotham J. M., Waddell L., Pavitt G. D., Owen-Hughes T., Spassky A., Buc H., Higgins C. F. Histone-like protein H1 (H-NS), DNA supercoiling, and gene expression in bacteria. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):631–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90458-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Drutsa V., Jansen H. W., Kramer B., Pflugfelder M., Fritz H. J. The gapped duplex DNA approach to oligonucleotide-directed mutation construction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9441–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurenson P., Rine J. Silencers, silencing, and heritable transcriptional states. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):543–560. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.543-560.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisser S., Margalit H. Compilation of E. coli mRNA promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 11;21(7):1507–1516. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.7.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F. The quest for the X-inactivation centre. Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):69–70. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90271-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan S., Wright A. A bacterial gene involved in transcription antitermination: regulation at a rho-independent terminator in the bgl operon of E. coli. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):485–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90502-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G. Use of sodium trichloroacetate and mung bean nuclease to increase sensitivity and precision during transcript mapping. Anal Biochem. 1986 Oct;158(1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90605-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Hughes T. A., Pavitt G. D., Santos D. S., Sidebotham J. M., Hulton C. S., Hinton J. C., Higgins C. F. The chromatin-associated protein H-NS interacts with curved DNA to influence DNA topology and gene expression. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90354-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Hall B. G. Mechanisms of activation of the cryptic cel operon of Escherichia coli K12. Genetics. 1990 Mar;124(3):473–482. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettijohn D. E. Histone-like proteins and bacterial chromosome structure. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12793–12796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad I., Schaefler S. Regulation of the beta-glucoside system in Escherchia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):638–650. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.638-650.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. E., Felton J., Wright A. Insertion of DNA activates the cryptic bgl operon in E. coli K12. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):625–629. doi: 10.1038/293625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. E., Mahadevan S., LeGrice S. F., Wright A. Enhancement of bacterial gene expression by insertion elements or by mutation in a CAP-cAMP binding site. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier D. H., Pillus L. Silencing speaks up. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):963–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90373-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefler S. Inducible system for the utilization of beta-glucosides in Escherichia coli. I. Active transport and utilization of beta-glucosides. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):254–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.254-263.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnetz K., Rak B. Regulation of the bgl operon of Escherichia coli by transcriptional antitermination. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3271–3277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03194.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnetz K., Toloczyki C., Rak B. Beta-glucoside (bgl) operon of Escherichia coli K-12: nucleotide sequence, genetic organization, and possible evolutionary relationship to regulatory components of two Bacillus subtilis genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2579–2590. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2579-2590.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spassky A., Rimsky S., Garreau H., Buc H. H1a, an E. coli DNA-binding protein which accumulates in stationary phase, strongly compacts DNA in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5321–5340. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tupper A. E., Owen-Hughes T. A., Ussery D. W., Santos D. S., Ferguson D. J., Sidebotham J. M., Hinton J. C., Higgins C. F. The chromatin-associated protein H-NS alters DNA topology in vitro. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):258–268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueguchi C., Mizuno T. The Escherichia coli nucleoid protein H-NS functions directly as a transcriptional repressor. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1039–1046. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05745.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Yoshida T., Tanaka K., Sasakawa C., Mizuno T. Molecular analysis of the Escherichia coli hns gene encoding a DNA-binding protein, which preferentially recognizes curved DNA sequences. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Nov;230(1-2):332–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00290685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber F., Kotlarz D., Rimsky S., Buc H. Modulated expression of promoters containing upstream curved DNA sequences by the Escherichia coli nucleoid protein H-NS. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Apr;12(2):231–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]