Abstract
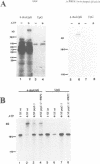
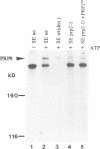
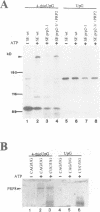
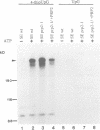
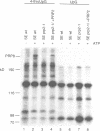
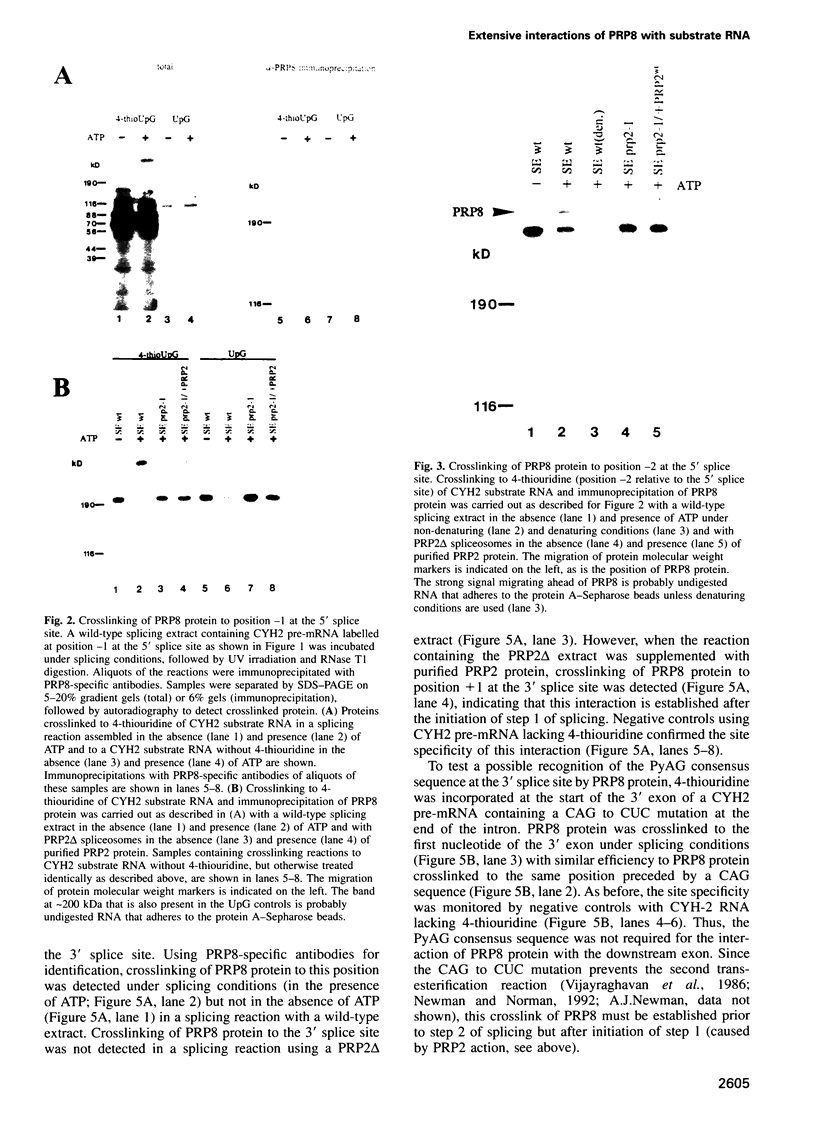
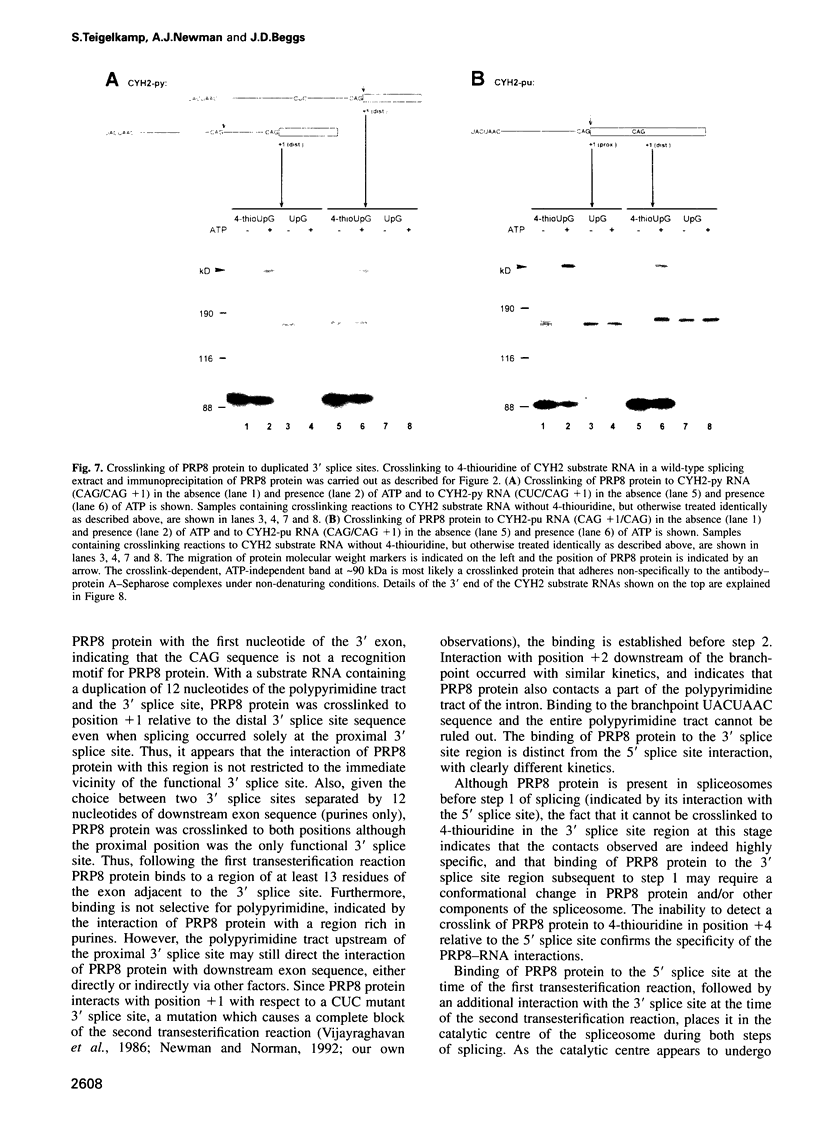
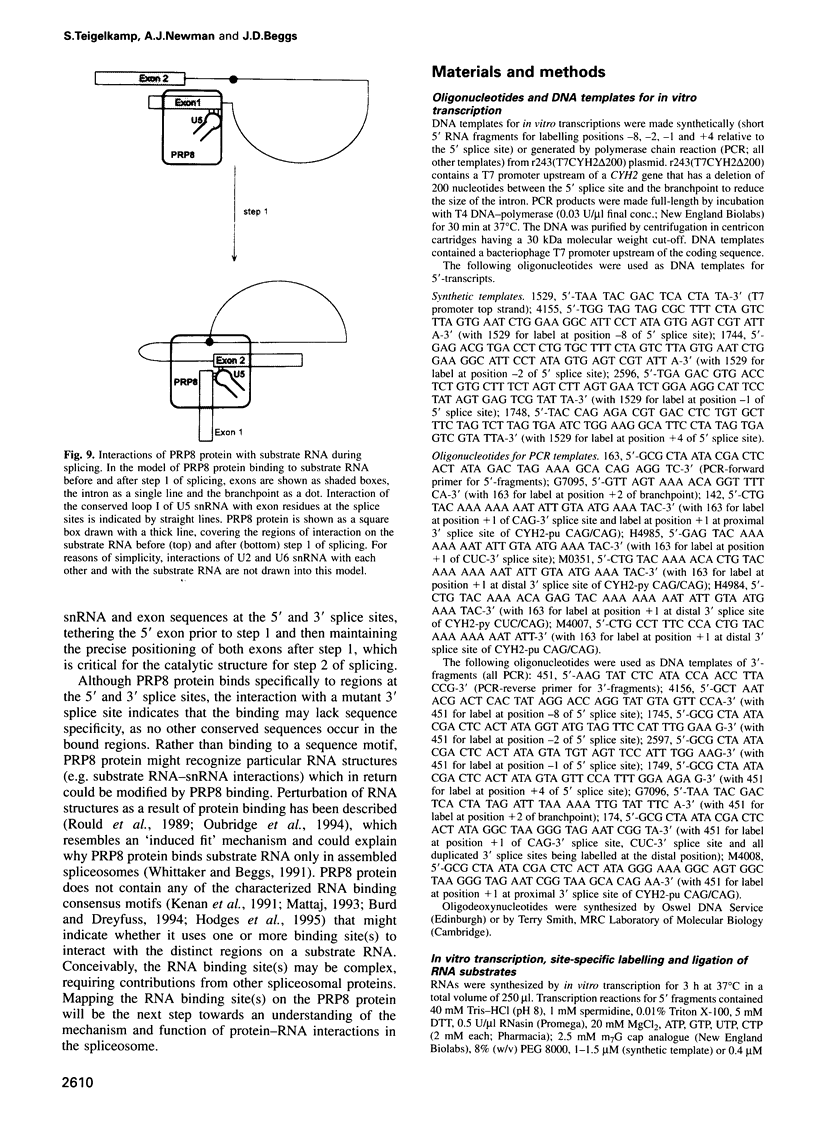
Precursor RNAs containing 4-thiouridine at specific sites were used with UV-crosslinking to map the binding sites of the yeast protein splicing factor PRP8. PRP8 protein interacts with a region of at least eight exon nucleotides at the 5' splice site and a minimum of 13 exon nucleotides and part of the polypyrimidine tract in the 3' splice site region. Crosslinking of PRP8 to mutant and duplicated 3' splice sites indicated that the interaction is not sequence specific, nor does it depend on the splice site being functional. Binding of PRP8 to the 5' exon was established before step 1 and to the 3' splice site region after step 1 of splicing. These interactions place PRP8 close to the proposed catalytic core of the spliceosome during both transesterification reactions. To date, this represents the most extensive mapping of the binding site(s) of a splicing factor on the substrate RNA. We propose that the large binding sites of PRP8 stabilize the intrinsically weaker interactions of U5 snRNA with both exons at the splice sites for exon alignment by the U5 snRNP.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abovich N., Liao X. C., Rosbash M. The yeast MUD2 protein: an interaction with PRP11 defines a bridge between commitment complexes and U2 snRNP addition. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 1;8(7):843–854. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.7.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson G. J., Bach M., Lührmann R., Beggs J. D. Conservation between yeast and man of a protein associated with U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):819–821. doi: 10.1038/342819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. D., Beggs J. D. Roles of PRP8 protein in the assembly of splicing complexes. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3721–3729. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05457.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd C. G., Dreyfuss G. Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science. 1994 Jul 29;265(5172):615–621. doi: 10.1126/science.8036511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes J. J., Sontheimer E. J., Seiwert S. D., Steitz J. A. Mutations in the conserved loop of human U5 snRNA generate use of novel cryptic 5' splice sites in vivo. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5181–5189. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta B., Weiner A. M. Genetic evidence for base pairing between U2 and U6 snRNA in mammalian mRNA splicing. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):821–824. doi: 10.1038/352821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Blanco M. A., Anderson G. J., Beggs J., Sharp P. A. A mammalian protein of 220 kDa binds pre-mRNAs in the spliceosome: a potential homologue of the yeast PRP8 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3082–3086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausner T. P., Giglio L. M., Weiner A. M. Evidence for base-pairing between mammalian U2 and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2146–2156. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges P. E., Beggs J. D. RNA splicing. U2 fulfils a commitment. Curr Biol. 1994 Mar 1;4(3):264–267. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges P. E., Jackson S. P., Brown J. D., Beggs J. D. Extraordinary sequence conservation of the PRP8 splicing factor. Yeast. 1995 Apr 15;11(4):337–342. doi: 10.1002/yea.320110406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., Lossky M., Beggs J. D. Cloning of the RNA8 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, detection of the RNA8 protein, and demonstration that it is essential for nuclear pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1067–1075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson D. J., Rahe B., Pringle J., Beggs J. D. A suppressor of a yeast splicing mutation (prp8-1) encodes a putative ATP-dependent RNA helicase. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):715–717. doi: 10.1038/349715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandels-Lewis S., Séraphin B. Involvement of U6 snRNA in 5' splice site selection. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):2035–2039. doi: 10.1126/science.8266100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Query C. C., Keene J. D. RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. H., Lin R. J. Pre-mRNA splicing within an assembled yeast spliceosome requires an RNA-dependent ATPase and ATP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):888–892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohtz J. D., Jamison S. F., Will C. L., Zuo P., Lührmann R., Garcia-Blanco M. A., Manley J. L. Protein-protein interactions and 5'-splice-site recognition in mammalian mRNA precursors. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):119–124. doi: 10.1038/368119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulesza H., Simpson G. G., Waugh R., Beggs J. D., Brown J. W. Detection of a plant protein analogous to the yeast spliceosomal protein, PRP8. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 22;318(1):4–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81315-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesser C. F., Guthrie C. Mutations in U6 snRNA that alter splice site specificity: implications for the active site. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):1982–1988. doi: 10.1126/science.8266093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. J., Newman A. J., Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Yeast mRNA splicing in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14780–14792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lossky M., Anderson G. J., Jackson S. P., Beggs J. Identification of a yeast snRNP protein and detection of snRNP-snRNP interactions. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1019–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90588-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMillan A. M., Query C. C., Allerson C. R., Chen S., Verdine G. L., Sharp P. A. Dynamic association of proteins with the pre-mRNA branch region. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):3008–3020. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.3008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhani H. D., Guthrie C. A novel base-pairing interaction between U2 and U6 snRNAs suggests a mechanism for the catalytic activation of the spliceosome. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):803–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90556-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhani H. D., Guthrie C. Dynamic RNA-RNA interactions in the spliceosome. Annu Rev Genet. 1994;28:1–26. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.28.120194.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. RNA recognition: a family matter? Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):837–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90265-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Krainer A. R. Regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing by hnRNP A1 and splicing factor SF2. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90477-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. J., Sharp P. A. Evidence for two active sites in the spliceosome provided by stereochemistry of pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):364–368. doi: 10.1038/365364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. J., Sharp P. A. Site-specific modification of pre-mRNA: the 2'-hydroxyl groups at the splice sites. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):992–997. doi: 10.1126/science.1589782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Norman C. U5 snRNA interacts with exon sequences at 5' and 3' splice sites. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):743–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A., Norman C. Mutations in yeast U5 snRNA alter the specificity of 5' splice-site cleavage. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90413-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. Small nuclear RNAs and pre-mRNA splicing. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;6(3):360–367. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W. RNA-RNA interactions in the spliceosome: unraveling the ties that bind. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90563-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oubridge C., Ito N., Evans P. R., Teo C. H., Nagai K. Crystal structure at 1.92 A resolution of the RNA-binding domain of the U1A spliceosomal protein complexed with an RNA hairpin. Nature. 1994 Dec 1;372(6505):432–438. doi: 10.1038/372432a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson T., Beggs J. D., Finnegan D. J., Lührmann R. Polypeptide components of Drosophila small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5877–5882. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto A. L., Steitz J. A. The mammalian analogue of the yeast PRP8 splicing protein is present in the U4/5/6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle and the spliceosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8742–8746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumpton M., McGarvey M., Beggs J. D. A dominant negative mutation in the conserved RNA helicase motif 'SAT' causes splicing factor PRP2 to stall in spliceosomes. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):879–887. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rould M. A., Perona J. J., Söll D., Steitz T. A. Structure of E. coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Gln) and ATP at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1135–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.2479982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Abelson J. Pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90276-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawa H., Abelson J. Evidence for a base-pairing interaction between U6 small nuclear RNA and 5' splice site during the splicing reaction in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11269–11273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawa H., Shimura Y. Association of U6 snRNA with the 5'-splice site region of pre-mRNA in the spliceosome. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):244–254. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer E. J., Steitz J. A. The U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs as active site components of the spliceosome. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):1989–1996. doi: 10.1126/science.8266094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A., Steitz J. A. A general two-metal-ion mechanism for catalytic RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6498–6502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. J., Guthrie C. A cold-sensitive mRNA splicing mutant is a member of the RNA helicase gene family. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):629–641. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teigelkamp S., McGarvey M., Plumpton M., Beggs J. D. The splicing factor PRP2, a putative RNA helicase, interacts directly with pre-mRNA. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):888–897. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teigelkamp S., Whittaker E., Beggs J. D. Interaction of the yeast splicing factor PRP8 with substrate RNA during both steps of splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Feb 11;23(3):320–326. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.3.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayraghavan U., Parker R., Tamm J., Iimura Y., Rossi J., Abelson J., Guthrie C. Mutations in conserved intron sequences affect multiple steps in the yeast splicing pathway, particularly assembly of the spliceosome. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1683–1695. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman D. A., Steitz J. A. RNA splicing. Alive with DEAD proteins. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):463–464. doi: 10.1038/349463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker E., Beggs J. D. The yeast PRP8 protein interacts directly with pre-mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5483–5489. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker E., Lossky M., Beggs J. D. Affinity purification of spliceosomes reveals that the precursor RNA processing protein PRP8, a protein in the U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle, is a component of yeast spliceosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2216–2219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. A., Manley J. L. Base pairing between U2 and U6 snRNAs is necessary for splicing of a mammalian pre-mRNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):818–821. doi: 10.1038/352818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Maniatis T. Specific interactions between proteins implicated in splice site selection and regulated alternative splicing. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1061–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90316-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. R., Sontheimer E. J., Steitz J. A. Site-specific cross-linking of mammalian U5 snRNP to the 5' splice site before the first step of pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2542–2553. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuo P., Manley J. L. The human splicing factor ASF/SF2 can specifically recognize pre-mRNA 5' splice sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3363–3367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]