Abstract
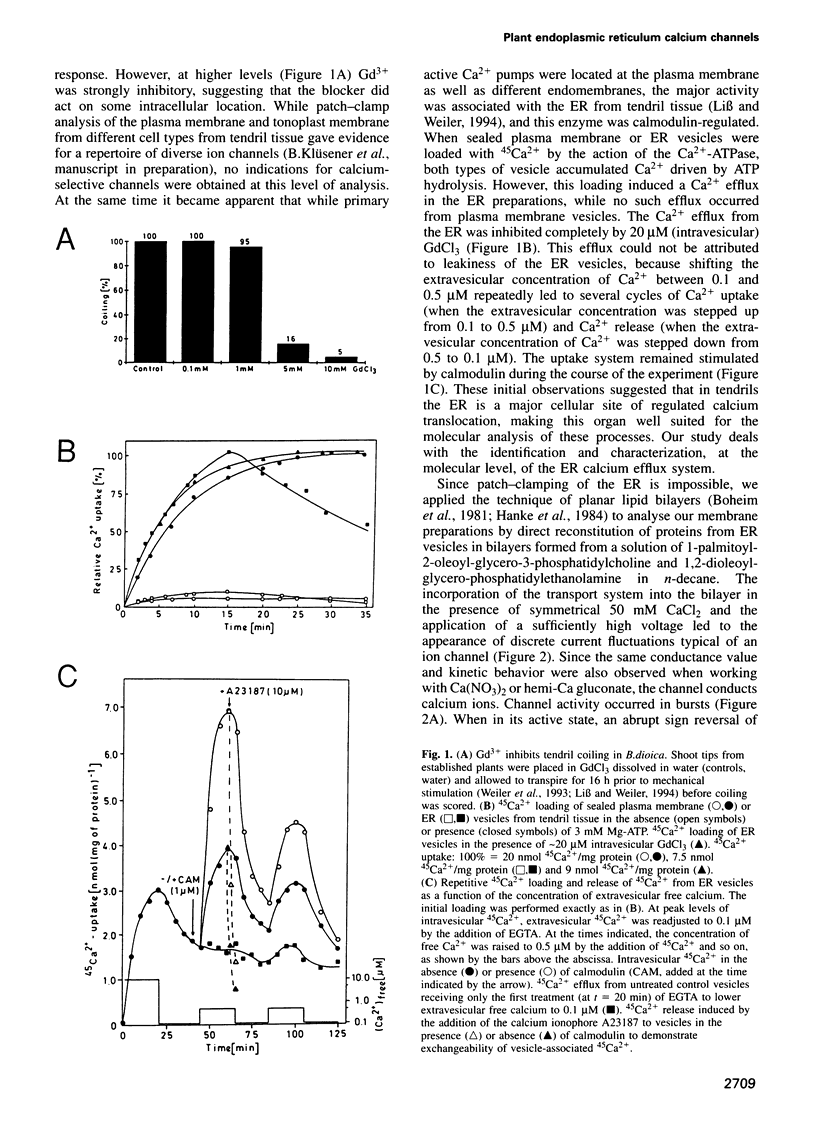
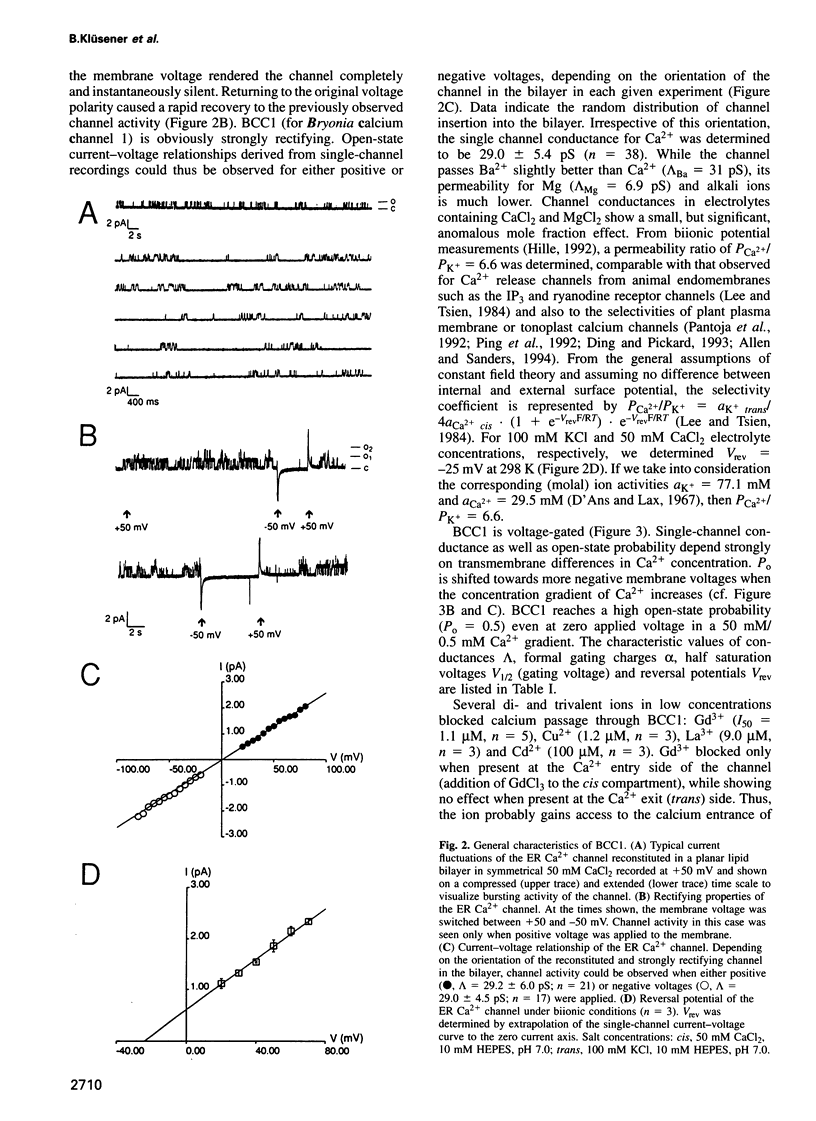
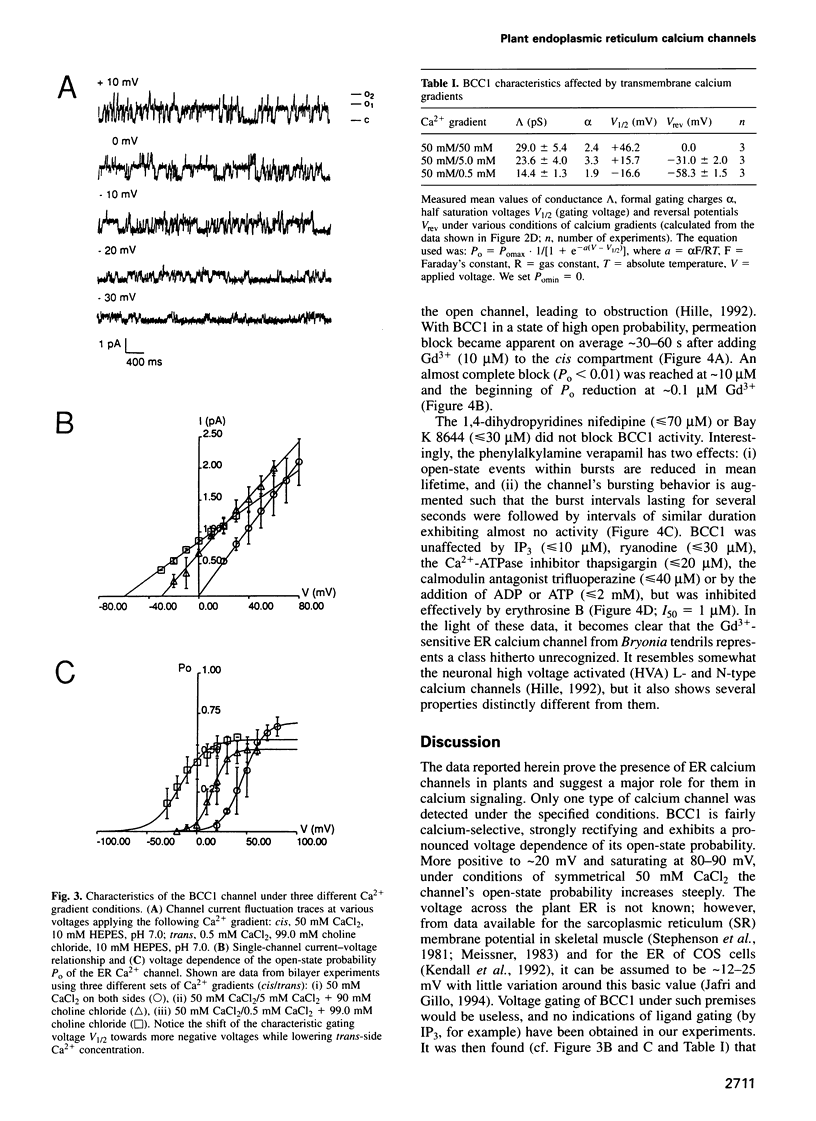
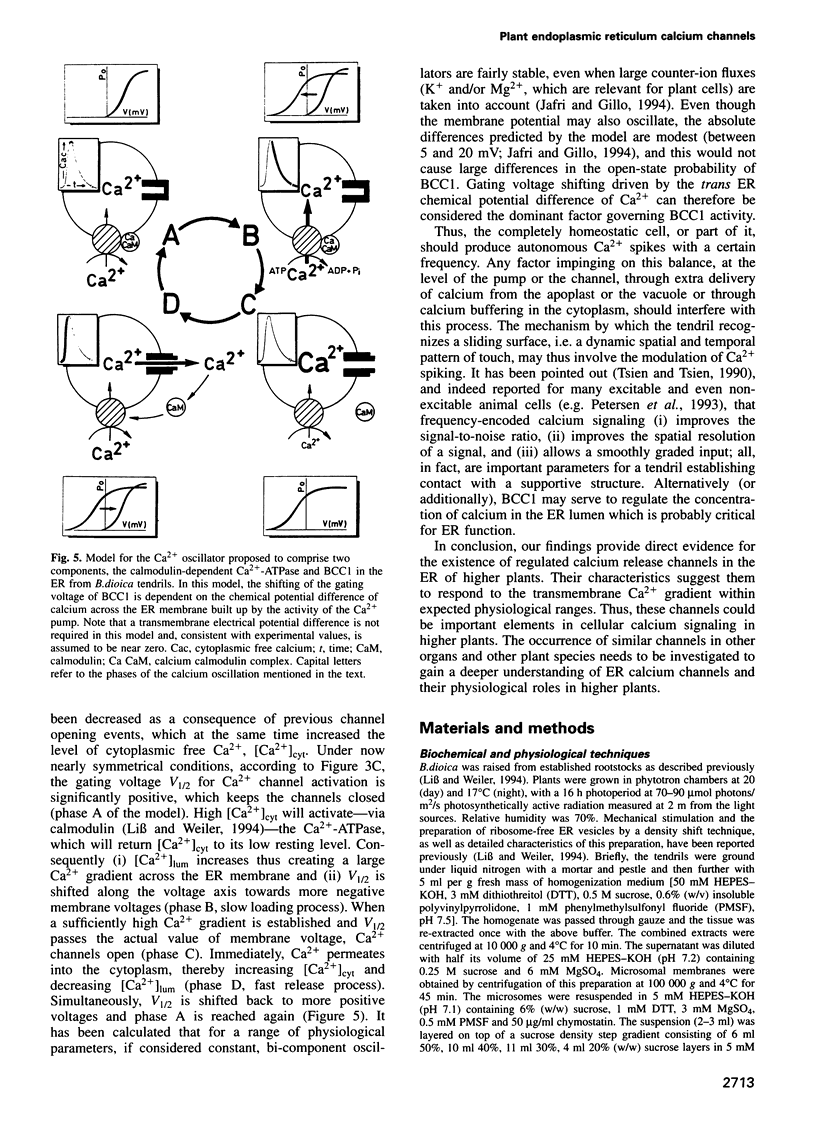
The lipid bilayer technique was adapted to the functional reconstitution of ion channels from the endoplasmic reticulum of a higher plant. This was obtained at high purity from touch-sensitive tendrils of Bryonia dioica. In this preparation, a calcium-selective strongly rectifying channel is prevailing whose single-channel properties have been characterized. The single-channel conductance is 29 pS in 50 mM CaCl2. The Ca2+: K+ selectivity was determined to be approximately 6.6. The channel is voltage-gated and, more importantly, the gating voltage is strongly shifted towards more negative voltages when a transmembrane Ca2+ gradient is applied. Thus, at physiological voltages across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, the channel's open probability will be governed largely by the chemical potential gradient of Ca2+, generated by the Ca(2+)-ATPase in that same membrane. The calcium release channel described here is effectively blocked by Gd3+ which also completely suppresses a tendril's reaction to touch, suggesting that this channel could be a key element of calcium signaling in higher plant mechanotransduction. Its molecular characteristics and inhibitor data show it to be the first known member of a hitherto unrecognized class of calcium channels.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen G. J., Sanders D. Two Voltage-Gated, Calcium Release Channels Coreside in the Vacuolar Membrane of Broad Bean Guard Cells. Plant Cell. 1994 May;6(5):685–694. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.5.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boheim G., Hanke W., Barrantes F. J., Eibl H., Sakmann B., Fels G., Maelicke A. Agonist-activated ionic channels in acetylcholine receptor reconstituted into planar lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3586–3590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braam J., Davis R. W. Rain-, wind-, and touch-induced expression of calmodulin and calmodulin-related genes in Arabidopsis. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90587-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding J. P., Pickard B. G. Modulation of mechanosensitive calcium-selective cation channels by temperature. Plant J. 1993 May;3(5):713–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elinder F., Arhem P. Effects of gadolinium on ion channels in the myelinated axon of Xenopus laevis: four sites of action. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):71–83. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80456-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilroy S., Fricker M. D., Read N. D., Trewavas A. J. Role of Calcium in Signal Transduction of Commelina Guard Cells. Plant Cell. 1991 Apr;3(4):333–344. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.4.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke W., Boheim G., Barhanin J., Pauron D., Lazdunski M. Reconstitution of highly purified saxitoxin-sensitive Na+-channels into planar lipid bilayers. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):509–515. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jafri M. S., Gillo B. A membrane potential model with counterions for cytosolic calcium oscillations. Cell Calcium. 1994 Jul;16(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4160(05)80003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall J. M., Dormer R. L., Campbell A. K. Targeting aequorin to the endoplasmic reticulum of living cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):1008–1016. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92304-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight M. R., Campbell A. K., Smith S. M., Trewavas A. J. Transgenic plant aequorin reports the effects of touch and cold-shock and elicitors on cytoplasmic calcium. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):524–526. doi: 10.1038/352524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight M. R., Smith S. M., Trewavas A. J. Wind-induced plant motion immediately increases cytosolic calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4967–4971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacampagne A., Gannier F., Argibay J., Garnier D., Le Guennec J. Y. The stretch-activated ion channel blocker gadolinium also blocks L-type calcium channels in isolated ventricular myocytes of the guinea-pig. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Apr 20;1191(1):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. High selectivity of calcium channels in single dialysed heart cells of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:253–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. Monovalent ion and calcium ion fluxes in sarcoplasmic reticulum. Mol Cell Biochem. 1983;55(1):65–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00229243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantoja O., Gelli A., Blumwald E. Voltage-dependent calcium channels in plant vacuoles. Science. 1992 Mar 20;255(5051):1567–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.255.5051.1567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen C. C., Petersen O. H., Berridge M. J. The role of endoplasmic reticulum calcium pumps during cytosolic calcium spiking in pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22262–22264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ping Z., Yabe I., Muto S. Voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane and the vacuolar membrane of Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 9;1112(2):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90404-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T., Bartel H., Jung G., Bannwarth W., Boheim G. Effects of polycations on ion channels formed by neutral and negatively charged alamethicins. Eur Biophys J. 1994;23(3):155–165. doi: 10.1007/BF01007607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. I., Hagiwara S. Repetitive increases in cytosolic Ca2+ of guard cells by abscisic acid activation of nonselective Ca2+ permeable channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9305–9309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Wendt I. R., Forrest Q. G. Non-uniform ion distributions and electrical potentials in sarcoplasmic regions of skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):690–692. doi: 10.1038/289690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuleau P., Ward J. M., Ranjeva R., Schroeder J. I. Voltage-dependent calcium-permeable channels in the plasma membrane of a higher plant cell. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 1;13(13):2970–2975. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06595.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Calcium channels, stores, and oscillations. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:715–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., Schroeder J. I. Calcium-Activated K+ Channels and Calcium-Induced Calcium Release by Slow Vacuolar Ion Channels in Guard Cell Vacuoles Implicated in the Control of Stomatal Closure. Plant Cell. 1994 May;6(5):669–683. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.5.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler E. W., Kutchan T. M., Gorba T., Brodschelm W., Niesel U., Bublitz F. The Pseudomonas phytotoxin coronatine mimics octadecanoid signalling molecules of higher plants. FEBS Lett. 1994 May 23;345(1):9–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00411-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. C., Sachs F. Block of stretch-activated ion channels in Xenopus oocytes by gadolinium and calcium ions. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1068–1071. doi: 10.1126/science.2466333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


