Abstract
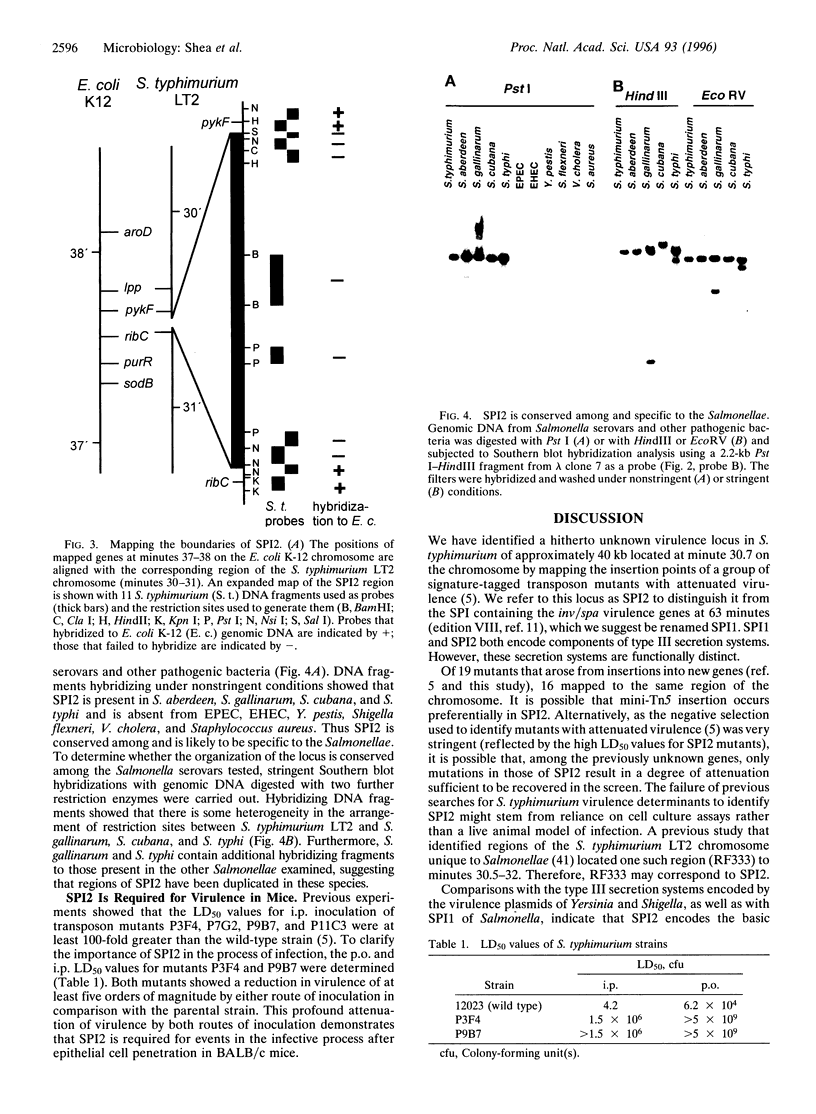
Mapping the insertion points of 16 signature-tagged transposon mutants on the Salmonella typhimurium chromosome led to the identification of a 40-kb virulence gene cluster at minute 30.7. This locus is conserved among all other Salmonella species examined but is not present in a variety of other pathogenic bacteria or in Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleotide sequencing of a portion of this locus revealed 11 open reading frames whose predicted proteins encode components of a type III secretion system. To distinguish between this and the type III secretion system encoded by the inv/spa invasion locus known to reside on a pathogenicity island, we refer to the inv/spa locus as Salmonella pathogenicity island (SPI) 1 and the new locus as SPI2. SPI2 has a lower G+C content than that of the remainder of the Salmonella genome and is flanked by genes whose products share greater than 90% identity with those of the E. coli ydhE and pykF genes. Thus SPI2 was probably acquired horizontally by insertion into a region corresponding to that between the ydhE and pykF genes of E. coli. Virulence studies of SPI2 mutants have shown them to be attenuated by at least five orders of magnitude compared with the wild-type strain after oral or intraperitoneal inoculation of mice.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allaoui A., Sansonetti P. J., Parsot C. MxiD, an outer membrane protein necessary for the secretion of the Shigella flexneri lpa invasins. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(1):59–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmeyer R. M., McNern J. K., Bossio J. C., Rosenshine I., Finlay B. B., Galán J. E. Cloning and molecular characterization of a gene involved in Salmonella adherence and invasion of cultured epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(1):89–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews G. P., Maurelli A. T. mxiA of Shigella flexneri 2a, which facilitates export of invasion plasmid antigens, encodes a homolog of the low-calcium-response protein, LcrD, of Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3287–3295. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3287-3295.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson N. R., Goldman B. S. Rapid mapping in Salmonella typhimurium with Mud-P22 prophages. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1673–1681. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1673-1681.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman T., Erickson K., Galyov E., Persson C., Wolf-Watz H. The lcrB (yscN/U) gene cluster of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is involved in Yop secretion and shows high homology to the spa gene clusters of Shigella flexneri and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1994 May;176(9):2619–2626. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.9.2619-2626.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum G., Ott M., Lischewski A., Ritter A., Imrich H., Tschäpe H., Hacker J. Excision of large DNA regions termed pathogenicity islands from tRNA-specific loci in the chromosome of an Escherichia coli wild-type pathogen. Infect Immun. 1994 Feb;62(2):606–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.2.606-614.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Collins F. M. The route of enteric infection in normal mice. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1189–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collazo C. M., Zierler M. K., Galán J. E. Functional analysis of the Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes invl and invJ and identification of a target of the protein secretion apparatus encoded in the inv locus. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Jan;15(1):25–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichelberg K., Ginocchio C. C., Galán J. E. Molecular and functional characterization of the Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes invB and invC: homology of InvC to the F0F1 ATPase family of proteins. J Bacteriol. 1994 Aug;176(15):4501–4510. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.15.4501-4510.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetherston J. D., Schuetze P., Perry R. D. Loss of the pigmentation phenotype in Yersinia pestis is due to the spontaneous deletion of 102 kb of chromosomal DNA which is flanked by a repetitive element. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2693–2704. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of Salmonella pathogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1994;192:163–185. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78624-2_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Ruschkowski S., Dedhar S. Cytoskeletal rearrangements accompanying salmonella entry into epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jun;99(Pt 2):283–296. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.2.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. L., Starnbach M. N., Falkow S. Morphological and cytoskeletal changes in epithelial cells occur immediately upon interaction with Salmonella typhimurium grown under low-oxygen conditions. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(21):3077–3087. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and molecular characterization of genes whose products allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Ginocchio C., Costeas P. Molecular and functional characterization of the Salmonella invasion gene invA: homology of InvA to members of a new protein family. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4338–4349. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4338-4349.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginocchio C. C., Olmsted S. B., Wells C. L., Galán J. E. Contact with epithelial cells induces the formation of surface appendages on Salmonella typhimurium. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):717–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90510-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginocchio C., Pace J., Galán J. E. Identification and molecular characterization of a Salmonella typhimurium gene involved in triggering the internalization of salmonellae into cultured epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouin E., Mengaud J., Cossart P. The virulence gene cluster of Listeria monocytogenes is also present in Listeria ivanovii, an animal pathogen, and Listeria seeligeri, a nonpathogenic species. Infect Immun. 1994 Aug;62(8):3550–3553. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.8.3550-3553.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Ochman H. Cognate gene clusters govern invasion of host epithelial cells by Salmonella typhimurium and Shigella flexneri. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3779–3787. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Ochman H. How to become a pathogen. Trends Microbiol. 1994 Aug;2(8):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(94)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Sturmoski M. A., Solomon F. R., Lin R., Ochman H. Molecular, functional, and evolutionary analysis of sequences specific to Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1033–1037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker J., Bender L., Ott M., Wingender J., Lund B., Marre R., Goebel W. Deletions of chromosomal regions coding for fimbriae and hemolysins occur in vitro and in vivo in various extraintestinal Escherichia coli isolates. Microb Pathog. 1990 Mar;8(3):213–225. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90048-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensel M., Shea J. E., Gleeson C., Jones M. D., Dalton E., Holden D. W. Simultaneous identification of bacterial virulence genes by negative selection. Science. 1995 Jul 21;269(5222):400–403. doi: 10.1126/science.7618105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden D. W., Kronstad J. W., Leong S. A. Mutation in a heat-regulated hsp70 gene of Ustilago maydis. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1927–1934. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03596.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaniga K., Bossio J. C., Galán J. E. The Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes invF and invG encode homologues of the AraC and PulD family of proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Aug;13(4):555–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp S., Hacker J., Jarchau T., Goebel W. Large, unstable inserts in the chromosome affect virulence properties of uropathogenic Escherichia coli O6 strain 536. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):22–30. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.22-30.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Ochman H., Groisman E. A., Boyd E. F., Solomon F., Nelson K., Selander R. K. Relationship between evolutionary rate and cellular location among the Inv/Spa invasion proteins of Salmonella enterica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 1;92(16):7252–7256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.16.7252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Hessel A., Sanderson K. E. The XbaI-BlnI-CeuI genomic cleavage map of Salmonella typhimurium LT2 determined by double digestion, end labelling, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(13):4104–4120. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.13.4104-4120.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R., Osmond B. C., Shekhtman E., Wong A., Botstein D. Functional interchangeability of DNA replication genes in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli demonstrated by a general complementation procedure. Genetics. 1984 Sep;108(1):1–23. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel T. K., Jarvis K. G., Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. A genetic locus of enterocyte effacement conserved among diverse enterobacterial pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1664–1668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels T., Vanooteghem J. C., Lambert de Rouvroit C., China B., Gustin A., Boudry P., Cornelis G. R. Analysis of virC, an operon involved in the secretion of Yop proteins by Yersinia enterocolitica. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):4994–5009. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.4994-5009.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. M., Bajaj V., Lee C. A. A 40 kb chromosomal fragment encoding Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes is absent from the corresponding region of the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Feb;15(4):749–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara O., Dorit R. L., Gilbert W. Direct genomic sequencing of bacterial DNA: the pyruvate kinase I gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6883–6887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plano G. V., Barve S. S., Straley S. C. LcrD, a membrane-bound regulator of the Yersinia pestis low-calcium response. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7293–7303. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7293-7303.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Ausubel F. M. Conserved domains in bacterial regulatory proteins that respond to environmental stimuli. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):579–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90530-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmond G. P., Reeves P. J. Membrane traffic wardens and protein secretion in gram-negative bacteria. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jan;18(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Hessel A., Rudd K. E. Genetic map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition VIII. Microbiol Rev. 1995 Jun;59(2):241–303. doi: 10.1128/mr.59.2.241-303.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Komatsu K., Tobe T., Suzuki T., Yoshikawa M. Eight genes in region 5 that form an operon are essential for invasion of epithelial cells by Shigella flexneri 2a. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(8):2334–2346. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.8.2334-2346.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A. Electron microscope studies of experimental Salmonella infection. I. Penetration into the intestinal epithelium by Salmonella typhimurium. Am J Pathol. 1967 Jan;50(1):109–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gijsegem F., Genin S., Boucher C. Conservation of secretion pathways for pathogenicity determinants of plant and animal bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 1993 Aug;1(5):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(93)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M. M., Buysse J. M., Oaks E. V. Surface presentation of Shigella flexneri invasion plasmid antigens requires the products of the spa locus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1990–2001. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1990-2001.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youderian P., Sugiono P., Brewer K. L., Higgins N. P., Elliott T. Packaging specific segments of the Salmonella chromosome with locked-in Mud-P22 prophages. Genetics. 1988 Apr;118(4):581–592. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Timmis K. N. Analysis and construction of stable phenotypes in gram-negative bacteria with Tn5- and Tn10-derived minitransposons. Methods Enzymol. 1994;235:386–405. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)35157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]