Abstract
Research on the environmental risk factors for schizophrenia has focused on either psychosocial stress or drug exposure, with limited investigation of their interaction. A heightened dopaminergic stress response in patients with schizophrenia and individuals at clinical high risk (CHR) supports the dopaminergic sensitization hypothesis. Cannabis is believed to contribute to the development of schizophrenia, possibly through a cross-sensitization with stress. Twelve CHR and 12 cannabis-using CHR (CHR-CU, 11 dependent) subjects underwent [11C]-(+)-PHNO positron emission tomography scans, while performing a Sensorimotor Control Task (SMCT) and a stress condition (Montreal Imaging Stress task). The simplified reference tissue model was used to obtain binding potential relative to non-displaceable binding (BPND) in the whole striatum, its functional subdivisions (limbic striatum (LST), associative striatum (AST), and sensorimotor striatum (SMST)), globus pallidus (GP), and substantia nigra (SN). Changes in BPND, reflecting alterations in synaptic dopamine (DA) levels, were tested with analysis of variance. SMCT BPND was not significantly different between groups in any brain region (p>0.21). Although stress elicited a significant reduction in BPND in the CHR group, CHR-CU group exhibited an increase in BPND. Stress-induced changes in regional BPND between CHR-CU and CHR were significantly different in AST (p<0.001), LST (p=0.007), SMST (p=0.002), SN (p=0.021), and whole striatum (p=0.001), with trend level in the GP (p=0.099). All subjects experienced an increase in positive (attenuated) psychotic symptoms (p=0.001) following the stress task. Our results suggest altered DA stress reactivity in CHR subjects who concurrently use cannabis, as compared with CHR subjects. Our finding does not support the cross-sensitization hypothesis, which posits greater dopaminergic reactivity to stress in CHR cannabis users, but adds to the growing body of literature showing reduced DA (stress) response in addiction.
Keywords: [11C]-(+)-PHNO, positron emission tomography, clinical high risk, schizophrenia, dopamine, cannabis
INTRODUCTION
Cannabis is the most widely used illicit substance around the world (Bauman and Phongsavan, 1999) and is the illicit drug most commonly used by people with psychosis (Fowler et al, 1998; Hafner et al, 1999; Menezes et al, 1996), and those at elevated clinical risk for schizophrenia (Rosen et al, 2006). Several epidemiological studies have found that cannabis use increases the likelihood of developing schizophrenia (and psychosis) 1.8- to 3.1-fold (Andreasson et al, 1987; Arseneault et al, 2002, as reviewed in Arseneault et al, 2004). However, little is known about its effects on brain neurochemistry, or its impact on dopamine (DA) transmission, which is important as schizophrenia presents with abnormal DA synthesis and release (Laruelle and Abi-Dargham, 1999).
Schizophrenia is now perceived as a complex multifactorial disorder in which genetic predisposition and environmental factors interact to cause the disease. Both cannabis (Thornicroft, 1990) and stress (Norman and Malla, 1993) can exacerbate pre-existing psychotic symptoms or trigger their re-emergence in some (but not all) individuals with psychotic-related disorders (Mathers and Ghodse, 1992; Negrete et al, 1986; Thornicroft, 1990). A dysregulated response to stress and cannabis has been proposed as a potential etiological factor in the development of schizophrenia and its relapse. This model suggests that an endogenous organic diathesis or vulnerability interacts with internal or external stressors or drugs in the development of psychotic disorders (Murray and Fearon, 1999), with a number of environmental risk factors such as social alienation, early-life adversity, and cannabis use exerting a much higher effect on a sensitive subgroup (van Os et al, 2011). Although the underlying neurobiological condition/event that leads to increased vulnerability and causes exaggerated responses to stressors or drugs is unknown, one proposed mechanism is DA sensitization, whereby repeated exposure to life stressors or drugs progresses into increased stress (or drug)-associated DA activity, thus precipitating psychosis in those at risk or relapse in patients (Laruelle and Abi-Dargham, 1999; van Os et al, 2005). Indeed, recent work has shown increased DA release in response to psychosocial stress in individuals at clinical high risk (CHR) of developing schizophrenia and in antipsychotic-naive patients with schizophrenia (Mizrahi, 2010; Mizrahi et al, 2012). However, no such effect was observed in nonpsychiatric chronic cannabis users (Mizrahi et al, 2013) or healthy volunteers with no past history of low maternal care (Pruessner et al, 2004).
Interestingly, cannabinoids produce behavioral as well as neurochemical changes dependent on the environmental conditions under which they are administered. For example, cannabinoids administered to rats housed in stressful conditions alter striatal DA uptake and metabolism in contrast to the absence of effect on rats housed in normal conditions (Littleton et al, 1976; MacLean and Littleton, 1977). Furthermore, cross-sensitization between Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and stress has been reported (Suplita et al, 2008), suggesting that the physiological and psychological effects of cannabis could be altered in individuals experiencing environmental adversity. Indeed, recent studies in humans have shown that levels of the stress hormone cortisol correlate with the magnitude of DA release in response to amphetamine (Oswald et al, 2005). In addition, risk of psychosis has been shown to increase with childhood trauma and cannabis use through a synergistic interaction (Harley et al, 2010).
Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging provides the means of estimating changes in DA concentrations in vivo. Endogenous DA competes with the radiotracer for binding to the D2/3 receptors in the brain reducing the measured radiotracer binding potential (as reviewed in Laruelle, 2000). [11C]-(+)-PHNO, a D2/3 receptor agonist radiotracer used in this study, binds with ∼20-fold higher affinity for D3 over D2 receptor, providing increased sensitivity and allowing for quantification of the D3 receptor subtype (Narendran et al, 2006; Rabiner and Laruelle, 2010). In recent years, the role of DA D3 receptors in the neurochemical changes associated with drug dependence and relapse has come under intense investigation (Heidbreder et al, 2005; Ikemoto and Panksepp, 1999), with proposals of using D3-selective inhibitors for treatment of substance dependence (Heidbreder and Newman, 2010).
On the basis of the potential cross-sensitization between stress and cannabis in those at risk of developing schizophrenia, and the well-known finding of increased incidence of schizophrenia with early cannabis use, we tested the hypothesis that individuals at CHR of developing schizophrenia with concurrent cannabis use (cannabis-using CHR (CHR-CU)) have greater dopaminergic responses (increased [11C]-(+)-PHNO displacement) to a validated psychosocial stress challenge (Pruessner et al, 2004), as compared with CHR individuals with no cannabis use.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects
All subjects completed two PET scans at the same time of the day at least a week apart, first while performing a Sensory Motor Control Task (SMCT) and second the Montreal Imaging Stress Task (MIST). Data on [11C]-(+)-PHNO imaging with CHR subjects (but not CHR-CU) were used from a previous study (Mizrahi et al, 2012). CHR-CU were asked to refrain from using cannabis on the day of the scan (information on hours since the last use is provided below). All subjects were scanned during the same time frame and recruited from the same geographical region.
Inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) men or women between 18 and 40 years old; (2) capacity to provide informed consent; (3) meet diagnostic criteria for prodromal syndrome as per the Criteria of Prodromal Syndromes (COPS); (4) ‘moderately ill' on the Clinical Global Impression Scale or significant impairment in functioning, ie, <52 on Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) scale (Miller et al, 2003) or >9 on Scale of Prodromal Symptoms-positive subscale (SOPS-P). In addition, for CHR-CU, (5) regular cannabis use at least three times weekly and/or meeting DSM-IV criteria for cannabis dependence, and (6) positive drug screen for cannabis both at screening and on the days of the PET scans. Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) current or lifetime Axis I psychotic disorder, including affective psychoses (excluding cannabis dependence in CHR-CU); (2) current treatment with antipsychotic medication or lifetime use >4 weeks; (3) past or current history of a clinically significant central nervous system disorder that may contribute to prodromal symptoms or confuse their assessment; (4) substance abuse or dependence in the past 6 months (excluding cannabis for the CHR-CU group); and (5) metal implants that would preclude magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Assessment
Psychopathology measures
CHR were classified as per the COPS using the Structured Interview for Prodromal Symptoms (SIPS), which was administered to assess attenuated psychotic symptoms (McGlashan et al, 2001; Miller et al, 2002), incorporating the family history, GAF, and schizotypal personality disorder information. The CHR criteria include the following: attenuated positive symptoms syndrome, the genetic risk and deterioration syndrome, and the brief intermittent psychosis syndrome. The SOPS, which is part of the SIPS, is a dimensional 19-item instrument for quantifying prodromal state severity and has been used with SIPS to identify COPS criteria with excellent inter-rater reliability (κ=0.81; Miller et al, 2003). These results give a positive predictive value of 54%, a psychotic/nonpsychotic sensitivity of 1.0, and a specificity of 0.73 (Miller et al, 2003), supporting the criteria's validity for defining prodromal states that mark high imminent risk for psychosis. In addition, all subjects were screened for any Axis I psychopathology with the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV by a qualified psychiatrist (RM), and for marijuana use with the Marijuana Craving Questionnaire (MCQ) scale (Heishman and Singleton, 2006) and detailed personal and medical history.
Montreal Imaging Stress Task
Psychological stress was induced using the MIST task, which has been validated in previous fMRI and PET studies (Booij et al, 2007; Dedovic et al, 2005; Lederbogen et al, 2011; Pruessner et al, 2004; Pruessner et al, 2007). Briefly, subjects perform six 6-min segments of arithmetic while lying in the scanner. During the stress condition, the time constraint is adjusted to be slightly beyond each individual's abilities. Subjects were given negative verbal feedback by the investigator between each block, telling them that they need to improve their performance to reach minimum performance requirements. Before the stress task, subjects performed the sensory motor control PET session, a similar arithmetic task without time constraints or negative verbal feedback. In all experiments, the control or stress task was started ∼6–8 min before tracer injection, with 6 min of arithmetic questions and ∼1 to 2 min for either neutral or negative feedback and salivary cortisol measurement. The non-stress control was also administered as a practice trial on a separate day before the PET experiments, to reduce the effect of novelty. Subjective perception of stress was assessed before and after each PET session by state anxiety questionnaires (SAQs) (Spielberger et al, 1977) and visual analog scales. Subjects also completed the Parental Bonding Index (Parker et al, 1979), which has been associated with DA release in healthy volunteers (Pruessner et al, 2004).
Physiological Measures
Saliva samples were collected every 12 min throughout the experiment. Saliva-derived cortisol was analyzed using a time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay (Dressendorfer et al, 1992) and the area under the curve (AUC; g/dl/min) was calculated for each scanning session (Dressendorfer et al, 1992; Pruessner et al, 2003).
Image and Data Analyses
MRI acquisition
Subjects undertook a standard fast spin echo T1 (FSPGR, TE=5.3–15, TR=8.9–12, FOV=20 cm, matrix=256 × 256, slice thickness=1.5, NEX=1) and a proton density (TE=17, TR=6000, FOV=22 cm, matrix=256 × 256, slice thickness=2 mm, NEX=2) brain MRI images acquired on a 1.5T Signa-GE scanner. These images were used for the analysis of the individual PET scans and to rule out structural lesions.
PET acquisition
[11C]-(+)-PHNO radiosynthesis was performed as previously described (Wilson et al, 2005). Studies were carried out using a high-resolution PET/CT Siemens-Biograph HiRez XVI scanner (Siemens Molecular Imaging, Knoxville, TN), which measures radioactivity in 81 brain sections with a thickness of 2.0 mm each. PET data was acquired for 90 min following administration of ∼9–10 mCi of radiotracer (Table 1). A custom-fitted thermoplastic mask was made for each subject and used with a head fixation system during PET measurements to minimize head movement. The images were reconstructed with 2D filtered back projection algorithms with a ramp filter at Nyquist cut-off frequency.
Table 1. No Significant Difference between Groups or Conditions was Observed in Any Variable, Except for Smoking Status (χ2=8.167, p=0.004) and Trend Level for the Maternal Portion of the PBI (F=3.323, df=1,22, p=0.082).
| Demographics (SD) | CHR n=12 | CHR-CU n=12 | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 23.00±4.6 | 24.25±4.7 | F=0.419, df=1,22, p=0.524 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 7 | 6 | χ2=0.167, p=0.683 |
| Female | 5 | 6 | |
| Mother PBI | 35.83±5.8 | 40.42±6.5 | F=3.323, df=1,22, p=0.082 |
| Smoking status | |||
| Non-smoker | 11 | 8 | χ2=8.167, p=0.004 |
| Smoker | 1 | 4 | |
| Cigarettes/day | 10 | 9.13±8.0 | |
| Years of education | 14.08±3.1 | 13.25±1.8 | F=0.631, df=1,22, p=0.435 |
| Lifetime use (joints) | NA | 4892.91±4100.2 | |
| Years of cannabis use | NA | 9.64±4.8 | |
| Age at first cannabis use (years) | NA | 14.82±2.7 | |
| Number of joints per week | |||
| Control task | NA | 17.00±7.3 | |
| Stress task | NA | 14.36±7.8 | |
| Hours since last joint smoked | |||
| Control task | NA | 11.00±5.3 | |
| Stress task | NA | 13.3±5.8 | |
| Cannabinoids value (μg/l) | |||
| Control task | NA | 1852.81±2909.7 | |
| Stress task | NA | 2730.20±3347.4 | |
| SOPS symptoms | |||
| Positive | 11.25±2.9 | 12.64±2.0 | F=1.771, df=1,21, p=0.198 |
| Negative | 10.17±5.3 | 6.18±3.6 | F=4.356, df=1,21, p=0.049 |
| Disorganized | 4.17±2.1 | 4.36±2.5 | F=0.042, df=1,21, p=0.840 |
| General | 5.25±3.2 | 4.36±3.5 | F=0.410, df=1,21, p=0.529 |
| PET scan parameters | |||
| Amount injected (mCi) | |||
| Control task | 9.17±2.2 | 9.98±1.1 | F=1.325, df=1,22, p=0.262 |
| Stress task | 9.89±0.96 | 9.69±0.99 | F=0.247, df=1,22, p=0.624 |
| Specific activity (mCi/μmol) | |||
| Control task | 1014.84±434.3 | 1199.83±569.2 | F=0.801, df=1,22, p=0.380 |
| Stress task | 1003.82±470.6 | 1484.04±628.2 | F=4.492, df=1,22, p=0.046 |
| Mass injected (μg) | |||
| Control task | 2.58±0.90 | 2.26±0.96 | F=0.743, df=1,22, p=0.398 |
| Stress task | 2.92±0.90 | 1.93±0.90 | F=7.255, df=1,22, p=0.013 |
Abbreviations: CHR, clinical high; CHR-CU, cannabis-using CHR; NA, not applicable; PBI, Parental Bonding Index; PET, positron emission tomography; SOPS, Scale of Prodromal Symptoms.
PET data analysis
Time activity curves from the regions of interest (ROIs) were obtained from the dynamic [11C]-(+)-PHNO PET images. The striatum was divided using the individual subject's MRI into subdivisions based on the functional connections to the limbic, frontal executive, and motor brain regions: limbic striatum (LST, including the ventral striatum), associative striatum (AST, including the pre-dorsal putamen, and pre-dorsal and post-dorsal caudate), and sensorimotor striatum (SMST, post-dorsal putamen), based on a set of landmarks as described previously (Martinez et al, 2003). We also report stress-induced changes in non-displaceable binding (BPND) in the globus pallidus (GP) and substantia nigra (SN), using ROI landmarks previously described (Tziortzi et al, 2011). The ROIs were delineated using an automated method implemented in an in-house software (ROMI), abolishing subjectivity in manual ROI drawing (Rusjan et al, 2006). Activity from the right and left regions were averaged together, weighted by subregion volume, and used to derive binding potential of the radiotracer with respect to the non-displaceable compartment (BPND) using the simplified reference tissue model (SRTM). BPND is proportional to the more fundamental parameters of receptor number (Bmax) and affinity (1/Kd) [BP≈Bmax/Kd]. This method has been validated for BPND with [11C]-(+)-PHNO (Ginovart et al, 2007). Partial volume effects were corrected using the method of Rousset et al (1998), with further details provided in the online Supplementary Data.
Voxel-wise images were generated using the Receptor Parametric Mapping software (Gunn et al, 1997), where the subregion of the cerebellar cortex (excluding the vermis) almost completely devoid of D2/3 receptors served as the reference region. Each parametric map was spatially normalized to an anatomical template (Montreal Neurological Institute) using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) normalization and coregistration tools. BPND maps were used to assess significant contrast between conditions as follows: between groups for the baseline SMCT with independent t-test and SMCT vs MIST paired t-test within each group (CHR and CHR-CU) at the voxel level using an implicit mask of BPND>0.3 as reported previously (Mizrahi et al, 2012). Family-wise error correction was used as implemented in SPM2 (www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm).
Statistical Analysis
The primary hypothesis was tested using analysis of variance (ANOVA) to investigate differences in stress-induced [11C]-(+)-PHNO % BPND change between CHR and CHR-CU subjects, defined as 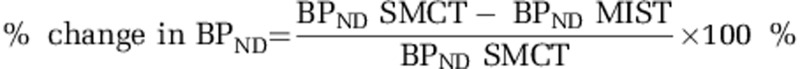 . Subjective perceived stress and cortisol stress levels were compared using ANOVAs between conditions (SMCT and MIST). Linear regression analyses were used to test the associations between stress-induced DA release and psychopathology. All analyses are two tailed with the conventional α=0.05.
. Subjective perceived stress and cortisol stress levels were compared using ANOVAs between conditions (SMCT and MIST). Linear regression analyses were used to test the associations between stress-induced DA release and psychopathology. All analyses are two tailed with the conventional α=0.05.
RESULTS
A total of 48 PET scans were acquired for the present study. CHR (n=12) and CHR-CU (n=12) groups had comparable demographics (Table 1). Out of 12 CHR-CU subjects, 11 met criteria for cannabis dependence and exhibited daily or higher use for at least 2 years (Table 1). Four subjects had no exposure to other drugs, whereas the remaining eight reported past recreational use (with only five using drugs in the past 12 months before scanning), with no abuse or dependence, of cocaine (n=6), amphetamine (n=1), ecstasy (n=5), mushrooms (n=2), LSD (n=2), ketamine (n=1), opioids (n=2), and methylphenidate (n=1). Within the CHR group, all subjects reported no history of drug use in the last 12 months before scanning, except for one subject who admitted to using cannabis three to five times per month (but had a negative drug screen on scanning days). At the time of the scan, urine drug screen confirmed lack of other substance abuse in all subjects, except for cannabis both at screening and on PET scan days, detected only in the CHR-CU group. None of the subjects exhibited any Axis I conditions at the time of the scan, except for cannabis dependence in the CHR-CU group. In the CHR group, one subject used fluoxetine (20 mg/day) and one used clonazepam (0.5 mg/day), whereas another one of the CHR-CU subjects used sertraline (100 mg/day).
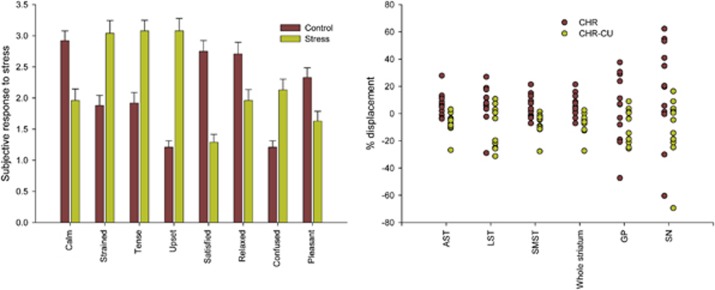
All subjects performed significantly worse at the MIST (number of errors 34.82±10.7 and 35.11±5.9 for CHR and CHR-CU, respectively), compared with the SMCT (5.17±3.4 and 6.40±3.0 for CHR and CHR-CU, respectively; paired sample t-test between conditions t=−9.96, p<0.001 for CHR and t=−15.15, p<0.001 for CHR-CU). CHR and CHR-CU subjects did not differ in their performance, quantified as number of errors and timeouts, either in the control (F=0.90, df=1,22, p=0.353) or stress task (F=0.054, df=1,21, p=0.82). As expected, SAQs revealed that all subjects were less calm (F=15.46, df=1,46, p<0.001) and satisfied (F=46.11, df=1,46, p<0.001), but more tense (F=23.73, df=1,46, p<0.001), strained (F=19.99, df=1,46, p<0.001), upset (F=69.83, df=1,46, p<0.001), and confused (F=20.54, df=1,46, p<0.001) following the stress task than following the control task, supporting the effectiveness of the stress paradigm (Figure 1, left panel). Comparing the differences between post-SMCT and post-MIST SAQ values, CHR-CU reported feeling more strained (F=7.00, df=1,22, p=0.015), tense (F=7.59, df=1,22, p=0.012), upset (F=18.267, df=1,22, p<0.001), and less satisfied (F=7.406, df=1,22, p=0.012) than the CHR subjects (additional behavioral information presented in the Supplementary Material). All subjects showed an increase in psychotic-like experiences following the stress task as opposed to the control task (t=−4.63, df=47, p<0.001). Both CHR and CHR-CU showed an increase in positive SOPS following the stress task (CHR: t=−2.292, df=11, p=0.043; CHR-CU: t=−3.527, df=11, p=0.005), but not the control task (CHR: t=−1.241, df=11, p=0.241; CHR-CU: t=−1.820, df=11, p=0.096), relative to the assessment at screening. Interestingly, although no significant difference was observed between the CHR- and CHR-CU-positive and disorganized SOPS scores at baseline screening, CHR-CU exhibited significantly less negative symptoms compared with CHR (F=4.356, df=1,21, p=0.049; Table 1). Comparing pre- and post-scan SOPS, significant increases were observed in positive attenuated symptoms following SMCT and MIST scans in the CHR group (SMCT: t=2.283, df=11, p=0.043; MIST: t=2.754, df=11, p=0.019) but only following the MIST in CHR-CU group (SMCT: t=1.915, df=11, p=0.082; MIST: t=3.079, df=11, p=0.010).
Figure 1.
Left: subjective response to stress for all subjects, depicting mean pre- vs post-scan change in State Anxiety Questionnaire (SAQ) categories (SE). Right: [11C]-(+)-PHNO positron emission tomography (PET) response to the stress in different regions of the brain.
BPND data did not show any difference between CHR and CHR-CU in any brain region investigated during the control task (Table 2): AST (F=0.22, df=1,22, p=0.644), LST (F=0.17, df=1,22, p=0.687), SMST (F=0.55, df=1,22, p=0.468), the whole striatum (F=0.11, df=1,22, p=0.743), GP (F=1.6, df=1,22, p=0.219), and SN (F=0.03, df=1,22, p=0.870). However, we found a significant difference in stress-induced %change in [11C]-(+)-PHNO BPND in CHR-CU relative to CHR in the entire striatum (Table 2; F=16.60, df=1,22, p=0.001), its subdivisions (AST: F=17.90, df=1,22, p<0.001), LST: F=9.03, df=1,22, p=0.007, and SMST: F=11.67, df=1,22, p=0.002), and SN (F=6.22, df=1,22, p=0.021), with a trend level in the GP (F=2.97, df=1,22, p=0.099). These findings present robust Cohen's d effect sizes of −1.61 (AST), −1.28 (LST), −1.32 (SMST), −1.56 (whole striatum), −0.55 (GP), and −0.77 (SN). Applying Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons, results remain significant in all regions, except for SN. Same results are obtained when the mass of [11C]-(+)-PHNO was added as a covariate to the analysis, with the exception of the difference in %change in SN, which becomes almost significant (F=3.172, p=0.063) but remains in the same direction. Differences in %change remain significant following partial volume effect correction, with the exception of the SN (F=1.638, df=1,22, p=0.214). The results also hold when the participants who used tobacco are excluded, with differences in %change in LST and SN becoming trend level: F=4.404, p=0.051 and F=3.624, p=0.074, respectively. In addition, even when the subjects with a history of drug use other than cannabis were excluded from the CHR-CU group, differences in % change remained significant in the whole striatum (F=7.415, df=1,14, p=0.016), AST (F=8.867, df=1,14, p=0.010), and LST (F=5.157, df=1,14, p=0.039), but not in the SMST (F=3.46, df=1,14, p=0.084), GP (F=0.697, df=1,14, p=0.418), and SN (F=1.723, df=1,14, p=0.210).
Table 2. BPND for Each Brain Region Studied in the Control Task (SMCT) and Stress Task (MIST) for Each Group.
| Regions |
CHR |
CHR-CU |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPND SMCT | BPND MIST | % Change | Paired t-test (df=11) | BPND SMCT | BPND MIST | % Change | Paired t-test (df=11) | |
| AST | 2.45±0.6 | 2.28±0.5 | 6.97±8.7 | t=2.39 | 2.36±0.4 | 2.52±0.4 | −7.04±7.5 | t=−3.66 |
| p=0.036 | p=0.004 | |||||||
| LST | 2.79±0.7 | 2.55±0.5 | 7.20±13.8 | t=2.08 | 2.89±0.4 | 3.17±0.5 | −10.48±15.0 | t=−2.33 |
| p=0.062 | p=0.040 | |||||||
| SMST | 2.64±0.6 | 2.45±0.5 | 4.55±8.7 | t=2.51 | 2.49±0.4 | 2.65±0.4 | −7.00±7.8 | t=−3.44 |
| p=0.029 | p=0.006 | |||||||
| Whole striatum | 2.53±0.5 | 2.35±0.5 | 6.32±8.8 | t=2.35 | 2.47±0.4 | 2.63±0.4 | −7.35±7.6 | t=−3.679 |
| p=0.039 | p=0.004 | |||||||
| GP | 2.51±1.5 | 2.21±1.1 | 3.96±25.0 | t=1.39 | 3.08±0.5 | 3.36±0.6 | −9.91 ±12.3 | t=−2.72 |
| p=0.192 | p=0.020 | |||||||
| Substantia nigra | 1.55±0.8 | 1.24±0.6 | 16.91±36.5 | t=1.94 | 1.51±0.4 | 1.71±0.4 | −17.15±30.1 | t=−1.64 |
| p=0.078 | p=0.129 | |||||||
Abbreviations: AST, associative striatum; BPND, non-displaceable binding; CHR, clinical high; CHR-CU, cannabis-using CHR; GP, globus pallidus; MIST, Montreal Imaging Stress Task; SMCT, Sensorimotor Control Task.
BPND data is consistent with % change data.
Negative SOPS scores were significantly inversely correlated with % change in BPND in the CHR group (Figure 2; LST (r=−0.66, p=0.020), GP (r=−0.72, p=0.009), and SN (r=−0.89, p<0.001), but not in the AST (r=−0.39, p=0.214), SMST (r=0.37, p=0.236), or the striatum taken as a whole (r=−0.10, p=0.762) in CHR subjects with higher scores in negative SOPS symptoms exhibiting lower %change in [11C]-PHNO BPND, with no correlation in the CHR-CU group (r=0.001, p=0.422). Correlations between changes in positive SOPS and BPND values are presented in the Supplementary Materials. No additional significant correlation was observed between positive, disorganization and general SOPS symptoms, and %change in any of the regions studied.
Figure 2.
Correlation between the % change of [11C]-(+)-PHNO non-displaceable binding (BPND) with negative Scale of Prodromal Symptoms (SOPS) in the limbic striatum (LST, top row), globus pallidus (GP, middle row), and substantia nigra (SN, bottom row) of clinical high risk (CHR, left column, solid circles) and cannabis-using CHR (CHR-CU) subjects (right column, empty circles).
We used a voxel-wise analysis to test without a priori anatomical hypotheses (ie, ROI definition) whether we could find a difference in SMCT [11C]-(+)-PHNO binding between groups and to confirm the increased tracer binding following the stress task in CHR-CU. In line with the ROI outcome, we found no difference (no clusters with p>0.05) between groups when comparing SMCT scans between groups. Clusters of robust stress-induced increase in BPND at the level of the dorsal striatum were detected in CHR-CU when comparing MIST to SMCT scan (Figure 3). In contrast, no significant clusters of increased BPND were detected in CHR (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
t-Statistical map overlaid on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) template (International Consortium for Brain Mapping template) illustrating clusters of significant increase in [11C]-(+)-PHNO binding (non-displaceable binding (BPND)) in response to the stress scan in clinical high risk (CHR, left) and CHR with concurrent cannabis use (CHR-CU, right) (MNI coordinates: −26–10 2; tmax=6.42, cluster size=495, p-uncorrected<0.001, p-corrected<0.002 and 22 6–6; tmax=5.17, cluster size=395, p-uncorrected<0.001, p-corrected<0.007).
Changes in salivary cortisol AUC were not significantly different between groups (F=1.37, df=1,20, p=0.256). However, the percent change in the cortisol response between the control task and stress task was significantly positively associated with the stress-induced change in [11C]-(+)-PHNO BPND in the AST (r=0.68, p=0.032), SMST (r=0.67, p=0.036), and the whole striatum (r=0.66, p=0.039) in CHR (Mizrahi et al, 2012) but not in CHR-CU.
There was a trend-level relationship between age of onset of cannabis use and AST %change in [11C]-(+)-PHNO BPND (r=0.56, p=0.09) such that a greater increase in tracer BPND was associated with earlier age of onset; however, there was no significant association with cannabis lifetime use or years used for any brain region (p>0.102). Exploring the behavioural aspects of cannabis use (as assessed with the MCQ), we observed an increase in the emotionality subscale such that CHR-CU were anticipating a relief from negative mood on the day of the stress scan but not on the day of the control scan (F=4.68, p=0.04). Interestingly, we observed that among the CHR-CU subjects, lower [11C]-(+)-PHNO BPND in the AST, LST, SMST, and whole striatum in the SMCT condition correlated with higher emotionality (r=0.74, p=0.009; r=0.75, p=0.008; r=0.60, p=0.05; and r=0.76, p=0.007, respectively) and expectancy (SMST: r=0.62, p=0.04 and whole striatum: r=0.62, p=0.04, respectively) following the MIST. In addition, CHR-CU subjects with higher emotionality scores preceding the MIST scan exhibited larger %change in [11C]-(+)-PHNO BPND in the LST (r=0.64, p=0.035). MCQ measurements did not correlate with the cortisol measurements.
PET scans took place on average 11±5.3 (3.5–18.5 range) and 13.3±5.8 (2.5–20 range) h (SMCT and MIST, respectively) since the last cannabis use (F=0.91, p=0.351), with 4 of 12 CHR-CU subjects reported using cannabis <10 h before the SMCT or MIST scan (Table 1). The PET imaging results presented in the study (increased stress-induced BPND in the CHR-CU, no significant difference in SMCT BPND) were no different when these four subjects are excluded from the analyses. In addition, no correlation was observed between the hours since last cannabis use before the scan and the PET outcomes (BPND of the SMCT or MIST session, % change in BPND).
DISCUSSION
Our results suggest increased stress-induced [11C]-(+)-PHNO binding in the striatum and all its functional subdivisions (AST, LST, and SMST), as well as in the SN in CHR cannabis-dependent individuals, despite increased positive attenuated psychotic symptoms in response to stress. Our findings using ROI approach are corroborated by the voxel-wise analysis.
Low striatal DA receptor (D2/3) availability and low amphetamine-induced DA release in the ventral striatum have been observed with substance-use disorders, including alcoholism (Martinez et al, 2005; Volkow et al, 1996), heroin (Martinez et al, 2012), cocaine (Volkow et al, 1993), and methamphetamine (Volkow et al, 2001) abuse. Conversely, studies in patients with schizophrenia and those in putative prodromal states have shown a sensitization of dopaminergic neurotransmission, manifested as increased DA release (ie, reduced tracer binding) in response to amphetamine (Abi-Dargham et al, 1998; Laruelle et al, 1999; Laruelle et al, 1996) or stress (Mizrahi et al, 2012), compared with healthy volunteers. Importantly, a recent study in patients with schizophrenia and substance dependence (including cannabis) showed a blunted DA response to amphetamine (Thompson et al, 2013), consistent with our results. Observed changes in stress-induced alterations in BPND in CHR-CU do not significantly differ from past observations in healthy volunteers (Mizrahi et al, 2012), although a clear trend is present where the CHR-CU group exhibits a general increase in BPND (hence, negative [11C]-(+)-PHNO binding %change) in response to stress (AST: HV=−2.87±9.21, CHR-CU=−7.04±7.46, F=1.48, df=1,22, p=0.236; LST: HV=−1.69±13.44, CHR-CU=−10.48±14.99, F=2.29, df=1,22, p=0.145; SMST: HV=−1.35±9.45, CHR-CU=−7.01±7.82, F=2.55, df=1,22, p=0.125; and whole striatum: HV=−2.41±9.10, CHR-CU=−7.35±7.63, F=2.08, df=1,22, p=0.162).
A major difference between the agonist [11C]-(+)-PHNO and the commonly used antagonist radiotracer [11C]-raclopride is its ∼20-fold higher affinity for the D3 receptors over the D2 (Narendran et al, 2006; Rabiner et al, 2009), resulting in increased sensitivity to DA levels in D3-rich regions. The D3 proportion of total DA receptor density varies from 100 and 67% in D3-rich regions (SN and GP, respectively; Searle et al, 2010; Tziortzi et al, 2011) to 10–40% in other striatal regions (Searle et al, 2010; Searle et al, 2013; Tziortzi et al, 2011). Recent studies have reported increased D3 receptor availability in addictions by showing increased [11C]-(+)-PHNO BPND in D3-rich areas of chronic methamphetamine users (Boileau et al, 2012) and elevated binding of the 3H-labeled version of (+)-PHNO in rats following prolonged THC exposure (Ginovart et al, 2012). In our current work we did not observe any differences in the control task BPND values between CHR and CHR-CU (albeit our baseline is not a ‘true' baseline). The stress-induced [11C]-(+)-PHNO BPND increase, however, is observed in both relatively D2-rich (striatum) and D3-rich (SN) regions of the brain. Although recent work in addiction research has been oriented towards the D3 DA receptor subtype, the differences in stress-induced %change in BPND observed in our study were more significant in the D2-rich regions. Taking into consideration that no stress-induced [11C]-(+)-PHNO BPND change was observed in healthy cannabis users (Mizrahi et al, 2013), our results suggest that cannabis dependence presents with a reversal of the dopaminergic sensitization in D2-rich regions of CHR subjects (Mizrahi et al, 2012).
The observed increase in the MCQ emotionality subscale at the day of the stress task (compared with the SMCT) confirms the link between stress and cannabis craving, suggesting that a stressful experience is associated with increased anticipation of relief from the negative mood. Linkage between lower receptor availability during the control task, reflective of either receptor downregulation or higher DA levels, and higher emotionality and expectancy indices may reflect the putative relationship between the dopaminergic system and craving (Volkow et al, 2006). Although our study is not powered to evaluate this further, the finding supports future investigations exploring the relationship between dopaminergic signaling in addictions and drug craving under stress. Considering that D3 receptors may be involved in the regulation of motivation and reward (Murray et al, 1994), [11C]-(+)-PHNO could have a major role in future efforts.
Reduced total scores in the negative dimension of SOPS observed in CHR-CU compared with CHR support previous reports of decreased negative symptoms among cannabis-using patients with schizophrenia (Addington and Addington, 1998; Bersani et al, 2002; Compton et al, 2004; Dubertret et al, 2006; Peralta and Cuesta, 1992). The patients with cannabis use may represent a higher-functioning subgroup of CHR (DeRosse et al, 2010), who present with better social skills needed to purchase drugs. Alternatively, cannabis use may alleviate the negative symptoms in CHR subjects. High rate of cannabis use among patients with schizophrenia and those at risk of developing the disease could therefore be consistent with the addiction vulnerability hypothesis (Chambers et al, 2001). Alternatively, a putative mechanism underlying the self-medication perspective comes from recent animal studies that have implicated the endogenous cannabinoid anandamide through its action on the brain CB1 receptors in the regulation of the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis of stress response (Hill et al, 2009; Hill et al, 2005; Rademacher et al, 2008). It is conceivable that stimulation of CB1 receptors by exogenous cannabis suppresses the HPA response, attenuating the stress-induced DA release. Future longitudinal studies will be able to address this issue. In our study, difference in cortisol response between the control and stress conditions in CHR correlated with stress-induced striatal BPND changes, but not in the CHR-CU group, warranting further studies into possible decoupling of HPA response from dopaminergic signaling in cannabis users.
Some limitations are typical in neurochemical brain-imaging studies. First, we did not control for type of marijuana used by subjects. Over the past decades, the THC content in marijuana consumed in North America has been increasing because of the availability of more potent strains. This may have significantly affected the results of the present study, given that the different components of the marijuana used may have opposite effects on brain DA function (Murphy et al, 1990); however, all study participants were recruited from the same geographical area and within the same time frame. Second, the inclusion in the CHR-CU subjects who have a past occasional use of drugs other than cannabis reflects the nature of the population from which the subjects were recruited. The use of illegal substances, as well as cigarette smoking, were suggested to alter striatal dopaminergic signaling. CHR population exhibits high rates of substance and tobacco use (Rosen et al, 2006), making exclusion of any past use or smokers impractical. However, present results (significant difference in stress-induced %change in BPND between CHR and CHR-CU groups) remain even after removing subjects that used tobacco or had a history of use of other drugs from the analysis. Third, the period of abstinence from cannabis use varied in the scanned subjects, as abstinence was not among the inclusion criteria. To exclude the possibility of acute effects of cannabis (considered to be modest or less; Bossong et al, 2009; Stokes et al, 2012), we re-analyzed the data excluding subjects who used cannabis <10 h before the scan, with the presented results remaining significant. In addition, because of the group sizes and the fact that our study was powered to test a difference on [11C]-(+)-PHNO binding between groups, the correlations we explored with clinical measures are not significant when correcting for multiple comparisons using the Bonferroni approach, except for the correlation between whole striatum %change in [11C]-(+)-PHNO BPND and emotionality index in CHR-CU subjects, and the total SOPS negative symptoms and %change in [11C]-(+)-PHNO BPND in the SN. In addition, it has recently been suggested that [11C]-(+)-PHNO may not be at tracer dose in the D3-rich regions such as the SN, which would hinder accurate quantification (Gallezot et al, 2009; Rabiner and Laruelle, 2010; Searle et al, 2013). Incorporation of the factor of injected mass in the comparison of %change of tracer BPND did reduce the difference observed in SN, but not in the D2-rich regions. Importantly, our findings are present in all brain regions investigated, including D2-specific regions such as the AST where this effect is not present (Shotbolt et al, 2011). To exclude any potential effect of the putative specific [11C]-(+)-PHNO binding in the cerebellum, we have compared cerebellar tracer uptake between SMCT and MIST tasks, showing almost complete overlap (Supplementary Materials). Although the cerebellum standard uptake values over time show CHR-CU tracer uptake during MIST scan to be slightly lower than the SMCT scan, the difference is unlikely to explain the findings of the study. Finally, independent confirmation of the PET findings using the MIST procedure in large cohorts are warranted to strengthen the general applicability of the [11C]-PHNO MIST data. Finally, it should be noted that owing to the number of analyses performed, correlations presented in the Supplementary Materials should be considered exploratory data.
In conclusion, our current work presents evidence of stress-induced increased [11C]-(+)-PHNO binding in CHR subjects who concurrently use cannabis compared with non-cannabis-using CHR, supporting recent publications exploring amphetamine DA response in patients with schizophrenia and substance dependence (Thompson et al, 2012), and cannabis users who have psychotic experiences (Bloomfield et al, 2013). Our findings highlight the interaction between stress, dopaminergic signaling, and cannabis, opening new venues for future research. Given that drug use is highly dependent on the environment, and recent epidemiological data showing how environmental risk factors affect brain function (Lederbogen et al, 2011), further studies exploring the neurochemical changes of the interaction between stress, cannabis use, and schizophrenia are warranted.
FUNDING AND DISCLOSURE
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank Armando Garcia, Winston Stableford, and Peter Bloomfield. Special thanks to Dr J Addington for her expertise on CHR and Dr J Pruessner for the MIST. This study was supported by the Ontario Mental Health Foundation (OMHF), Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI), and the Ontario Ministry of Research and Innovation. RM is supported by the New Investigator Award from CIHR and the OMHF New Investigator Fellowship.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Neuropsychopharmacology website (http://www.nature.com/npp)
Supplementary Material
References
- Abi-Dargham A, Gil R, Krystal J, Baldwin RM, Seibyl JP, Bowers M, et al. Increased striatal dopamine transmission in schizophrenia: confirmation in a second cohort. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155:761–767. doi: 10.1176/ajp.155.6.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Addington J, Addington D. Effect of substance misuse in early psychosis. Br J Psychiatry Suppl. 1998;172:134–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasson S, Allebeck P, Engstrom A, Rydberg U. Cannabis and schizophrenia. A longitudinal study of Swedish conscripts. Lancet. 1987;2:1483–1486. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92620-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arseneault L, Cannon M, Poulton R, Murray R, Caspi A, Moffitt TE. Cannabis use in adolescence and risk for adult psychosis: longitudinal prospective study. BMJ. 2002;325:1212–1213. doi: 10.1136/bmj.325.7374.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arseneault L, Cannon M, Witton J, Murray RM. Causal association between cannabis and psychosis: examination of the evidence. Br J Psychiatry. 2004;184:110–117. doi: 10.1192/bjp.184.2.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauman A, Phongsavan P. Epidemiology of substance use in adolescence: prevalence, trends and policy implications. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1999;55:187–207. doi: 10.1016/s0376-8716(99)00016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bersani G, Orlandi V, Gherardelli S, Pancheri P. Cannabis and neurological soft signs in schizophrenia: absence of relationship and influence on psychopathology. Psychopathology. 2002;35:289–295. doi: 10.1159/000067064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield MA, Morgan CJ, Egerton A, Kapur S, Curran HV, Howes OD. Dopaminergic function in cannabis users and its relationship to cannabis-induced psychotic symptoms. Biol Psychiatry. 2013;S0006-3223:00502–00507. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.05.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boileau I, Payer D, Houle S, Behzadi A, Rusjan PM, Tong J, et al. Higher binding of the dopamine D3 receptor-preferring ligand [11C]-(+)-propyl-hexahydro-naphtho-oxazin in methamphetamine polydrug users: a positron emission tomography study. J Neurosci. 2012;32:1353–1359. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4371-11.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booij L, Welfeld K, Dagher A, Leyton M, Boileau I, Sibon I, et al. Cross-sensitization between stimulants and stress in humans: behavioral and neurochemical correlates. SOBP, San Diego. 2007;61:236S. [Google Scholar]
- Bossong MG, van Berckel BN, Boellaard R, Zuurman L, Schuit RC, Windhorst AD, et al. Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol induces dopamine release in the human striatum. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009;34:759–766. doi: 10.1038/npp.2008.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers RA, Krystal JH, Self DW. A neurobiological basis for substance abuse comorbidity in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2001;50:71–83. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(01)01134-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton MT, Furman AC, Kaslow NJ. Lower negative symptom scores among cannabis-dependent patients with schizophrenia-spectrum disorders: preliminary evidence from an African American first-episode sample. Schizophr Res. 2004;71:61–64. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2004.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedovic K, Renwick R, Mahani NK, Engert V, Lupien SJ, Pruessner JC. The Montreal Imaging Stress Task: using functional imaging to investigate the effects of perceiving and processing psychosocial stress in the human brain. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2005;30:319–325. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRosse P, Kaplan A, Burdick KE, Lencz T, Malhotra AK. Cannabis use disorders in schizophrenia: effects on cognition and symptoms. Schizophr Res. 2010;120:95–100. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2010.04.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressendorfer RA, Kirschbaum C, Rohde W, Stahl F, Strasburger CJ. Synthesis of a cortisol-biotin conjugate and evaluation as a tracer in an immunoassay for salivary cortisol measurement. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;43:683–692. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90294-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubertret C, Bidard I, Ades J, Gorwood P. Lifetime positive symptoms in patients with schizophrenia and cannabis abuse are partially explained by co-morbid addiction. Schizophr Res. 2006;86:284–290. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2006.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler IL, Carr VJ, Carter NT, Lewin TJ. Patterns of current and lifetime substance use in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1998;24:443–455. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.schbul.a033339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallezot J, Beaver J, Nabulsi N, Weinzimmer D, Slifstein M, R G, et al. 2009[11C]-PHNO studies in rhesus monkey: In vivo affinity for D2 and D3 receptors and dosimetryJ Nucl Med 50601
- Ginovart N, Tournier BB, Moulin-Sallanon M, Steimer T, Ibanez V, Millet P. Chronic Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol exposure induces a sensitization of dopamine d2/3 receptors in the mesoaccumbens and nigrostriatal systems. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37:2355–2367. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginovart N, Willeit M, Rusjan P, Graff A, Bloomfield PM, Houle S, et al. Positron emission tomography quantification of [11C]-(+)-PHNO binding in the human brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27:857–871. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn RN, Lammertsma AA, Hume SP, Cunningham VJ. Parametric imaging of ligand-receptor binding in PET using a simplified reference region model. Neuroimage. 1997;6:279–287. doi: 10.1006/nimg.1997.0303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafner H, Maurer K, Loffler W, Wan der Heiden W, Stein A, Konecke R, et al. 1999Onset and prodromal phase as a determinants of the courseIn: Gattaz W, Haffner H (eds)Search for the cause of schizophrenia, Vol IVSpringer, Verlag: Berlin [Google Scholar]
- Harley M, Kelleher I, Clarke M, Lynch F, Arseneault L, Connor D, et al. Cannabis use and childhood trauma interact additively to increase the risk of psychotic symptoms in adolescence. Psychol Med. 2010;40:1627–1634. doi: 10.1017/S0033291709991966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidbreder CA, Gardner EL, Xi ZX, Thanos PK, Mugnaini M, Hagan JJ, et al. The role of central dopamine D3 receptors in drug addiction: a review of pharmacological evidence. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2005;49:77–105. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.12.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidbreder CA, Newman AH. Current perspectives on selective dopamine D(3) receptor antagonists as pharmacotherapeutics for addictions and related disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1187:4–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05149.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heishman SJ, Singleton EG. Assessment of cannabis craving using the Marijuana Craving Questionnaire. Methods Mol Med. 2006;123:209–216. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-999-0:209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill MN, McLaughlin RJ, Morrish AC, Viau V, Floresco SB, Hillard CJ, et al. Suppression of amygdalar endocannabinoid signaling by stress contributes to activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009;34:2733–2745. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill MN, Patel S, Carrier EJ, Rademacher DJ, Ormerod BK, Hillard CJ, et al. Downregulation of endocannabinoid signaling in the hippocampus following chronic unpredictable stress. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30:508–515. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemoto S, Panksepp J. The role of nucleus accumbens dopamine in motivated behavior: a unifying interpretation with special reference to reward-seeking. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1999;31:6–41. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(99)00023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laruelle M. Imaging synaptic neurotransmission with in vivo binding competition techniques: a critical review. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20:423–451. doi: 10.1097/00004647-200003000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A. Dopamine as the wind of the psychotic fire: new evidence from brain imaging studies. J Psychopharmacol. 1999;13:358–371. doi: 10.1177/026988119901300405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A, Gil R, Kegeles L, Innis R. Increased dopamine transmission in schizophrenia: relationship to illness phases. Biol Psychiatry. 1999;46:56–72. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(99)00067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A, van Dyck CH, Gil R, D'Souza CD, Erdos J, et al. Single photon emission computerized tomography imaging of amphetamine-induced dopamine release in drug-free schizophrenic subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:9235–9240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.17.9235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederbogen F, Kirsch P, Haddad L, Streit F, Tost H, Schuch P, et al. City living and urban upbringing affect neural social stress processing in humans. Nature. 2011;474:498–501. doi: 10.1038/nature10190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littleton JM, Maclean KI, Brownlee G. Proceedings: Alterations in dopamine uptake in rat corpus striatum induced by combinations of stress and delta8-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta8-THC) Br J Pharmacol. 1976;56:370P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean KI, Littleton JM. Environmental stress as a factor in the response of rat brain catecholamine metabolism to delta8-tetrahydrocannabinol. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977;41:171–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90206-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez D, Gil R, Slifstein M, Hwang DR, Huang Y, Perez A, et al. Alcohol dependence is associated with blunted dopamine transmission in the ventral striatum. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;58:779–786. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.04.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez D, Saccone PA, Liu F, Slifstein M, Orlowska D, Grassetti A, et al. Deficits in dopamine D(2) receptors and presynaptic dopamine in heroin dependence: commonalities and differences with other types of addiction. Biol Psychiatry. 2012;71:192–198. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.08.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez D, Slifstein M, Broft A, Mawlawi O, Hwang DR, Huang Y, et al. Imaging human mesolimbic dopamine transmission with positron emission tomography. Part II: amphetamine-induced dopamine release in the functional subdivisions of the striatum. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003;23:285–300. doi: 10.1097/01.WCB.0000048520.34839.1A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathers DC, Ghodse AH. Cannabis and psychotic illness. Br J Psychiatry. 1992;161:648–653. doi: 10.1192/bjp.161.5.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlashan TH, Miller TJ, Woods SW. Pre-onset detection and intervention research in schizophrenia psychoses: current estimates of benefit and risk. Schizophr Bull. 2001;27:563–570. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.schbul.a006896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes PR, Johnson S, Thornicroft G, Marshall J, Prosser D, Bebbington P, et al. Drug and alcohol problems among individuals with severe mental illness in south London. Br J Psychiatry. 1996;168:612–619. doi: 10.1192/bjp.168.5.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller TJ, McGlashan TH, Rosen JL, Cadenhead K, Cannon T, Ventura J, et al. Prodromal assessment with the structured interview for prodromal syndromes and the scale of prodromal symptoms: predictive validity, interrater reliability, and training to reliability. Schizophr Bull. 2003;29:703–715. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.schbul.a007040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller TJ, McGlashan TH, Rosen JL, Somjee L, Markovich PJ, Stein K, et al. Prospective diagnosis of the initial prodrome for schizophrenia based on the Structured Interview for Prodromal Syndromes: preliminary evidence of interrater reliability and predictive validity. Am J Psychiatry. 2002;159:863–865. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.159.5.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi R. Advances in PET analyses of stress and dopamine. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35:348–349. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi R, Addington J, Rusjan PM, Suridjan I, Ng A, Boileau I, et al. Increased stress-induced dopamine release in psychosis. Biol Psychiatry. 2012;71:561–567. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi R, Suridjan I, Kenk M, George TP, Wilson A, Houle S, et al. Dopamine response to psychosocial stress in chronic cannabis users: a PET study with [11C]-(+)-PHNO. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013;38:673–682. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy LL, Steger RW, Smith MS, Bartke A. Effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabinol and cannabidiol, alone and in combinations, on luteinizing hormone and prolactin release and on hypothalamic neurotransmitters in the male rat. Neuroendocrinology. 1990;52:316–321. doi: 10.1159/000125604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray AM, Ryoo HL, Gurevich E, Joyce JN. Localization of dopamine D3 receptors to mesolimbic and D2 receptors to mesostriatal regions of human forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:11271–11275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray RM, Fearon P. The developmental ‘risk factor' model of schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res. 1999;33:497–499. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3956(99)00032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narendran R, Slifstein M, Guillin O, Hwang Y, Hwang DR, Scher E, et al. Dopamine (D2/3) receptor agonist positron emission tomography radiotracer [11C]-(+)-PHNO is a D3 receptor preferring agonist in vivo. Synapse. 2006;60:485–495. doi: 10.1002/syn.20325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negrete JC, Knapp WP, Douglas DE, Smith WB. Cannabis affects the severity of schizophrenic symptoms: results of a clinical survey. Psychol Med. 1986;16:515–520. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700010278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman RM, Malla AK. Stressful life events and schizophrenia. I: A review of the research. Br J Psychiatry. 1993;162:161–166. doi: 10.1192/bjp.162.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald LM, Wong DF, McCaul M, Zhou Y, Kuwabara H, Choi L, et al. Relationships among ventral striatal dopamine release, cortisol secretion, and subjective responses to amphetamine. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30:821–832. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker G, Tupling H, Brown LB. A parental bonding instrument. Br J Med Psychology. 1979;52:1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Peralta V, Cuesta MJ. Influence of cannabis abuse on schizophrenic psychopathology. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1992;85:127–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1992.tb01456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruessner JC, Champagne F, Meaney MJ, Dagher A. Dopamine release in response to a psychological stress in humans and its relationship to early life maternal care: a positron emission tomography study using [11C]raclopride. J Neurosci. 2004;24:2825–2831. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3422-03.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruessner JC, Dedovic K, Khalili-Mahani N, Engert V, Pruessner M, Buss C, et al. Deactivation of the limbic system during acute psychosocial stress: evidence from positron emission tomography and functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;63:234–240. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.04.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruessner JC, Kirschbaum C, Meinlschmid G, Hellhammer DH. Two formulas for computation of the area under the curve represent measures of total hormone concentration versus time-dependent change. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2003;28:916–931. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4530(02)00108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabiner EA, Laruelle M. Imaging the D3 receptor in humans in vivo using [11C](+)-PHNO positron emission tomography (PET) Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;13:289–290. doi: 10.1017/S1461145710000088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabiner EA, Slifstein M, Nobrega J, Plisson C, Huiban M, Raymond R, et al. In vivo quantification of regional dopamine-D3 receptor binding potential of (+)-PHNO: Studies in non-human primates and transgenic mice. Synapse. 2009;63:782–793. doi: 10.1002/syn.20658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rademacher DJ, Meier SE, Shi L, Ho WS, Jarrahian A, Hillard CJ. Effects of acute and repeated restraint stress on endocannabinoid content in the amygdala, ventral striatum, and medial prefrontal cortex in mice. Neuropharmacology. 2008;54:108–116. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen JL, Miller TJ, D'Andrea JT, McGlashan TH, Woods SW. Comorbid diagnoses in patients meeting criteria for the schizophrenia prodrome. Schizophr Res. 2006;85:124–131. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2006.03.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset OG, Ma Y, Evans AC. Correction for partial volume effects in PET: principle and validation. J Nucl Med. 1998;39:904–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusjan P, Mamo D, Ginovart N, Hussey D, Vitcu I, Yasuno F, et al. An automated method for the extraction of regional data from PET images. Psychiatry Res. 2006;147:79–89. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2006.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle G, Beaver JD, Comley RA, Bani M, Tziortzi A, Slifstein M, et al. Imaging dopamine D3 receptors in the human brain with positron emission tomography, [11C]PHNO, and a selective D3 receptor antagonist. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;68:392–399. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.04.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle GE, Beaver JD, Tziortzi A, Comley RA, Bani M, Ghibellini G, et al. Mathematical modelling of [11C]-(+)-PHNO human competition studies. Neuroimage. 2013;68:119–132. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.11.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotbolt P, Tziortzi AC, Searle GE, Colasanti A, van der Aart J, Abanades S, et al. Within-subject comparison of [(11)C]-(+)-PHNO and [(11)C]raclopride sensitivity to acute amphetamine challenge in healthy humans. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011;32:127–136. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2011.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielberger CD, Gorusch RL, Lushene RE, Vagg PR, Jacobs GA. State and Trait Anxiety Inventory for Adults. Mind Garden: Redwood City, CA; 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes PR, Egerton A, Watson B, Reid A, Lappin J, Howes OD, et al. History of cannabis use is not associated with alterations in striatal dopamine D2/D3 receptor availability. J Psychopharmacol. 2012;26:144–149. doi: 10.1177/0269881111414090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suplita RL, 2nd, Eisenstein SA, Neely MH, Moise AM, Hohmann AG. Cross-sensitization and cross-tolerance between exogenous cannabinoid antinociception and endocannabinoid-mediated stress-induced analgesia. Neuropharmacology. 2008;54:161–171. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson JL, Urban N, Slifstein M, Xu X, Kegeles LS, Girgis RR, et al. Striatal dopamine release in schizophrenia comorbid with substance dependence. Mol Psychiatry. 2012;18:909–915. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson JL, Urban N, Slifstein M, Xu X, Kegeles LS, Girgis RR, et al. Striatal dopamine release in schizophrenia comorbid with substance dependence. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;18:909–915. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornicroft G. Cannabis and psychosis. Is there epidemiological evidence for an association. Br J Psychiatry. 1990;157:25–33. doi: 10.1192/bjp.157.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tziortzi AC, Searle GE, Tzimopoulou S, Salinas C, Beaver JD, Jenkinson M, et al. Imaging dopamine receptors in humans with [11C]-(+)-PHNO: dissection of D3 signal and anatomy. Neuroimage. 2011;54:264–277. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Os J, Kenis G, Rutten BP. The environment and schizophrenia. Nature. 2011;468:203–212. doi: 10.1038/nature09563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Os J, Krabbendam L, Myin-Germeys I, Delespaul P. The schizophrenia envirome. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2005;18:141–145. doi: 10.1097/00001504-200503000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkow ND, Chang L, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Franceschi D, Sedler M, et al. Loss of dopamine transporters in methamphetamine abusers recovers with protracted abstinence. J Neurosci. 2001;21:9414–9418. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-23-09414.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang GJ, Hitzemann R, Logan J, Schlyer DJ, et al. Decreased dopamine D2 receptor availability is associated with reduced frontal metabolism in cocaine abusers. Synapse. 1993;14:169–177. doi: 10.1002/syn.890140210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Logan J, Hitzemann R, Ding YS, et al. Decreases in dopamine receptors but not in dopamine transporters in alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1996;20:1594–1598. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1996.tb05936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Telang F, Fowler JS, Logan J, Childress AR, et al. Cocaine cues and dopamine in dorsal striatum: mechanism of craving in cocaine addiction. J Neurosci. 2006;26:6583–6588. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1544-06.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson AA, McCormick P, Kapur S, Willeit M, Garcia A, Hussey D, et al. Radiosynthesis and evaluation of [11C]-(+)-4-propyl-3,4,4a,5,6,10b-hexahydro-2H-naphtho[1,2-b][1,4]oxazin-9-ol as a potential radiotracer for in vivo imaging of the dopamine D2 high-affinity state with positron emission tomography. J Med Chem. 2005;48:4153–4160. doi: 10.1021/jm050155n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.