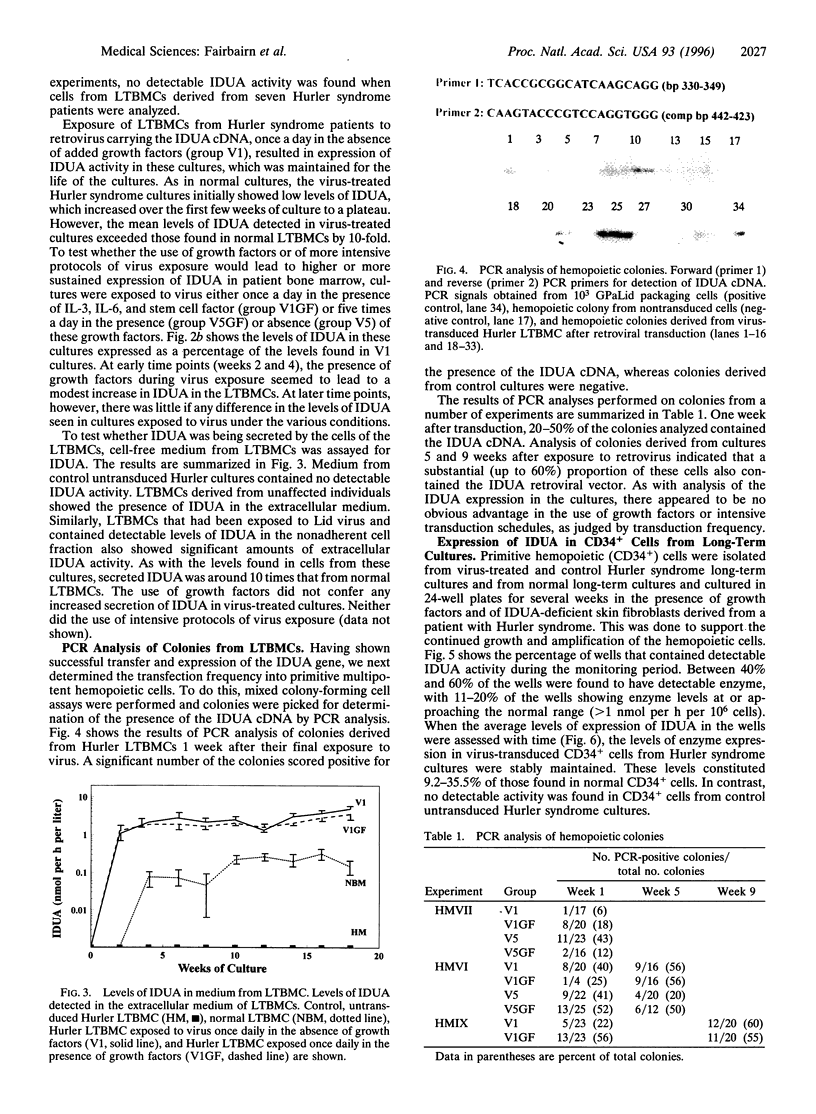
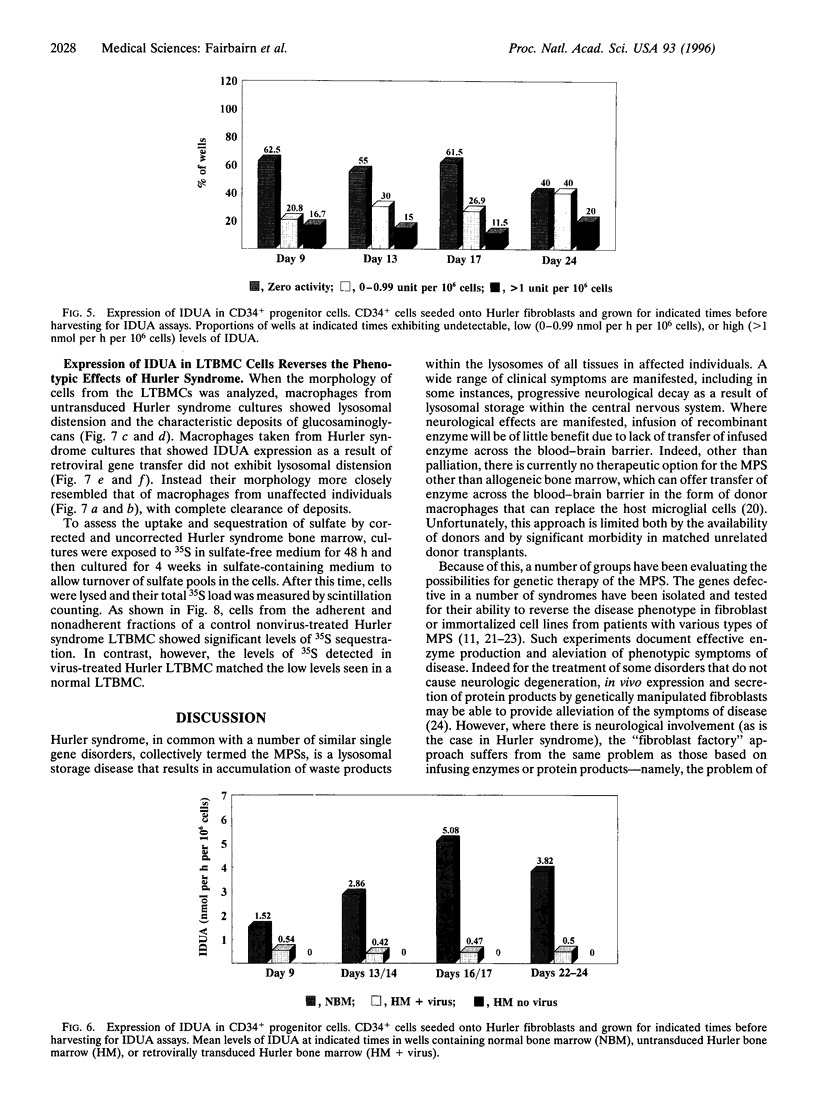
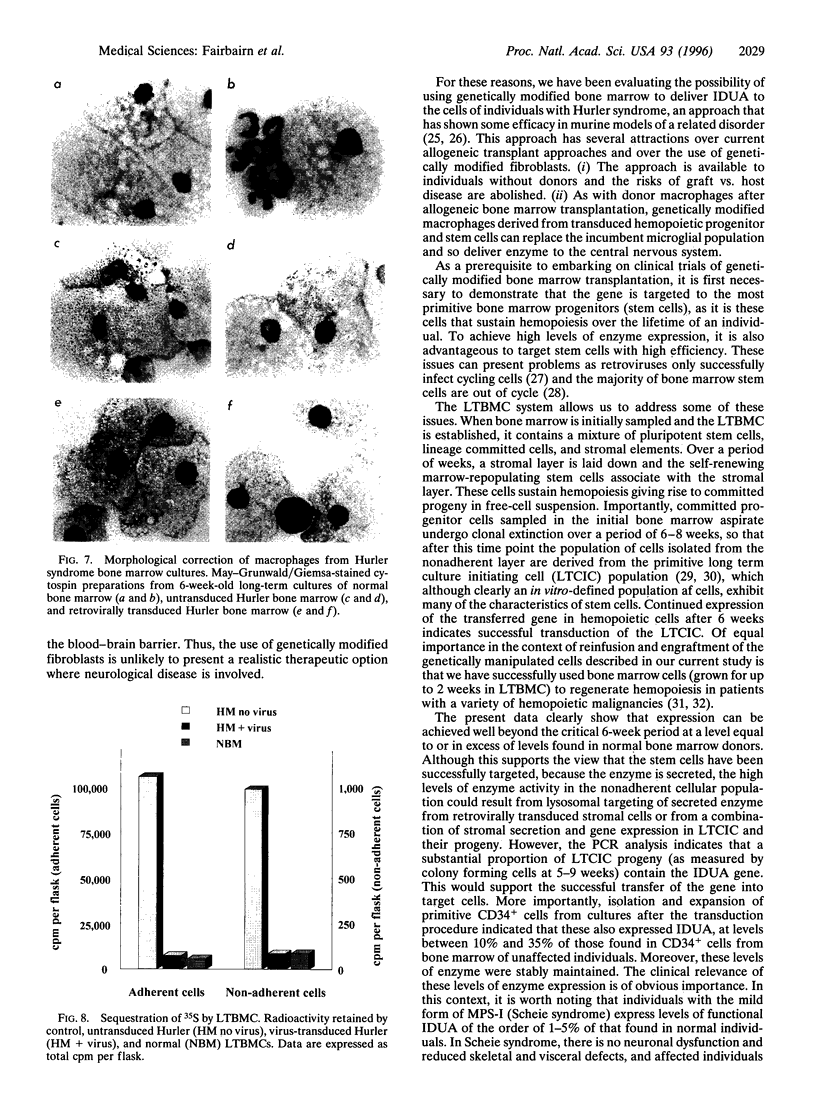
Abstract
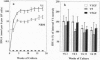
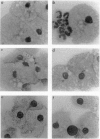
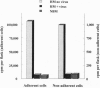
Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is the most effective treatment for Hurler syndrome but, since this therapy is not available to all patients, we have considered an alternative approach based on transfer and expression of the normal gene in autologous bone marrow. A retroviral vector carrying the full-length cDNA for alpha-L-iduronidase has been constructed and used to transduce bone marrow from patients with this disorder. Various gene-transfer protocols have been assessed including the effect of intensive schedules of exposure of bone marrow to viral supernatant and the influence of growth factors. With these protocols, we have demonstrated successful gene transfer into primitive CD34+ cells and subsequent enzyme expression in their maturing progeny. Also, by using long-term bone marrow cultures, we have demonstrated high levels of enzyme expression sustained for several months. The efficiency of gene transfer has been assessed by PCR analysis of hemopoietic colonies as 25-56%. No advantage has been demonstrated for the addition of growth factors or intensive viral exposure schedules. The enzyme is secreted into the medium and functional localization has been demonstrated by reversal of the phenotypic effects of lysosomal storage in macrophages. This work suggests that retroviral gene transfer into human bone marrow may offer the prospect for gene therapy of Hurler syndrome in young patients without a matched sibling donor.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anson D. S., Bielicki J., Hopwood J. J. Correction of mucopolysaccharidosis type I fibroblasts by retroviral-mediated transfer of the human alpha-L-iduronidase gene. Hum Gene Ther. 1992 Aug;3(4):371–379. doi: 10.1089/hum.1992.3.4-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anson D. S., Muller V., Bielicki J., Harper G. S., Hopwood J. J. Overexpression of N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulphatase induces a multiple sulphatase deficiency in mucopolysaccharidosis-type-VI fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 15;294(Pt 3):657–662. doi: 10.1042/bj2940657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton L. J., Brooks D. A., McCourt P. A., Muller V. J., Clements P. R., Hopwood J. J. Immunoquantification and enzyme kinetics of alpha-L-iduronidase in cultured fibroblasts from normal controls and mucopolysaccharidosis type I patients. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):787–794. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun S. E., Aronovich E. L., Anderson R. A., Crotty P. L., McIvor R. S., Whitley C. B. Metabolic correction and cross-correction of mucopolysaccharidosis type II (Hunter syndrome) by retroviral-mediated gene transfer and expression of human iduronate-2-sulfatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11830–11834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J., Coutinho L., Morgenstern G., Scarffe J. H., Deakin D., Harrison C., Testa N. G., Dexter T. M. Reconstitution of haemopoietic system with autologous marrow taken during relapse of acute myeloblastic leukaemia and grown in long-term culture. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):294–295. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90828-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J., Morgenstern G. R., Coutinho L. H., Scarffe J. H., Carr T., Deakin D. P., Testa N. G., Dexter T. M. The use of bone marrow cells grown in long-term culture for autologous bone marrow transplantation in acute myeloid leukaemia: an update. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1989 Jan;4(1):5–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs J. R., Hugh-Jones K., Barrett A. J., Byrom N., Chambers D., Henry K., James D. C., Lucas C. F., Rogers T. R., Benson P. F. Reversal of clinical features of Hurler's disease and biochemical improvement after treatment by bone-marrow transplantation. Lancet. 1981 Oct 3;2(8249):709–712. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood J. J., Morris C. P. The mucopolysaccharidoses. Diagnosis, molecular genetics and treatment. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Oct;7(5):381–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood J. J., Vellodi A., Scott H. S., Morris C. P., Litjens T., Clements P. R., Brooks D. A., Cooper A., Wraith J. E. Long-term clinical progress in bone marrow transplanted mucopolysaccharidosis type I patients with a defined genotype. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1993;16(6):1024–1033. doi: 10.1007/BF00711520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes P. F., Thacker J. D., Hogge D., Sutherland H. J., Thomas T. E., Lansdorp P. M., Eaves C. J., Humphries R. K. Retroviral gene transfer to primitive normal and leukemic hematopoietic cells using clinically applicable procedures. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):1817–1824. doi: 10.1172/JCI115786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krall W. J., Challita P. M., Perlmutter L. S., Skelton D. C., Kohn D. B. Cells expressing human glucocerebrosidase from a retroviral vector repopulate macrophages and central nervous system microglia after murine bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1994 May 1;83(9):2737–2748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord B. I., Woolford L. B. Proliferation of spleen colony forming units (CFU-S8, CFU-S13) and cells with marrow repopulating ability. Stem Cells. 1993 May;11(3):212–217. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530110308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz D., Goff S., Bank A. Construction and use of a safe and efficient amphotropic packaging cell line. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maréchal V., Naffakh N., Danos O., Heard J. M. Disappearance of lysosomal storage in spleen and liver of mucopolysaccharidosis VII mice after transplantation of genetically modified bone marrow cells. Blood. 1993 Aug 15;82(4):1358–1365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. G., Adam M. A., Miller A. D. Gene transfer by retrovirus vectors occurs only in cells that are actively replicating at the time of infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4239–4242. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. A., Deisseroth A. B., Reading C. L., Williams D. E., Belmont J. W. Stromal support enhances cell-free retroviral vector transduction of human bone marrow long-term culture-initiating cells. Blood. 1992 Mar 15;79(6):1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moullier P., Bohl D., Heard J. M., Danos O. Correction of lysosomal storage in the liver and spleen of MPS VII mice by implantation of genetically modified skin fibroblasts. Nat Genet. 1993 Jun;4(2):154–159. doi: 10.1038/ng0693-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolta J. A., Yu X. J., Bahner I., Kohn D. B. Retroviral-mediated transfer of the human glucocerebrosidase gene into cultured Gaucher bone marrow. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):342–348. doi: 10.1172/JCI115868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. S., Anson D. S., Orsborn A. M., Nelson P. V., Clements P. R., Morris C. P., Hopwood J. J. Human alpha-L-iduronidase: cDNA isolation and expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9695–9699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. S., Guo X. H., Hopwood J. J., Morris C. P. Structure and sequence of the human alpha-L-iduronidase gene. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1311–1313. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90053-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull R. M., Kakkis E. D., McEntee M. F., Kania S. A., Jonas A. J., Neufeld E. F. Enzyme replacement in a canine model of Hurler syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12937–12941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling J. L., Robinson D., Fensom A. H., Benson P. F., Baker J. E. Fluorimetric assay for prenatal detection of Hurler and Scheie homozygotes or heterozygotes. Lancet. 1978 Jan 21;1(8056):147–147. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland H. J., Eaves C. J., Lansdorp P. M., Thacker J. D., Hogge D. E. Differential regulation of primitive human hematopoietic cells in long-term cultures maintained on genetically engineered murine stromal cells. Blood. 1991 Aug 1;78(3):666–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland H. J., Lansdorp P. M., Henkelman D. H., Eaves A. C., Eaves C. J. Functional characterization of individual human hematopoietic stem cells cultured at limiting dilution on supportive marrow stromal layers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3584–3588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley C. B., Belani K. G., Chang P. N., Summers C. G., Blazar B. R., Tsai M. Y., Latchaw R. E., Ramsay N. K., Kersey J. H. Long-term outcome of Hurler syndrome following bone marrow transplantation. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Apr 15;46(2):209–218. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J. H., Sands M. S., Barker J. E., Gwynn B., Rowe L. B., Vogler C. A., Birkenmeier E. H. Reversal of pathology in murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII by somatic cell gene transfer. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):749–753. doi: 10.1038/360749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J. H., Schuchman E. H., Stramm L. E., Concaugh E. A., Haskins M. E., Aguirre G. D., Patterson D. F., Desnick R. J., Gilboa E. Restoration of normal lysosomal function in mucopolysaccharidosis type VII cells by retroviral vector-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2877–2881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]