Abstract
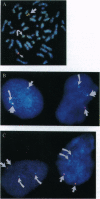
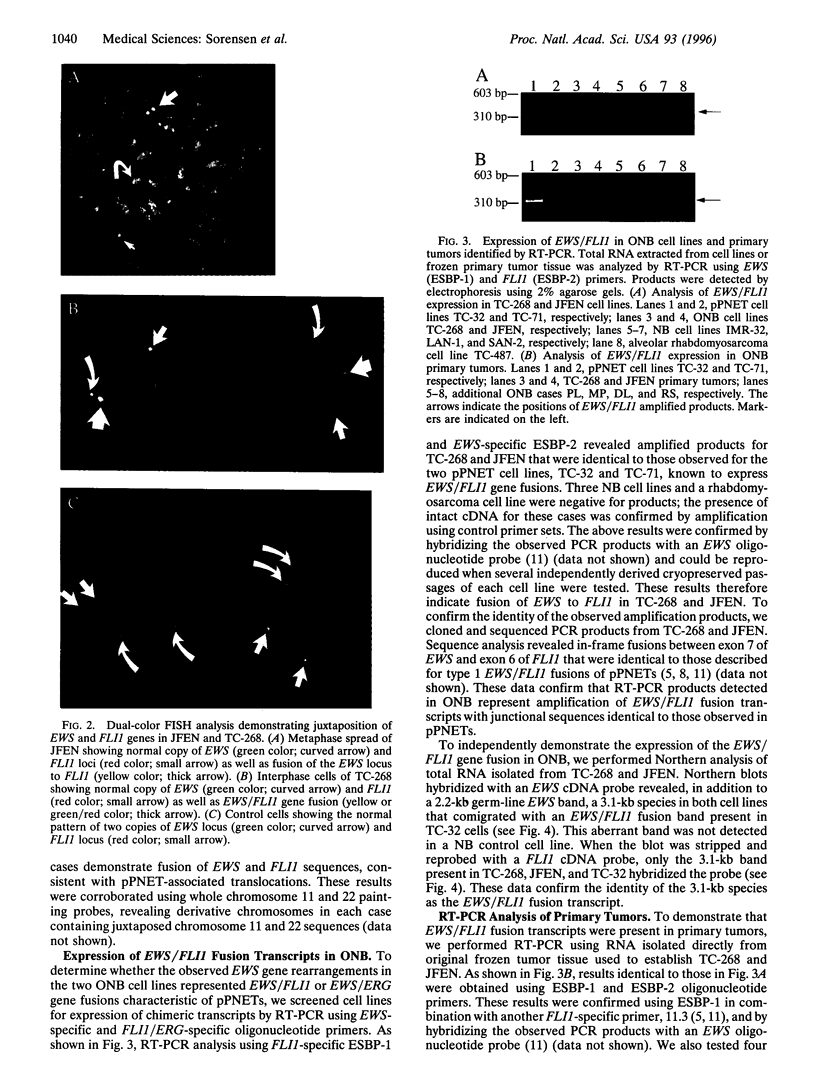
Olfactory neuroblastoma (ONB) is a malignant tumor of the nasal mucosa whose histogenesis is unclear. A relationship to neuroblastoma (NB), a pediatric tumor of the sympathetic nervous system, is based on morphologic similarities and the expression of similar neural antigens. However, the clinical presentation of ONB differs from that of NB, and MYCN amplification characteristic of NB is not observed. We have therefore examined the relationship of this malignancy to other classes of neural tumors. In previous studies, two ONB cell lines demonstrated cytogenetic features and patterns of protooncogene expression suggestive of a relationship to the Ewing sarcoma family of childhood peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors (pPNETs). The pPNETs show t(11;22)(q24;q12) or t(21;22)(q22;q12) chromosomal translocations fusing the EWS gene from 22q12 with either the FL11 gene on 11q24 or the ERG gene on 21q22. We therefore analyzed ONBs for the presence of pPNET-associated gene fusions. Both cell lines showed rearrangement of the EWS gene, and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) of each case demonstrated fusion of EWS and FL11 genomic sequences. Moreover, both lines expressed EWS/FL11 fusion transcripts with in-frame junctions between exon 7 of EWS and exon 6 of FL11 as described for pPNETs. We identified similar gene fusions in four of six primary ONB cases. None of the cases expressed tyrosine hydroxylase, a catecholamine biosynthetic enzyme widely expressed in NB. Our studies indicate that ONB is not a NB but is a member of the pPNET family.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brodeur G. M., Fong C. T. Molecular biology and genetics of human neuroblastoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989 Sep;41(2):153–174. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(89)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur G. M., Seeger R. C., Schwab M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Amplification of N-myc in untreated human neuroblastomas correlates with advanced disease stage. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1121–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.6719137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavazzana A. O., Miser J. S., Jefferson J., Triche T. J. Experimental evidence for a neural origin of Ewing's sarcoma of bone. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jun;127(3):507–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavazzana A. O., Navarro S., Noguera R., Reynolds P. C., Triche T. J. Olfactory neuroblastoma is not a neuroblastoma but is related to primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET). Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;271:463–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi H. S., Anderson P. J. Olfactory neuroblastoma: an immuno-electron microscopic study of S-100 protein-positive cells. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1986 Sep;45(5):576–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coker G. T., 3rd, Studelska D., Harmon S., Burke W., O'Malley K. L. Analysis of tyrosine hydroxylase and insulin transcripts in human neuroendocrine tissues. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 Jul;8(2):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90052-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delattre O., Zucman J., Melot T., Garau X. S., Zucker J. M., Lenoir G. M., Ambros P. F., Sheer D., Turc-Carel C., Triche T. J. The Ewing family of tumors--a subgroup of small-round-cell tumors defined by specific chimeric transcripts. N Engl J Med. 1994 Aug 4;331(5):294–299. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199408043310503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delattre O., Zucman J., Plougastel B., Desmaze C., Melot T., Peter M., Kovar H., Joubert I., de Jong P., Rouleau G. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):162–165. doi: 10.1038/359162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon D., Hightower S. I., Lim M. L., Cantrell R. W., Constable W. C. Esthesioneuroblastoma. Cancer. 1979 Sep;44(3):1087–1094. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197909)44:3<1087::aid-cncr2820440343>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong C. T., Dracopoli N. C., White P. S., Merrill P. T., Griffith R. C., Housman D. E., Brodeur G. M. Loss of heterozygosity for the short arm of chromosome 1 in human neuroblastomas: correlation with N-myc amplification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3753–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frierson H. F., Jr, Mills S. E., Fechner R. E., Taxy J. B., Levine P. A. Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma. An aggressive neoplasm derived from schneiderian epithelium and distinct from olfactory neuroblastoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1986 Nov;10(11):771–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frierson H. F., Jr, Ross G. W., Mills S. E., Frankfurter A. Olfactory neuroblastoma. Additional immunohistochemical characterization. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 Nov;94(5):547–553. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/94.5.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannini M., Biegel J. A., Serra M., Wang J. Y., Wei Y. H., Nycum L., Emanuel B. S., Evans G. A. EWS-erg and EWS-Fli1 fusion transcripts in Ewing's sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumors with variant translocations. J Clin Invest. 1994 Aug;94(2):489–496. doi: 10.1172/JCI117360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalava A. M., Heikkilä J. E., Akerman K. E. Decline in c-myc mRNA expression but not the induction of c-fos mRNA expression is associated with differentiation of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Nov;179(1):10–17. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90343-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. Migration and differentiation of neural crest cells. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1980;16:31–85. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnoila R. I., Tsokos M., Triche T. J., Marangos P. J., Chandra R. S. Evidence for neural origin and PAS-positive variants of the malignant small cell tumor of thoracopulmonary region ("Askin tumor"). Am J Surg Pathol. 1986 Feb;10(2):124–133. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198602000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinsson T., Weith A., Cziepluch C., Schwab M. Chromosome 1 deletions in human neuroblastomas: generation and fine mapping of microclones from the distal 1p region. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1989 Sep;1(1):67–78. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870010111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May W. A., Gishizky M. L., Lessnick S. L., Lunsford L. B., Lewis B. C., Delattre O., Zucman J., Thomas G., Denny C. T. Ewing sarcoma 11;22 translocation produces a chimeric transcription factor that requires the DNA-binding domain encoded by FLI1 for transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5752–5756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May W. A., Lessnick S. L., Braun B. S., Klemsz M., Lewis B. C., Lunsford L. B., Hromas R., Denny C. T. The Ewing's sarcoma EWS/FLI-1 fusion gene encodes a more potent transcriptional activator and is a more powerful transforming gene than FLI-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7393–7398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micheau C., Guerinot F., Bohuon C., Brugere J. Dopamine-B-hydroxylase and catecholamines in an olfactory esthesioneuroma. Cancer. 1975 May;35(5):1309–1312. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197505)35:5<1309::aid-cncr2820350509>3.0.co;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills S. E., Frierson H. F., Jr Olfactory neuroblastoma. A clinicopathologic study of 21 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1985 May;9(5):317–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugneret F., Lizard S., Aurias A., Turc-Carel C. Chromosomes in Ewing's sarcoma. II. Nonrandom additional changes, trisomy 8 and der(16)t(1;16). Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Jun;32(2):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito H., Kuzumaki N., Uchino J., Kobayashi R., Shikano T., Ishikawa Y., Matsumoto S. Detection of tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA and minimal neuroblastoma cells by the reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27(6):762–765. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(91)90184-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. L., Zarbo R. J., Clark J. L. Olfactory neuroblastoma: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical characterization of four representative cases. Laryngoscope. 1990 Oct;100(10 Pt 1):1052–1058. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199010000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen P. H., Lessnick S. L., Lopez-Terrada D., Liu X. F., Triche T. J., Denny C. T. A second Ewing's sarcoma translocation, t(21;22), fuses the EWS gene to another ETS-family transcription factor, ERG. Nat Genet. 1994 Feb;6(2):146–151. doi: 10.1038/ng0294-146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen P. H., Liu X. F., Delattre O., Rowland J. M., Biggs C. A., Thomas G., Triche T. J. Reverse transcriptase PCR amplification of EWS/FLI-1 fusion transcripts as a diagnostic test for peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors of childhood. Diagn Mol Pathol. 1993 Sep;2(3):147–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen P. H., Shimada H., Liu X. F., Lim J. F., Thomas G., Triche T. J. Biphenotypic sarcomas with myogenic and neural differentiation express the Ewing's sarcoma EWS/FLI1 fusion gene. Cancer Res. 1995 Mar 15;55(6):1385–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemple D. L., Anderson D. J. Isolation of a stem cell for neurons and glia from the mammalian neural crest. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):973–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90393-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taxy J. B., Bharani N. K., Mills S. E., Frierson H. F., Jr, Gould V. E. The spectrum of olfactory neural tumors. A light-microscopic immunohistochemical and ultrastructural analysis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1986 Oct;10(10):687–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele C. J., McKeon C., Triche T. J., Ross R. A., Reynolds C. P., Israel M. A. Differential protooncogene expression characterizes histopathologically indistinguishable tumors of the peripheral nervous system. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):804–811. doi: 10.1172/JCI113137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V., Pillsbury N., Lee S. Neuronal origin of human esthesioneuroblastoma demonstrated with anti-neurofilament monoclonal antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jul 15;307(3):159–161. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198207153070305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turc-Carel C., Aurias A., Mugneret F., Lizard S., Sidaner I., Volk C., Thiery J. P., Olschwang S., Philip I., Berger M. P. Chromosomes in Ewing's sarcoma. I. An evaluation of 85 cases of remarkable consistency of t(11;22)(q24;q12). Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Jun;32(2):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang-Peng J., Freter C. E., Knutsen T., Nanfro J. J., Gazdar A. Translocation t(11;22) in esthesioneuroblastoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1987 Nov;29(1):155–157. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(87)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang-Peng J., Knutsen T., Theil K., Horowitz M. E., Triche T. Cytogenetic studies in subgroups of rhabdomyosarcoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Nov;5(4):299–310. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870050405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang-Peng J., Triche T. J., Knutsen T., Miser J., Kao-Shan S., Tsai S., Israel M. A. Cytogenetic characterization of selected small round cell tumors of childhood. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1986 Apr 1;21(3):185–208. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(86)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee D., Favoni R. E., Lebovic G. S., Lombana F., Powell D. R., Reynolds C. P., Rosen N. Insulin-like growth factor I expression by tumors of neuroectodermal origin with the t(11;22) chromosomal translocation. A potential autocrine growth factor. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1806–1814. doi: 10.1172/JCI114910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucman J., Melot T., Desmaze C., Ghysdael J., Plougastel B., Peter M., Zucker J. M., Triche T. J., Sheer D., Turc-Carel C. Combinatorial generation of variable fusion proteins in the Ewing family of tumours. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4481–4487. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]