Abstract
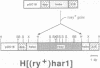
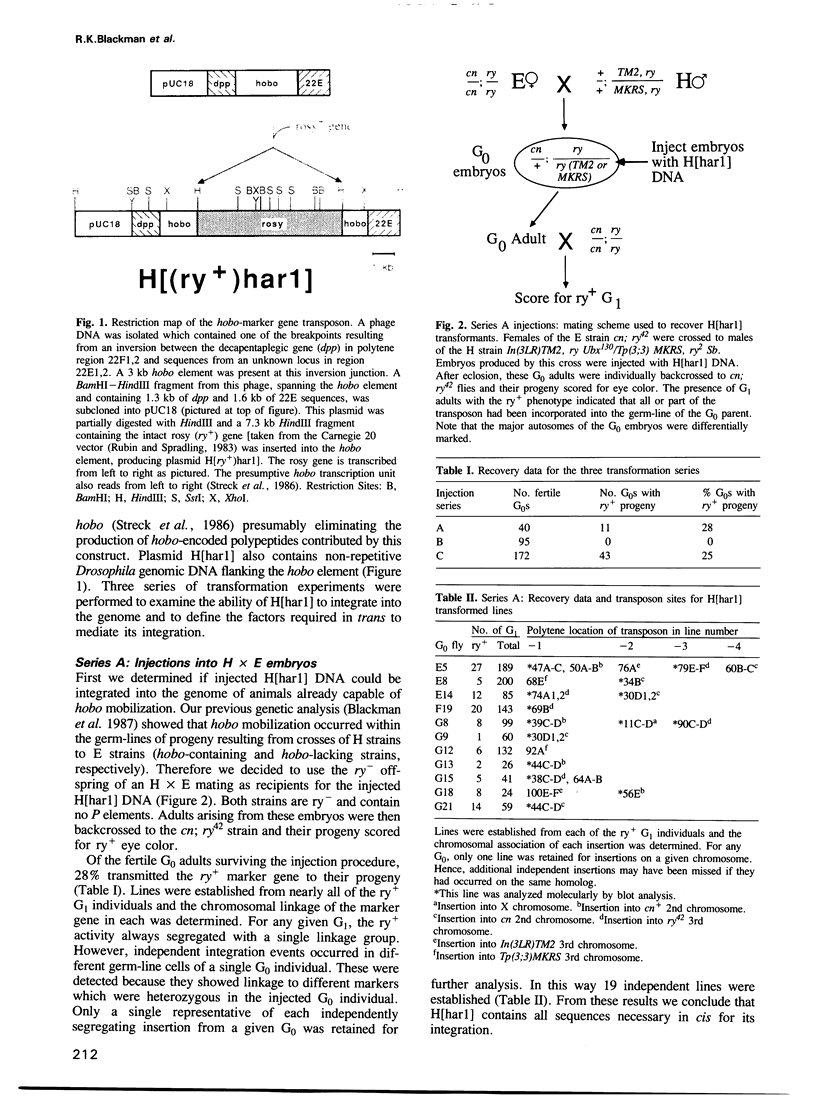
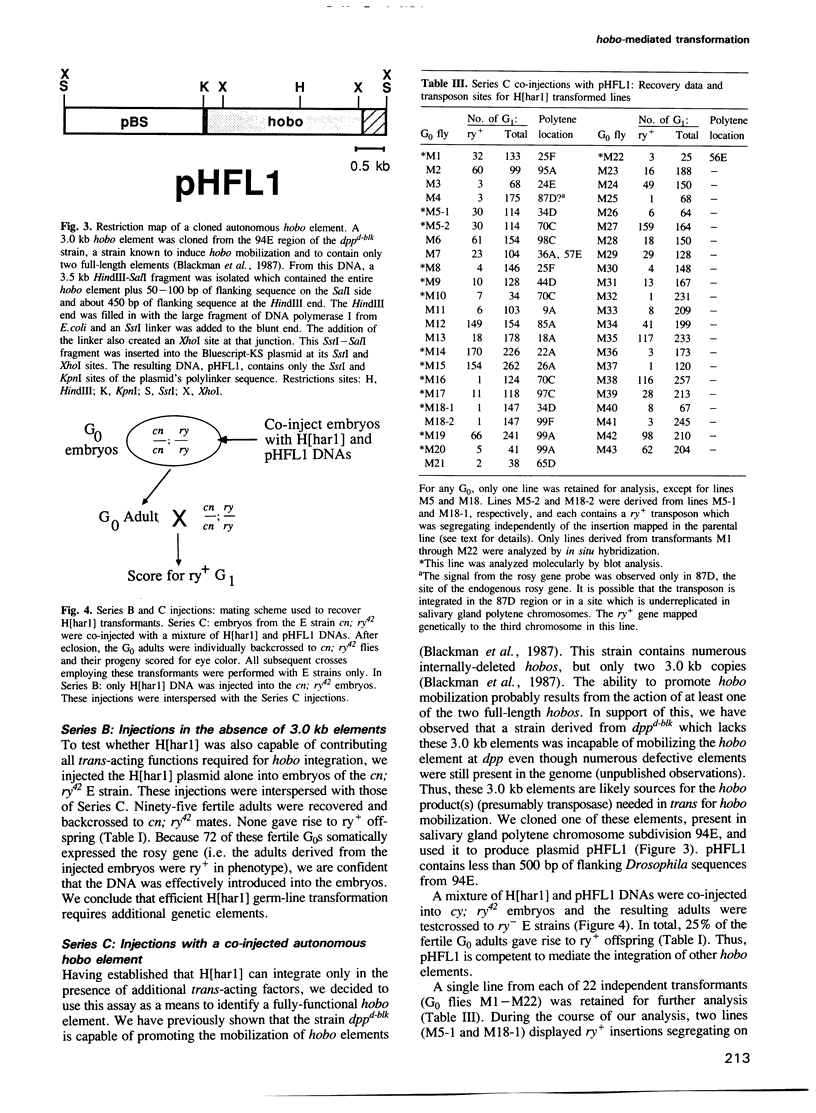
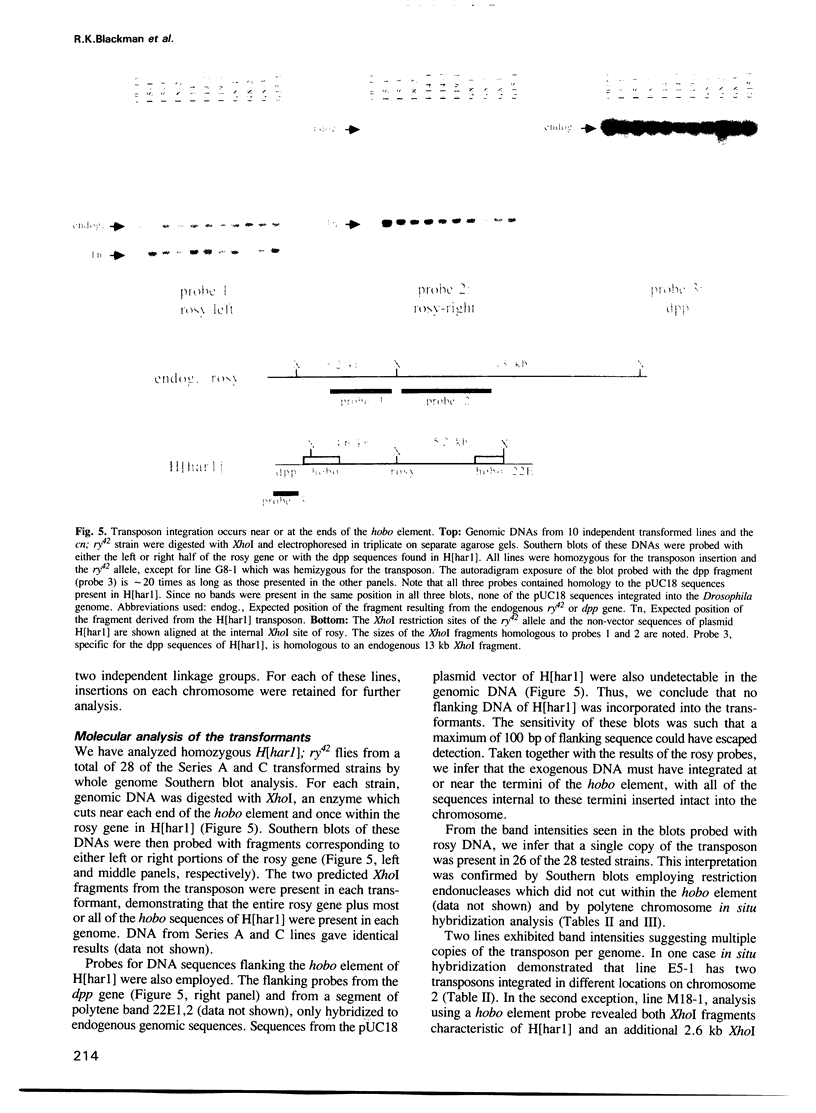
The transposable element hobo can be mobilized to induce a variety of genetic abnormalities within the germ-line of Drosophila melanogaster. Strains containing hobos have 3.0 kb elements and numerous smaller derivatives of the element. By analogy with other transposable element systems, it is likely that only the 3.0 kb elements are capable of inducing hobo mobilization. Here, we report that a cloned 3.0 kb hobo, called HFL1, is able to mediate germ-line transformation and therefore is an autonomous (fully-functional) transposable element. Germ-line transformation was observed when HFL1 and a marked hobo element were co-injected into recipient embryos devoid of endogenous hobos. Integration did not occur in the absence of the 3.0 kb element. A single copy of the marked hobo transposon inserted at each site, and the target sites were widely distributed throughout the genome. Integration occurred at (or very near) the termini of hobo, without internal rearrangement of the hobo or marker gene sequences. The hobo transformation system will allow us to determine the structural and regulatory features of hobo responsible for its mobilization and will provide novel approaches for the molecular and genetic manipulation of the Drosophila genome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackman R. K., Grimaila R., Koehler M. M., Gelbart W. M. Mobilization of hobo elements residing within the decapentaplegic gene complex: suggestion of a new hybrid dysgenesis system in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):497–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90452-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooley L., Kelley R., Spradling A. Insertional mutagenesis of the Drosophila genome with single P elements. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1121–1128. doi: 10.1126/science.2830671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggleston W. B., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Engels W. R. P-M hybrid dysgenesis does not mobilize other transposable element families in D. melanogaster. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):368–370. doi: 10.1038/331368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W. R. Extrachromosomal control of mutability in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelbart W. M., Chovnick A. Spontaneous unequal exchange in the rosy region of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1979 Jul;92(3):849–859. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzopoulos P., Monastirioti M., Yannopoulos G., Louis C. The instability of the TE-like mutation Dp(2:2)GYL of Drosophila melanogaster is intimately associated with the hobo element. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3091–3096. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski F. A., Rio D. C., Rubin G. M. Tissue specificity of Drosophila P element transposition is regulated at the level of mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):7–19. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim J. K. Intrachromosomal rearrangements mediated by hobo transposons in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9153–9157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElwain M. C. The absence of somatic effects of P-M hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1986 Aug;113(4):897–918. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Shermoen A. W., Beckendorf S. K. A transposable element inserted just 5' to a Drosophila glue protein gene alters gene expression and chromatin structure. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Structures of P transposable elements and their sites of insertion and excision in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Laski F. A., Rubin G. M. Identification and immunochemical analysis of biologically active Drosophila P element transposase. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90481-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. M., Preston C. R., Phillis R. W., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Benz W. K., Engels W. R. A stable genomic source of P element transposase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Mar;118(3):461–470. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Vectors for P element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6341–6351. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.6289435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streck R. D., Macgaffey J. E., Beckendorf S. K. The structure of hobo transposable elements and their insertion sites. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3615–3623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04690.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yannopoulos G., Stamatis N., Monastirioti M., Hatzopoulos P., Louis C. hobo is responsible for the induction of hybrid dysgenesis by strains of Drosophila melanogaster bearing the male recombination factor 23.5MRF. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):487–495. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90451-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]