Abstract
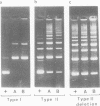
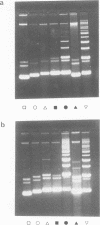
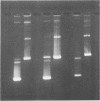
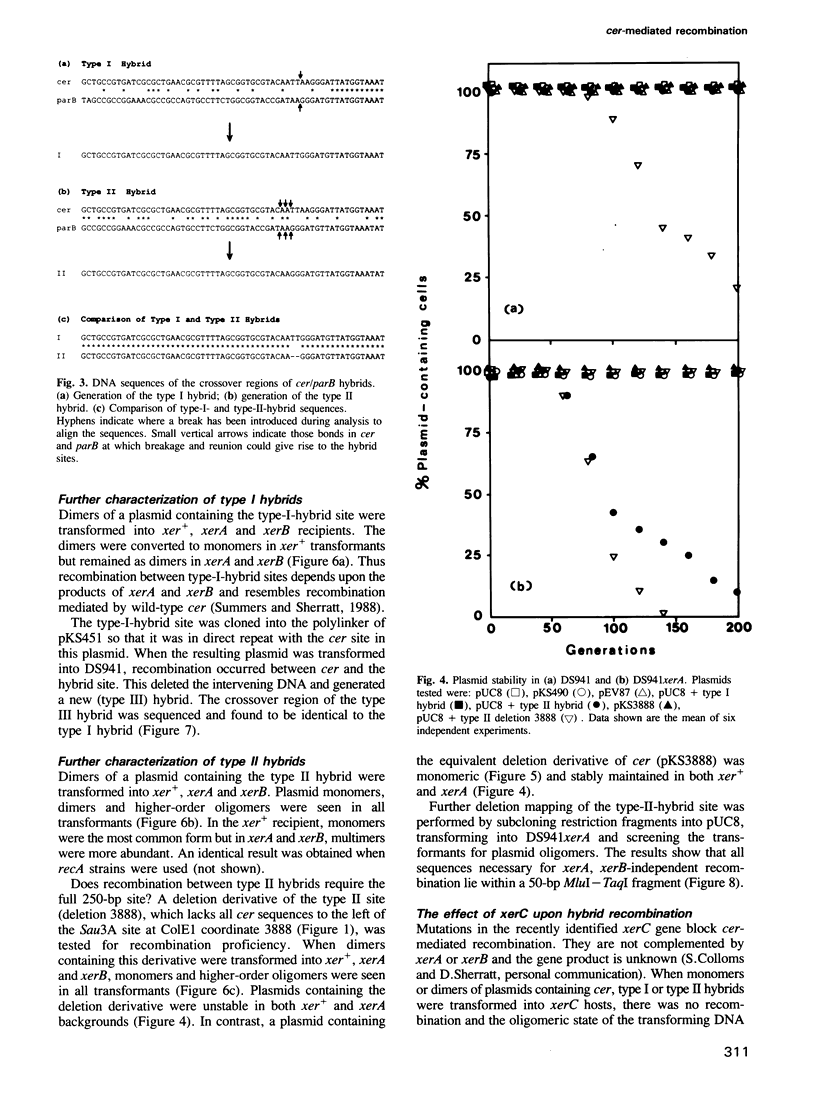
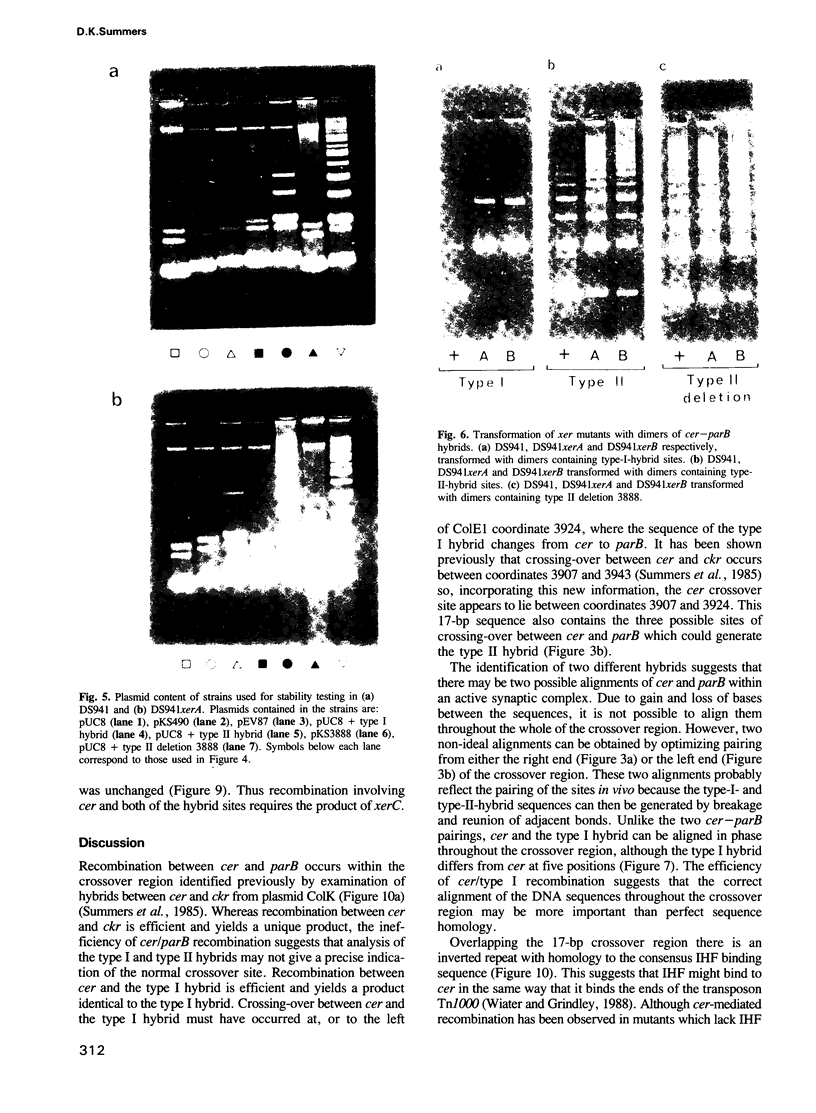
ColE1 contains a 250-bp sequence (cer) which is required in cis for the conversion of plasmid dimers to monomers. Recombination between cer and parB (a dimer resolution site from plasmid CloDF13) occurs in vivo at low frequency. The properties of the resulting hybrid sites have been studied. The type I hybrid closely resembles wild-type cer. It supports intramolecular recombination and requires the products of the chromosomal xerA, xerB and xerC genes together with the 250-bp site. In contrast, the type II hybrid (although differing from type I by only 2 bp) functions independently of the topological relationship of the participating sites, supporting both inter- and intramolecular recombination. Furthermore, recombination between type II sites is independent of the products of the xerA and xerB genes and requires a site of less than 50 bp.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyko W. L., Ganschow R. E. Rapid identification of Escherichia coli transformed by pBR322 carrying inserts at the PstI Site. Anal Biochem. 1982 May 1;122(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. T., Ohmori H., Tomizawa J., Lebowitz J. Nucleotide sequence and gene organization of ColE1 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8925–8935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi K. Role of DNA topology in Mu transposition: mechanism of sensing the relative orientation of two DNA segments. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90554-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishel R. A., James A. A., Kolodner R. recA-independent general genetic recombination of plasmids. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):184–186. doi: 10.1038/294184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakkaart M. J., van den Elzen P. J., Veltkamp E., Nijkamp H. J. Maintenance of multicopy plasmid Clo DF13 in E. coli cells: evidence for site-specific recombination at parB. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Bruist M. B., Glaccum M. B., Simon M. I. In vitro analysis of Hin-mediated site-specific recombination. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:751–760. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C. K. Induction of colicin production by high temperature or inhibition of protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):10–19. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.10-19.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnow M. A., Cozzarelli N. R. Site-specific relaxation and recombination by the Tn3 resolvase: recognition of the DNA path between oriented res sites. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1313–1324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim D. B., Oppenheim J. D., Eckhardt T., Maas W. K. Nucleotide sequence of the argR gene of Escherichia coli K-12 and isolation of its product, the arginine repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6697–6701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morisato D., Kleckner N. Tn10 transposition and circle formation in vitro. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Van de Putte P. Genetic switches by DNA inversions in prokaryotes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 16;782(2):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spengler S. J., Stasiak A., Cozzarelli N. R. The stereostructure of knots and catenanes produced by phage lambda integrative recombination: implications for mechanism and DNA structure. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):325–334. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. K., Sherratt D. J. Multimerization of high copy number plasmids causes instability: CoIE1 encodes a determinant essential for plasmid monomerization and stability. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1097–1103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. K., Sherratt D. J. Resolution of ColE1 dimers requires a DNA sequence implicated in the three-dimensional organization of the cer site. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):851–858. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02884.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D., Yaish S., Archer J., Sherratt D. Multimer resolution systems of ColE1 and ColK: localisation of the crossover site. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(2):334–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00425680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiater L. A., Grindley N. D. Gamma delta transposase and integration host factor bind cooperatively at both ends of gamma delta. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1907–1911. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03024.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]