Abstract
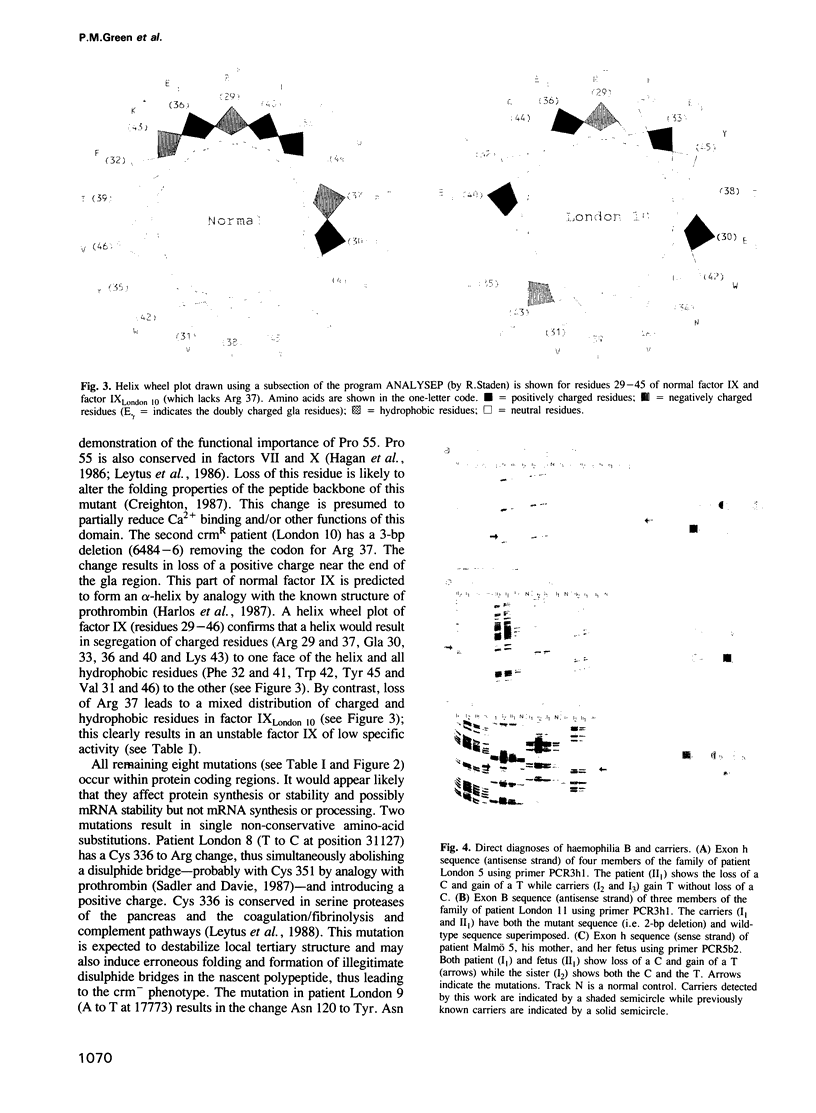
Direct sequencing of amplified genomic DNA has been used to investigate the molecular basis of haemophilia B and thus identify specific amino acids that are essential for maintenance of structure or function of factor IX. Substitution of Cys 336, Asn 120 results in loss of circulating factor IX antigen and deletion of Arg 37 in gross reduction of circulating protein and loss of activity, while substitution of Arg -4, Arg 333, Asp 64 and Pro 55 cause loss of function without marked reduction in protein serum levels. Frameshift or point mutations resulting in marked loss of coding information are found in patients who develop antibodies to administered factor IX. An enhanced rate of mutation is evident at two CpG dinucleotides in the factor IX gene, which accounts for approximately 25% of all point mutations causing haemophilia B known to date. Direct sequencing of mutations also permits, for the first time, rapid and unequivocal prenatal and carrier diagnoses, in all cases, by eliminating the need for informative segregation of markers.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anson D. S., Choo K. H., Rees D. J., Giannelli F., Gould K., Huddleston J. A., Brownlee G. G. The gene structure of human anti-haemophilic factor IX. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1053–1060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. K., Rees D. J., Rizza C., Brownlee G. G. Defective propeptide processing of blood clotting factor IX caused by mutation of arginine to glutamine at position -4. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance P. F., Dyer K. A., Kurachi K., Yoshitake S., Ropers H. H., Wieacker P., Gartler S. M. Regional localization of the human factor IX gene by molecular hybridization. Hum Genet. 1983;65(2):207–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00286666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. M., Wilkinson A. J., Baron M., Pastore A., Tappin M. J., Campbell I. D., Gregory H., Sheard B. The solution structure of human epidermal growth factor. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):339–341. doi: 10.1038/327339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulondre C., Miller J. H., Farabaugh P. J., Gilbert W. Molecular basis of base substitution hotspots in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):775–780. doi: 10.1038/274775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. M., McGraw R. A., Ware J. L., Roberts H. R., Stafford D. W. Factor IXAlabama: a point mutation in a clotting protein results in hemophilia B. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):140–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diuguid D. L., Rabiet M. J., Furie B. C., Liebman H. A., Furie B. Molecular basis of hemophilia B: a defective enzyme due to an unprocessed propeptide is caused by a point mutation in the factor IX precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5803–5807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. C., Rudinski M. S., Schach B. G., Berkner K. L., Kumar A. A., Hagen F. S., Sprecher C. A., Insley M. Y., Davie E. W. Propeptide of human protein C is necessary for gamma-carboxylation. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):7003–7011. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannelli F., Choo K. H., Rees D. J., Boyd Y., Rizza C. R., Brownlee G. G. Gene deletions in patients with haemophilia B and anti-factor IX antibodies. Nature. 1983 May 12;303(5913):181–182. doi: 10.1038/303181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitschier J., Wood W. I., Tuddenham E. G., Shuman M. A., Goralka T. M., Chen E. Y., Lawn R. M. Detection and sequence of mutations in the factor VIII gene of haemophiliacs. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):427–430. doi: 10.1038/315427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen F. S., Gray C. L., O'Hara P., Grant F. J., Saari G. C., Woodbury R. G., Hart C. E., Insley M., Kisiel W., Kurachi K. Characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlos K., Holland S. K., Boys C. W., Burgess A. I., Esnouf M. P., Blake C. C. Vitamin K-dependent blood coagulation proteins form hetero-dimers. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):82–84. doi: 10.1038/330082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leytus S. P., Foster D. C., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Gene for human factor X: a blood coagulation factor whose gene organization is essentially identical with that of factor IX and protein C. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5098–5102. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leytus S. P., Loeb K. R., Hagen F. S., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. A novel trypsin-like serine protease (hepsin) with a putative transmembrane domain expressed by human liver and hepatoma cells. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 9;27(3):1067–1074. doi: 10.1021/bi00403a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I. M., Berntorp E., Zettervall O. Induction of split tolerance and clinical cure in high-responding hemophiliacs with factor IX antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9169–9173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes C. M., Griffith M. J., Roberts H. R., Lundblad R. L. Identification of the molecular defect in factor IX Chapel Hill: substitution of histidine for arginine at position 145. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4200–4202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. J., Jones I. M., Handford P. A., Walter S. J., Esnouf M. P., Smith K. J., Brownlee G. G. The role of beta-hydroxyaspartate and adjacent carboxylate residues in the first EGF domain of human factor IX. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2053–2061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. J., Rizza C. R., Brownlee G. G. Haemophilia B caused by a point mutation in a donor splice junction of the human factor IX gene. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):643–645. doi: 10.1038/316643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma P. H., Bertina R. M., Ploos van Amstel J. K., Riemens A., Briët E. The putative factor IX gene promoter in hemophilia B Leyden. Blood. 1988 Sep;72(3):1074–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schach B. G., Yoshitake S., Davie E. W. Hemophilia B (factor IXSeattle 2) due to a single nucleotide deletion in the gene for factor IX. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1023–1028. doi: 10.1172/JCI113155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C., Fitch N., Phelan M. C., Richer C. L., Stevenson R. Two sisters with a distal deletion at the Xq26/Xq27 interface: DNA studies indicate that the gene locus for factor IX is present. Hum Genet. 1987 May;76(1):54–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00283050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer S. G., Pendurthi U. R., Kasper C. K., Bajaj S. P. Molecular defect in factor IXBm Lake Elsinore. Substitution of Ala390 by Val in the catalytic domain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10545–10548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Lundwall A., Dahlbäck B. beta-Hydroxyasparagine in domains homologous to the epidermal growth factor precursor in vitamin K-dependent protein S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):368–372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang T. C., Bentley D. R., Mibashan R. S., Giannelli F. A factor IX mutation, verified by direct genomic sequencing, causes haemophilia B by a novel mechanism. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3009–3015. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallmark A., Ljung R., Nilsson I. M. Determination of factor IX allotypes for carrier identification in haemophilia B. Br J Haematol. 1987 Dec;67(4):427–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb06164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitake S., Schach B. G., Foster D. C., Davie E. W., Kurachi K. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human factor IX (antihemophilic factor B). Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3736–3750. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





