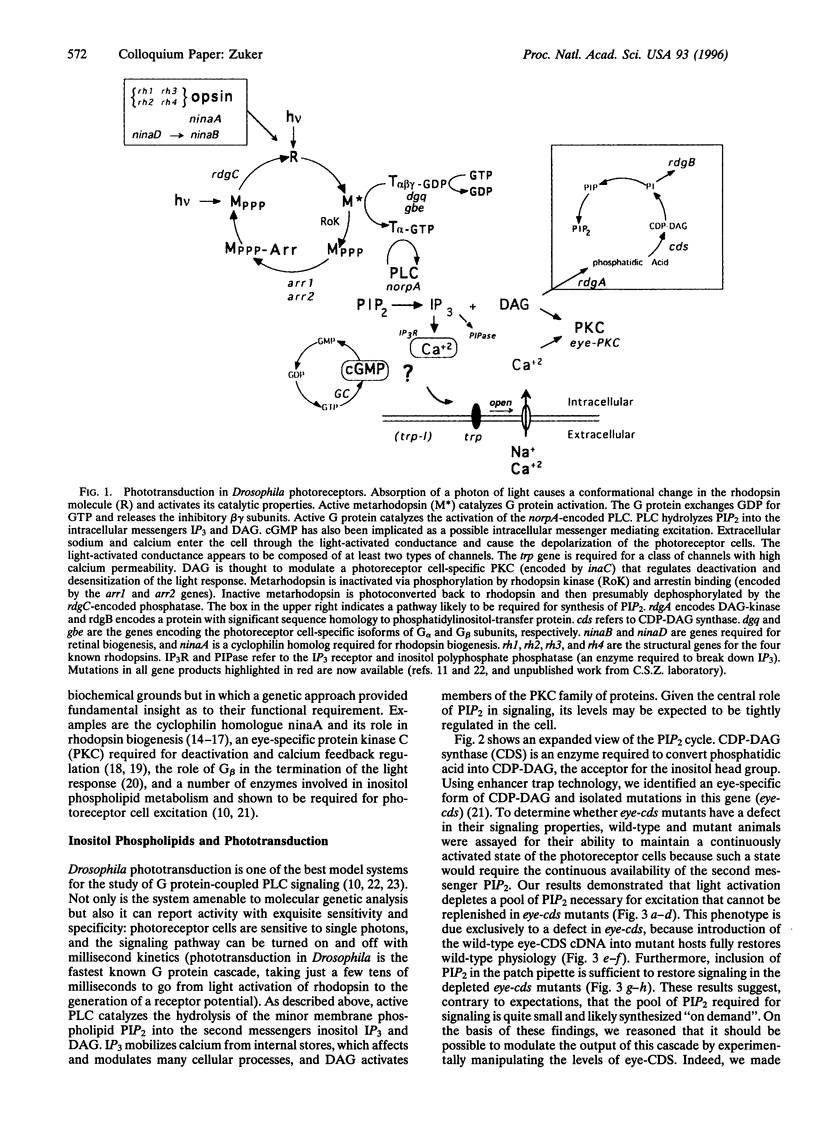
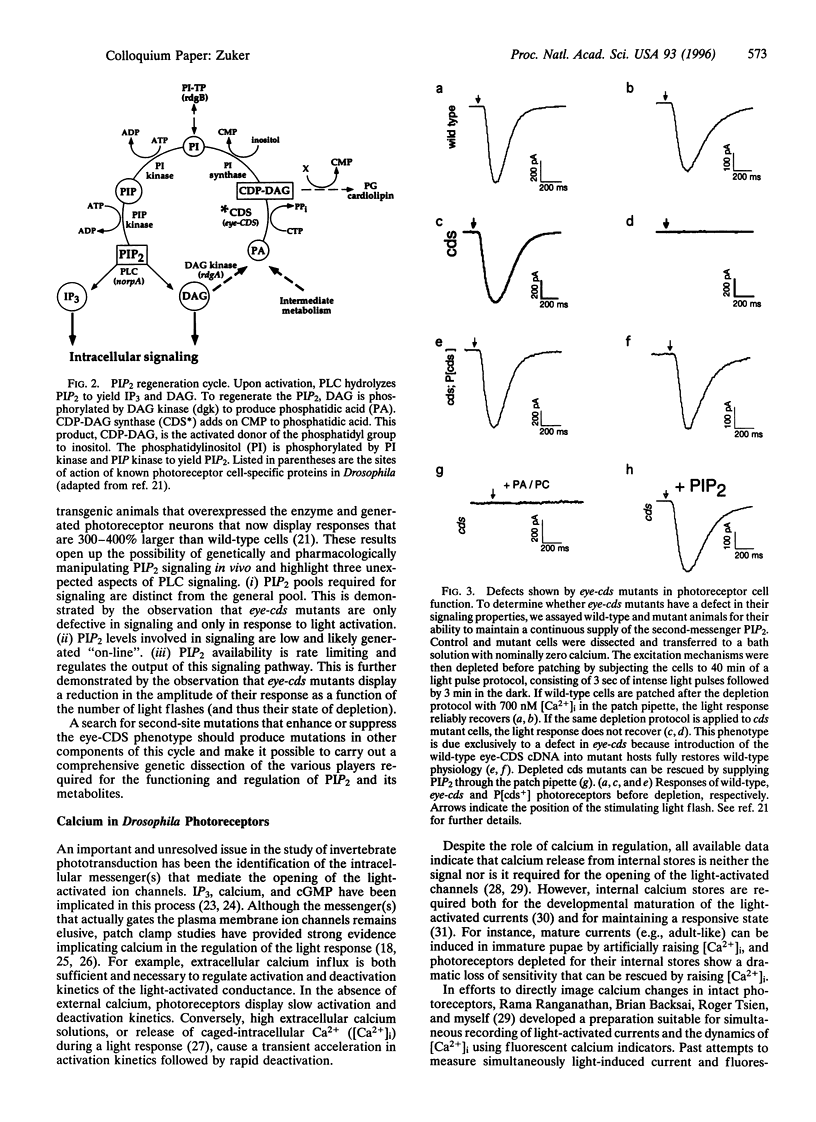
Abstract
Phototransduction systems in vertebrates and invertebrates share a great deal of similarity in overall strategy but differ significantly in the underlying molecular machinery. Both are rhodopsin-based G protein-coupled signaling cascades displaying exquisite sensitivity and broad dynamic range. However, light activation of vertebrate photoreceptors leads to activation of a cGMP-phosphodiesterase effector and the generation of a hyperpolarizing response. In contrast, activation of invertebrate photoreceptors, like Drosophila, leads to stimulation of phospholipase C and the generation of a depolarizing receptor potential. The comparative study of these two systems of phototransduction offers the opportunity to understand how similar biological problems may be solved by different molecular mechanisms of signal transduction. The study of this process in Drosophila, a system ideally suited to genetic and molecular manipulation, allows us to dissect the function and regulation of such a complex signaling cascade in its normal cellular environment. In this manuscript I review some of our recent findings and the strategies used to dissect this process.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augustine G. J., Neher E. Neuronal Ca2+ signalling takes the local route. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Jun;2(3):302–307. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker E. K., Colley N. J., Zuker C. S. The cyclophilin homolog NinaA functions as a chaperone, forming a stable complex in vivo with its protein target rhodopsin. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4886–4895. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06816.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzer S. BEHAVIORAL MUTANTS OF Drosophila ISOLATED BY COUNTERCURRENT DISTRIBUTION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1112–1119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomquist B. T., Shortridge R. D., Schneuwly S., Perdew M., Montell C., Steller H., Rubin G., Pak W. L. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):723–733. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley N. J., Baker E. K., Stamnes M. A., Zuker C. S. The cyclophilin homolog ninaA is required in the secretory pathway. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90177-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley N. J., Cassill J. A., Baker E. K., Zuker C. S. Defective intracellular transport is the molecular basis of rhodopsin-dependent dominant retinal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):3070–3074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.3070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosens D. J., Manning A. Abnormal electroretinogram from a Drosophila mutant. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):285–287. doi: 10.1038/224285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolph P. J., Man-Son-Hing H., Yarfitz S., Colley N. J., Deer J. R., Spencer M., Hurley J. B., Zuker C. S. An eye-specific G beta subunit essential for termination of the phototransduction cascade. Nature. 1994 Jul 7;370(6484):59–61. doi: 10.1038/370059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolph P. J., Ranganathan R., Colley N. J., Hardy R. W., Socolich M., Zuker C. S. Arrestin function in inactivation of G protein-coupled receptor rhodopsin in vivo. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1910–1916. doi: 10.1126/science.8316831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryja T. P. Doyne Lecture. Rhodopsin and autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Eye (Lond) 1992;6(Pt 1):1–10. doi: 10.1038/eye.1992.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiler R., Bjornson R., Kirschfeld K., Mismer D., Rubin G. M., Smith D. P., Socolich M., Zuker C. S. Ectopic expression of ultraviolet-rhodopsins in the blue photoreceptor cells of Drosophila: visual physiology and photochemistry of transgenic animals. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):3862–3868. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-03862.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray-Keller M. P., Detwiler P. B. The calcium feedback signal in the phototransduction cascade of vertebrate rods. Neuron. 1994 Oct;13(4):849–861. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. C., Minke B. Novel Ca2+ channels underlying transduction in Drosophila photoreceptors: implications for phosphoinositide-mediated Ca2+ mobilization. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Sep;16(9):371–376. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. C., Minke B. Spontaneous activation of light-sensitive channels in Drosophila photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Mar;103(3):389–407. doi: 10.1085/jgp.103.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. C., Minke B. The trp gene is essential for a light-activated Ca2+ channel in Drosophila photoreceptors. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):643–651. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90086-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. C., Peretz A., Pollock J. A., Minke B. Ca2+ limits the development of the light response in Drosophila photoreceptors. Proc Biol Sci. 1993 Jun 22;252(1335):223–229. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1993.0069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. C. Photolysis of caged Ca2+ facilitates and inactivates but does not directly excite light-sensitive channels in Drosophila photoreceptors. J Neurosci. 1995 Jan;15(1 Pt 2):889–902. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-01-00889.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. A., Stark W. S., Walker J. A. Genetic dissection of the photoreceptor system in the compound eye of Drosophila melanogaster. J Physiol. 1976 Apr;256(2):415–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Tracing the roots of ion channels. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):715–718. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90280-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaupp U. B., Niidome T., Tanabe T., Terada S., Bönigk W., Stühmer W., Cook N. J., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Hirose T. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of the rod photoreceptor cyclic GMP-gated channel. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):762–766. doi: 10.1038/342762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. J., Dobbs M. B., Verardi M. L., Hyde D. R. dgq: a drosophila gene encoding a visual system-specific G alpha molecule. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):889–898. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90349-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minke B. Light-induced reduction in excitation efficiency in the trp mutant of Drosophila. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Mar;79(3):361–385. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.3.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minke B., Wu C., Pak W. L. Induction of photoreceptor voltage noise in the dark in Drosophila mutant. Nature. 1975 Nov 6;258(5530):84–87. doi: 10.1038/258084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Rubin G. M. Molecular characterization of the Drosophila trp locus: a putative integral membrane protein required for phototransduction. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1313–1323. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Hogness D. S. Isolation, sequence analysis, and intron-exon arrangement of the gene encoding bovine rhodopsin. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90537-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel J. P., Hamm H. E., Sigler P. B. The 2.2 A crystal structure of transducin-alpha complexed with GTP gamma S. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):654–663. doi: 10.1038/366654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Tousa J. E., Baehr W., Martin R. L., Hirsh J., Pak W. L., Applebury M. L. The Drosophila ninaE gene encodes an opsin. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):839–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90343-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pak W. L., Grossfield J., Arnold K. S. Mutants of the visual pathway of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1970 Aug 1;227(5257):518–520. doi: 10.1038/227518b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peretz A., Sandler C., Kirschfeld K., Hardie R. C., Minke B. Genetic dissection of light-induced Ca2+ influx into Drosophila photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Dec;104(6):1057–1077. doi: 10.1085/jgp.104.6.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peretz A., Suss-Toby E., Rom-Glas A., Arnon A., Payne R., Minke B. The light response of Drosophila photoreceptors is accompanied by an increase in cellular calcium: effects of specific mutations. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1257–1267. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. M., Bull A., Kelly L. E. Identification of a Drosophila gene encoding a calmodulin-binding protein with homology to the trp phototransduction gene. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):631–642. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90085-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan R., Bacskai B. J., Tsien R. Y., Zuker C. S. Cytosolic calcium transients: spatial localization and role in Drosophila photoreceptor cell function. Neuron. 1994 Oct;13(4):837–848. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan R., Harris G. L., Stevens C. F., Zuker C. S. A Drosophila mutant defective in extracellular calcium-dependent photoreceptor deactivation and rapid desensitization. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):230–232. doi: 10.1038/354230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan R., Harris G. L., Stevens C. F., Zuker C. S. A Drosophila mutant defective in extracellular calcium-dependent photoreceptor deactivation and rapid desensitization. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):230–232. doi: 10.1038/354230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan R., Malicki D. M., Zuker C. S. Signal transduction in Drosophila photoreceptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1995;18:283–317. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.18.030195.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratto G. M., Payne R., Owen W. G., Tsien R. Y. The concentration of cytosolic free calcium in vertebrate rod outer segments measured with fura-2. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3240–3246. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03240.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K., Becker A., Sun Y., Hardy R., Zuker C. Gq alpha protein function in vivo: genetic dissection of its role in photoreceptor cell physiology. Neuron. 1995 Oct;15(4):919–927. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. P., Ranganathan R., Hardy R. W., Marx J., Tsuchida T., Zuker C. S. Photoreceptor deactivation and retinal degeneration mediated by a photoreceptor-specific protein kinase C. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1478–1484. doi: 10.1126/science.1962207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. P., Stamnes M. A., Zuker C. S. Signal transduction in the visual system of Drosophila. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:161–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamnes M. A., Rutherford S. L., Zuker C. S. Cyclophilins: a new family of proteins involved in intracellular folding. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;2(9):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamnes M. A., Shieh B. H., Chuman L., Harris G. L., Zuker C. S. The cyclophilin homolog ninaA is a tissue-specific integral membrane protein required for the proper synthesis of a subset of Drosophila rhodopsins. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90156-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. Fluorescent probes of cell signaling. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:227–253. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Niemeyer B., Colley N., Socolich M., Zuker C. S. Regulation of PLC-mediated signalling in vivo by CDP-diacylglycerol synthase. Nature. 1995 Jan 19;373(6511):216–222. doi: 10.1038/373216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C. S., Cowman A. F., Rubin G. M. Isolation and structure of a rhodopsin gene from D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C. S. Phototransduction in Drosophila: a paradigm for the genetic dissection of sensory transduction cascades. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Oct;2(5):622–627. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90029-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




