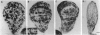Abstract
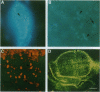
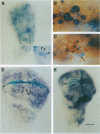
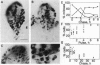
The pattern of cell proliferation in the Drosophila imaginal wing primordium is spatially and temporally heterogeneous. Direct visualization of cells in S, G2, and mitosis phases of the cell cycle reveals several features invariant throughout development. The fraction of cells in the disc in the different cell cycle stages is constant, the majority remaining in G1. Cells in the different phases of the cell cycle mainly appear in small synchronic clusters that are nonclonally derived but result from changing local cell-cell interactions. Cluster synchronization occurs before S and in the G2/M phases. Rates of cell division are neither constant nor clonal features. Cell cycle progression is linear rather than concentric. Clusters appear throughout the disc but with symmetries related to presumptive wing patterns, compartment boundaries, and vein clonal restrictions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler P. N., MacQueen M. Partial coupling of the cell cycles of neighboring imaginal disc cells. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Jun;133(2):452–456. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant P. J., Schmidt O. The genetic control of cell proliferation in Drosophila imaginal discs. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1990;13:169–189. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1990.supplement_13.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B., McGuffin M. E., Pfeifle C., Segal D., Cohen S. M. apterous, a gene required for imaginal disc development in Drosophila encodes a member of the LIM family of developmental regulatory proteins. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):715–729. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez M., Campuzano S. asense, a member of the Drosophila achaete-scute complex, is a proneural and neural differentiation gene. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2049–2060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar B. A., O'Farrell P. H. Genetic control of cell division patterns in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):177–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90183-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar B. A., O'Farrell P. H. The three postblastoderm cell cycles of Drosophila embryogenesis are regulated in G2 by string. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):469–480. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90012-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foe V. E. Mitotic domains reveal early commitment of cells in Drosophila embryos. Development. 1989 Sep;107(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser S. E., Bryant P. J. Patterns of dye coupling in the imaginal wing disk of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):533–536. doi: 10.1038/317533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bellido A., Merriam J. R. Parameters of the wing imaginal disc development of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1971 Jan;24(1):61–87. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bellido A., de Celis J. F. Developmental genetics of the venation pattern of Drosophila. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:277–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Bellido A. Pattern reconstruction by dissociated imaginal disk cells of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1966 Oct;14(2):278–306. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(66)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Gaitán M., Capdevila M. P., García-Bellido A. Cell proliferation patterns in the wing imaginal disc of Drosophila. Mech Dev. 1994 Jun;46(3):183–200. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(94)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hama C., Ali Z., Kornberg T. B. Region-specific recombination and expression are directed by portions of the Drosophila engrailed promoter. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1079–1093. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J., Dorsett D., Delotto Y., Liu S. Expression of the cut locus in the Drosophila wing margin is required for cell type specification and is regulated by a distant enhancer. Development. 1991 Nov;113(3):735–747. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.3.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brochta D. A., Bryant P. J. A zone of non-proliferating cells at a lineage restriction boundary in Drosophila. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):138–141. doi: 10.1038/313138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orsulic S., Peifer M. A method to stain nuclei of Drosophila for confocal microscopy. Biotechniques. 1994 Mar;16(3):441–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):397–400. doi: 10.1038/356397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. E., O'Keefe L. V., Reed S. I., Saint R. A Drosophila G1-specific cyclin E homolog exhibits different modes of expression during embryogenesis. Development. 1993 Nov;119(3):673–690. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.3.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubiger M., Palka J. Changing spatial patterns of DNA replication in the developing wing of Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1987 Sep;123(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truman J. W., Bate M. Spatial and temporal patterns of neurogenesis in the central nervous system of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1988 Jan;125(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Paddock S. W., Carroll S. B. Pattern formation in a secondary field: a hierarchy of regulatory genes subdivides the developing Drosophila wing disc into discrete subregions. Development. 1993 Feb;117(2):571–584. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.2.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuste R., Nelson D. A., Rubin W. W., Katz L. C. Neuronal domains in developing neocortex: mechanisms of coactivation. Neuron. 1995 Jan;14(1):7–17. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]