Abstract
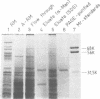
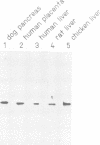
We have purified a glycosylated, membrane-spanning protein of relative molecular mass approximately 34,000 (Mr approximately 34 K) from canine microsomes that appears to be essential for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) as shown by the inhibitory action of antibodies directed against it and of monovalent Fab-fragments produced from them. The ER membrane contains at least as many molecules of the 34 K membrane protein as bound ribosomes. The protein can be detected immunologically in tissues of various organisms, indicating an universal function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benndorf R., Nürnberg P., Bielka H. Growth phase-dependent proteins of the Ehrlich ascites tumor analyzed by one- and two-dimensional electrophoresis. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jan;174(1):130–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. II. Reconstitution of functional rough microsomes from heterologous components. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):852–862. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Gilmore R., Blobel G. Purification of microsomal signal peptidase as a complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):581–585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Blobel G. Transient involvement of signal recognition particle and its receptor in the microsomal membrane prior to protein translocation. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):677–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Blobel G., Walter P. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Detection in the microsomal membrane of a receptor for the signal recognition particle. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):463–469. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Walter P., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. II. Isolation and characterization of the signal recognition particle receptor. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):470–477. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Ulrich B. L., Sabatini D. D. Proteins of rough microsomal membranes related to ribosome binding. I. Identification of ribophorins I and II, membrane proteins characteristics of rough microsomes. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):464–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg U. C., Walter P., Johnson A. E. Photocrosslinking of the signal sequence of nascent preprolactin to the 54-kilodalton polypeptide of the signal recognition particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8604–8608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzchalia T. V., Wiedmann M., Girshovich A. S., Bochkareva E. S., Bielka H., Rapoport T. A. The signal sequence of nascent preprolactin interacts with the 54K polypeptide of the signal recognition particle. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):634–636. doi: 10.1038/320634a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinowski K., Manski W. Microprocedures for quantitative immunochemical analysis of antigenic molecules and antigenic determinants. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):418–436. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Dobberstein B. Identification and characterization of a membrane component essential for the translocation of nascent proteins across the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):503–508. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport T. A. Protein translocation across and integration into membranes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;20(1):73–137. doi: 10.3109/10409238609115901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima S., Lauffer L., Rath V. L., Walter P. The signal recognition particle receptor is a complex that contains two distinct polypeptide chains. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1167–1178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Preparation of microsomal membranes for cotranslational protein translocation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:84–93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition particle: a ribonucleoprotein required for cotranslational translocation of proteins, isolation and properties. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:682–691. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Subcellular distribution of signal recognition particle and 7SL-RNA determined with polypeptide-specific antibodies and complementary DNA probe. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1693–1699. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum III. Signal recognition protein (SRP) causes signal sequence-dependent and site-specific arrest of chain elongation that is released by microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):557–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Ibrahimi I., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Signal recognition protein (SRP) binds to in-vitro-assembled polysomes synthesizing secretory protein. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):545–550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmann M., Huth A., Rapoport T. A. Xenopus oocytes can secrete bacterial beta-lactamase. Nature. 1984 Jun 14;309(5969):637–639. doi: 10.1038/309637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmann M., Kurzchalia T. V., Bielka H., Rapoport T. A. Direct probing of the interaction between the signal sequence of nascent preprolactin and the signal recognition particle by specific cross-linking. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):201–208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmann M., Kurzchalia T. V., Hartmann E., Rapoport T. A. A signal sequence receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):830–833. doi: 10.1038/328830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]