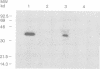
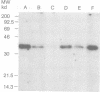
Abstract
Insulin-like growth factors bind with high affinity to specific binding proteins in extracellular fluids. To identify structural characteristics of IGF-binding proteins that might define their physiological roles, we determined the complete primary structure of a novel human IGF-binding protein (IGFBP-2) from a cloned cDNA. The cDNA encodes a 328 amino acid IGF-binding protein precursor which contains a 39-residue signal peptide. The mature 289 amino acid IGFBP-2 has a predicted Mr of 31,325. Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells stably transformed with the IGFBP-2 cDNA secreted a 36 kd protein which bound, with different affinities, IGFII and IGFI, but did not bind insulin. The predicted protein sequence of this IGF-binding protein shares extensive amino acid homology (greater than 85%) with the IGF-binding protein secreted by rat BRL-3A cells, but less than 40% homology with human IGFBP-1. Therefore IGFBP-2, and not IGFBP-1 as previously suggested, represents the human homologue of the rat BRL-BP (alpha IGFBP-2). Moreover, from alignment of the predicted protein sequences of IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-2, extensive conservation of the distribution of cysteine residues is observed. Although the overall amino acid homology shared by these proteins is not high, we suggest that they represent a family of structurally related human IGFBPs. Southern blot analysis of human DNA demonstrates that IGFBP-2 is encoded by a single-copy gene, different from that of IGFBP-1.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L., Wood M. H. Two immunoreactive binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors in human amniotic fluid: relationship to fetal maturity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Sep;65(3):423–431. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer M. T., Stetler G. L., Squires C. H., Thompson R. C., Busby W. H., Clemmons D. R. Cloning, characterization, and expression of a human insulin-like growth factor binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1289–1297. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman A., Groffen C., Kortleve D. J., Geurts van Kessel A., Drop S. L. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding the low molecular weight insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IBP-1). EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2417–2423. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Elgin R. G., Han V. K., Casella S. J., D'Ercole A. J., Van Wyk J. J. Cultured fibroblast monolayers secrete a protein that alters the cellular binding of somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor I. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1548–1556. doi: 10.1172/JCI112470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin R. G., Busby W. H., Jr, Clemmons D. R. An insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein enhances the biologic response to IGF-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3254–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fechheimer M., Boylan J. F., Parker S., Sisken J. E., Patel G. L., Zimmer S. G. Transfection of mammalian cells with plasmid DNA by scrape loading and sonication loading. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8463–8467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Bertics P. J., Santon J. B. Epidermal growth factor and its receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Jun;51(3):169–186. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Watson J. Biochemical and biological characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. V. Identification of an interleukin 2-producing human leukemia T cell line. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1709–1719. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundmann U., Nerlich C., Bohn H., Rein T. Cloning of cDNA encoding human placental protein 12 (PP12): binding protein for IGF I and somatomedin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8711–8711. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Short-term metabolic effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I in healthy adults. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):137–140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardouin S., Hossenlopp P., Segovia B., Seurin D., Portolan G., Lassarre C., Binoux M. Heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and relationships between structure and affinity. 1. Circulating forms in man. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):121–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich G., Traunecker A., Tonegawa S. Somatic mutation creates diversity in the major group of mouse immunoglobulin kappa light chains. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):417–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Seurin D., Segovia-Quinson B., Hardouin S., Binoux M. Analysis of serum insulin-like growth factor binding proteins using western blotting: use of the method for titration of the binding proteins and competitive binding studies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhtala M. L., Koistinen R., Palomäki P., Partanen P., Bohn H., Seppälä M. Biologically active domain in somatomedin-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 26;141(1):263–270. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80363-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Lanahan A., Buck C. R., Sehgal A., Morgan C., Mercer E., Bothwell M., Chao M. Expression and structure of the human NGF receptor. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90619-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen M., Koistinen R., Aalto-Setälä K., Seppälä M., Jänne O. A., Kontula K. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor-binding protein/placental protein 12 and tissue-specific expression of its mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 29;236(2):295–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. L., Hintz R. L., James P. M., Lee P. D., Shively J. E., Powell D. R. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein complementary deoxyribonucleic acid from human HEP G2 hepatoma cells: predicted protein sequence suggests an IGF binding domain different from those of the IGF-I and IGF-II receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 May;2(5):404–411. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-5-404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Smith G. L. Characterization of Multiplication-Stimulating Activity (MSA) carrier protein. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 May;45(2-3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nessley S. P., Cohen K. L., Rechler M. M. Specific binding of a somatomedin-like polypeptide in rat serum depends on growth hormone. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):137–140. doi: 10.1038/263137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottola C., MacDonald R. G., Brackett J. L., Mole J. E., Anderson J. K., Czech M. P. Purification and amino-terminal sequence of an insulin-like growth factor-binding protein secreted by rat liver BRL-3A cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11180–11188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. The nature and regulation of the receptors for insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:425–442. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor II. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritvos O., Ranta T., Jalkanen J., Suikkari A. M., Voutilainen R., Bohn H., Rutanen E. M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein from human decidua inhibits the binding and biological action of IGF-I in cultured choriocarcinoma cells. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2150–2157. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. Arg-Gly-Asp: a versatile cell recognition signal. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):517–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutanen E. M., Pekonen F., Mäkinen T. Soluble 34K binding protein inhibits the binding of insulin-like growth factor I to its cell receptors in human secretory phase endometrium: evidence for autocrine/paracrine regulation of growth factor action. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Jan;66(1):173–180. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek J. S., Temple P. A., Wilkens K. M., Leary A. C., Luxenberg D. P., Jones S. S., Brown E. L., Kay R. M., Orr E. C. Human GM-CSF: molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and purification of the natural and recombinant proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):810–815. doi: 10.1126/science.3923623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Hauri C., Waldvogel M., Froesch E. R. Acute metabolic effects and half-lives of intravenously administered insulinlike growth factors I and II in normal and hypophysectomized rats. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1768–1775. doi: 10.1172/JCI112500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Morell B., Walter H., Laron Z., Froesch E. R. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and its carrier protein in various metabolic disorders. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1980 Dec;95(4):505–517. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0950505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]